Sukhoi Su-17
| Su-17/-20/-22 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A Su-22M4 of the Czech Republic | |
| Role | Fighter-bomber |
National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi |
| First flight | 2 August 1966 |
| Introduction | 1970 |
| Status | In limited service |
| Primary users | Syrian Air Force Iranian Air Force Polish Air Force Peruvian Air Force Vietnam People's Air Force |
| Produced | 1969–1990 |
Number built | 2,867 |
Developed from | Sukhoi Su-7 |
The Sukhoi Su-17 (NATO reporting name: Fitter) is a Soviet variable-sweep wing fighter-bomber developed from the Sukhoi Su-7. It enjoyed a long career in Soviet, later Russian, service and was widely exported to Eastern Bloc, Arab air forces, Angola and Peru as the Su-20 and Su-22. It is the first variable-sweep wing of Russian/Soviet origin.
Contents
1 Development
2 Operational history
2.1 Soviet Union/Russia
2.2 Angola
2.3 Iraq
2.4 Libya
2.5 Peru
2.6 Poland
2.7 Syria
2.8 Yemen
3 Variants
3.1 In-house OKB designations
4 Operators
4.1 Former operators
5 Specifications (Su-17M4)
6 See also
7 References
7.1 Notes
7.2 Bibliography
8 External links
Development

A Su-20 (left) next to an older, similar Su-7BKL.
Seeking to improve low-speed and take-off/landing performance of the Su-7B fighter-bomber, in 1963 the Sukhoi OKB with input from TsAGI created a variable-sweep wing technology demonstrator. The Su-7IG (internal designation S-22I, NATO designation "Fitter-B"), converted from a production Su-7BM, had fixed inner portions of the wing with movable outer segments which could be swept to 28°, 45°, or 62°.[1] A fixed inner wing simplified construction, allowing the manufacturer to retain the Su-7 landing gear and avoiding the need for complex pivoting underwing hardpoints, and it minimized the shift in the center of pressure relative to the center of mass with change in wing sweep.[2] The new wing also had extensive leading-edge slats and trailing-edge flaps. Su-7IG first flew on 2 August 1966 with V. S. Ilyushin at the controls, becoming the first Soviet variable geometry aircraft.[2] Testing revealed that take-off and landing speeds had decreased by 50–60 km/h (31–37 mph) compared to the conventional Su-7.[2]
The production aircraft was named Su-17 (NATO designation "Fitter-C", factory designation S-32) and was unofficially dubbed Strizh (Стриж, martlet) in service. Aside from the new wing, it differed from its predecessor Su-7 in having a new canopy and a dorsal fuselage spine for additional fuel and avionics. The Su-17 first flew on 1 July 1969 with E. K. Kukushev at the controls.[2]
A total of 2,867 Su-17 and its variants were built, of which 1,165 were exported to 15 nations.[2]
Operational history

A Soviet Su-17M.
Soviet Union/Russia
The Su-17 entered service with the Soviet Air Force in 1970. The aircraft was used by both the Soviets and the Afghanistan government forces during the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan. High-altitude airfields and hot dusty climate created special operational challenges. In the summer, the takeoff roll of the Su-17 increased 1.5-fold and landings frequently ended with burst tires and brake fires. Avionics failures were common due to heat and sand contamination.
However, the AL-21F engine proved tolerant of routine ingestion of sand and sand-contaminated fuel and by 1985 the combat readiness of the Su-17 fleet exceeded that of the Sukhoi Su-25 and the helicopters.[3] The first-series Su-17s were quickly replaced with more capable Su-17M3 and Su-17M4. Despite its durability and payload, the aircraft proved ill-adapted for combat in the mountainous terrain due to high attack speeds, low maneuverability, and the need to stay out of range of anti-aircraft artillery due to lack of significant armor protection. Although external armor was added around the engine, hydraulics, and fuel systems based on damage analysis, this was still insufficient compared to dedicated close air support Su-25s.[3]
The appearance of MANPADS such as the Soviet-made Strela 2 (smuggled from Egypt), and the American FIM-43 Redeye and later FIM-92 Stinger, presented a new threat and forced Su-17s to even higher operational altitudes. Revised tactics and retrofit of up to 12 flare dispensers which fired automatically during the attack run proved effective, and in 1985 only one Soviet Su-17 was lost to ground fire.[3]
Forced to operate 3,500–4,000 m (11,500–13,100 ft) above ground, Su-17s shifted from using unguided rockets to bombs, including thermobaric weapons, while Su-25s were tasked with precision strikes.[3] Toward the end of the war, the Su-17 force was partially replaced by the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-27s in order to perform operational testing of the new fighter-bomber.
The Su-17M3/4 were used during the First Chechen War alongside Sukhoi Su-24s and Sukhoi Su-25s in ground attack and reconnaissance missions.[4]
In a move to eliminate single-engine strike aircraft from its inventory, the Russian Air Force retired its last Su-17M4 along with its fleet of MiG-23/27s in 1998.
Angola
The Soviets supplied the communist government of Angola with 12 Su-20Ms in 1982 or 1983, which formed the basis of the 15th FS. The squadron suffered a swift loss of at least six aircraft – most in mishaps – by 1985, and three more by 1988, and had only two aircraft left when it was reinforced with another Soviet batch of 14 Su-22M-4Ks and two Su-22UM-3Ks in 1989–90 (incorporated into the 26th Air Regiment, based in Moçâmedes).[5] A second shipment from Belarus in 1999 consisted of two Su-22UBs and four Su-22Ms, and a third one from Slovakia in 1999–2001 consisted of 10 Su-22M-4s and one Su-22UM-3K.[6]
These aircraft saw heavy use in the war against UNITA. From the aforementioned losses, which can not be classified as mishaps or combat attrition, only an Su-20M, serialled C510 was reportedly downed in 1987 and a better-documented case occurred on 6 November 1994 when an Su-22 based at Catumbela was shot down by a SAM fired by UNITA during a raid against Huambo. The pilot managed to eject and flee naked after stripping off his flight suit.[7][8]
Iraq

Iraqi Su-22M aircraft in a hangar damaged by Coalition air strikes during Operation Desert Storm.
From 22 September 1980 to 20 August 1988, during the Iran–Iraq War, Iraq used Su-17 export versions (Su-20 and Su-22) alongside older Su-7s. They were mostly used in ground-attack and in close air support role. Iranian F-14s shot down 21 Su-20/-22s, that have been confirmed by western sources. 18 Su-20/-22s were also shot down by Iranian McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs.[9] and three by Iranian Northrop F-5s.[10]
Official Iraqi accounts show no loss of Su-20 aircraft throughout the war against the Kurds and Iran. 20 Su-22M2, two Su-22M3 and seven Su-22M4 were lost during the war with Iran, the majority to anti-aircraft fire sustained during low level bombing raids against the Iranian front lines.[11]
In 1991, during the Gulf War, Iraqi Su-22's saw limited active service because the Iraqi regime distrusted the Air Force. On 7 February 1991, two Su-20/22 and one Su-7 were shot down by USAF F-15C using AIM-7 air to air missiles[12] when the IQAF was moving its aircraft to Iran. Many more were destroyed on the ground by coalition air forces or evacuated to Iran and were never returned.
On 20 and 22 March 1991, two other Su-20/22s were downed by a USAF F-15C during Operation Provide Comfort that started soon after the war.[13]
Libya

Libyan Su-22M.
Two Libyan Su-22s were shot down in the Gulf of Sidra incident by U.S. Navy Grumman F-14 Tomcats on 19 August 1981. One Su-22 fired a K-13 missile head-on at one of the F-14s from an estimated 300-meter (984-foot) closing distance, however the missile was evaded. Both were then downed by AIM-9 Sidewinder missiles.
On 8 October 1987, in the aftermath of the Chadian–Libyan conflict, a Su-22MK was shot down by a FIM-92A fired by Chadian forces. The pilot, Capt. Diya al-Din, ejected and was captured. He was later granted political asylum by the French government. During the recovery operation, a Libyan MiG-23MS was shot down by a FIM-92A.[14]
A Libyan Su-22 crashed near Benghazi on 23 February 2011. The crew members, Captain Attia Abdel Salem al Abdali and his number two, Ali Omar Gaddafi, were ordered to bomb the city in response to the Libyan Civil War. They refused, bailing out of the aircraft and parachuting to the ground.[15][16] Su-22s were heavily used by the Libyan loyalist forces against the insurgent forces from mid February up to mid March 2011, when the international mission started and the no fly zone was imposed. Among other missions, Su-22s also attacked Anti-Gaddafi positions in Bin Jawad in early March 2011 as government forces retook the town.[17][18]
One Libyan Air Force Su-22 was destroyed on the ground by a Belgian Air Force F-16AM on 27 March.[19]
Peru

Sukhoi Su-22 "Fitter F" aircraft of the Peruvian Air Force.
Peru was the only export customer of the type in the Americas. On 24 April 1992, Peruvian "Fitters" attacked a U.S. Air Force Lockheed C-130H Hercules of the 310th Airlift Squadron which was intercepted at sea, west of Lima, injuring six of the 14 crew members. Crew member Joseph C. Beard, Jr., was killed, when he was blown from the cabin at 18,500 feet, and crew member Ronald Hetzel sustained severe injuries, with his chest blown open and his jugular vein severed.[20] The incident caused an almost year-long interruption to the US anti-drug Air Bridge Denial Program and the establishment of a Joint Air Operation Center at Howard Air Force Base in Panama.[21]
During the 1995 Cenepa War between Peru and Ecuador, two Peruvian Sukhoi Su-22 were lost.
On 10 February 1995, two Ecuadorian Air Force Mirage F1JAs, piloted by Maj. R. Banderas and Capt. C. Uzcátegui, were directed over five targets approaching the disputed Cenepa valley. After making visual contact, the Mirages fired their missiles, claiming two Peruvian Su-22A Fitter F shot down, while a Kfir claimed a further A-37B Dragonfly.[22][23][24][25] Peru, however, denied that the two Su-22A Fitter F were shot down by Mirages, stating that one was struck by Ecuadorian anti-aircraft artillery during a low flying ground-attack mission, and the second because of an engine fire.[26][27][28]
The Su-22s flew 45 sorties into the combat zone. A 20-strong force of "Fitters" was also set up at El Pato as a retaliatory force should Ecuador decide to attack the coastal port.[29]
Poland
On 19 August 2003, a Polish Air Force Su-22M4K was accidentally shot down by friendly fire during an exercise by a Polish 2K12 Kub battery. The aircraft was flying 21 km from the coast over the Baltic Sea near Ustka. The pilot ejected and was rescued after two hours in the water. He later died in a C-295M crash on 23 January 2008.[30] As of 2012, Poland was planning to replace its Su-22s with three squadrons of UAVs.[31]
As of 2014 the Polish Air Force was planning to retain the Su-22s in service. It is hoped that this decision will have a positive impact on Polish industry, as the WZL nr 2 repair facility in Bydgoszcz will maintain the remaining aircraft under contract to the Air Force. The decision would also allow the Air Force to retain the well-trained ground crews and pilots, currently operating the machines. The Poles consider the Su-22 easier to maintain and repair than the other main combat aircraft types currently in Polish service (mainly the MiG-29 and the F-16). They also suffer from fewer malfunctions and other problems (high, 70–75% non-error index). It is also the only plane in Polish inventory equipped for electronic intelligence, warfare, and support of ground systems. The Polish Air Force has retained a large stockpile of air-to-ground weapons for use with the Su-22. By some estimates, the cost of destroying these resources would be higher than the projected cost of continuing Su-22 operations.[32] It was decided, that starting from 2015, only 12 Su-22M4 and 4-6 Su-22UM3K out of 32 remaining would undergo a refit, increasing their lifespan for another ten years.[33] For economical reasons the aircraft are not modernized, apart from fitting an additional radio RS-6113-2 C2M with a blade antenna on the top, but they receive a new grey multishade camouflage, similar to other Polish aircraft.[33][34]
There is one exhibited at the Museum of Polish Arms in Kołobrzeg.[35]
Syria
The Syrian Air Force used Su-20/-22s to attack Israeli forces in the Yom Kippur War[4] and 1982 Lebanon War. Several Su-20/-22s were shot down by the Israeli Air Force.[36][37] From mid-2012, in the Syrian civil war, Syrian Air Force Su-22s have been involved in combat operations against Syrian insurgents.[38] Like other SyAAF fixed wing aircraft, videos showed Su-22s using unguided munitions, mostly general purpose bombs, cluster bombs and incendiary bombs and unguided rockets. Attack tactics were low to medium altitude flat bombing runs with pull up after rocketing or bombing, with decoy flares fired for self-defense.[39] As of the end of 2015, the SyAAF Su-22s suffered a limited number of losses compared to the SyAAF MiG-21 and MiG-23 during the same period. The first confirmed loss of a SyAAF Su-22 was recorded on 14 February 2013, when rebel forces shot it down using a MANPADS.[40] On 18 June 2017, a US F/A-18E Super Hornet engaged and shot down a SyAAF Su-22[41] for dropping munitions on US-backed forces;[42] according to the wingman of the Super Hornet that made the kill, the Syrian pilot was able to eject.[43] On 24 July 2018, a SyAAF Su-22 which entered Israeli air space was shot down by two Israeli Patriot missiles.[44][45]
Yemen
On 11 August 2009, Yemeni armed forces started Operation Scorched Earth in northern Yemen to fight the Houthis.
The Yemeni Air Force backed the army with air raids on rebel-held positions. On 5 October 2009, a Yemeni Su-22 crashed when it was flying in formation with another aircraft, on the way back from a mission. The rebels claimed to have shot it down, while Yemeni armed forces denied shooting the claim and claimed that crashed due to technical problems.[46]
Earlier on 2 October, the Yemeni revolutionaries said they shot down a "MiG-21" while again the military insisted technical problems caused the crash.[47]
On 8 November, a third Yemeni fighter aircraft reported to be a Sukhoi was destroyed. Again the military claimed it crashed due to technical problems, while the Yemeni revolutionaries claimed they shot it down.[48] The pilot ejected and was recovered by friendly forces. The Yemeni Air force once again used Sukhoi aircraft during the Arab Spring uprising. On 28 September 2011, a Yemeni Air Force Su-22 was shot down by tribesmen opposed to the rule of President Saleh. The government confirmed that rebels were responsible for the shoot-down, and that the pilot had been captured.[49][50] On February 19, 2013 a Yemen Su-22 on a training mission crashed for unknown reasons into Sana'a, killing 12 civilians.[51] On May 13, 2013 a Yemen Su-22 on a training mission crashed in Sana'a, killing the pilot.[52]
Variants

Polish Su-22M4 in the markings of 7th Tactical Sqn.

Polish Su-22M4 in flight
Sources[2]
- Su-7IG (S-22I, "Fitter-B")
- Su-7BM variable geometry wing demonstrator.
- Su-17 (S-32, "Fitter-B")
- Limited production run based on the longer fuselage of the two-seat Su-7U trainer, with bulged dorsal spine for extra fuel (4,550 L/1,200 U.S. gal total). Retained Su-7s Lyulka AL-7F-1 engine. Manufactured 1969–1973.
- Su-17K
- export version of the Su-17 for Egyptian Air Force
- Su-17M (S-32M, "Fitter-C")
- First major production version, introduced Lyulka AL-21F-3 engine, twin pitot tubes, new navigation and attack computer (retaining Su-7BMK's SRD-5M ranging radar), angle of attack vane, single brake parachute. Variable-position intake centerbody providing maximum speed of Mach 2.1. First flight: 28 December 1971 with V. S. Soloviev at the controls. The export version was designated Su-20, first flying 15 December 1972 with A. N. Isakov at the controls. Manufactured 1972–1975, entered service in 1973. Exported to Egypt, Poland, and Syria.
- Su-17M-28
- Testbed for Kh-28 (AS-9 Kyle) anti-radiation missile
- Su-17MKG
- Testbed for Kh-25 (AS-10 'Karen') and Kh-29 (AS-14 "Kedge") missiles
- Su-17R
- Small number of Su-17M aircraft equipped to carry reconnaissance pods. Equivalent export version designated Su-20R.
- Su-17M2 (S-32M2, "Fitter-D")
- Nose extended 38 cm (15 in), deleting ranging radar and 'drooping' to improve pilot visibility. Fon-1400 laser rangefinder/marked-target seeker (LRMTS). ASP-17 and PBK-3-17s aiming avionics. RSBN-6S short-range navigation and instrument landing system. Undernose fairing for DISS-7 Doppler navigation radar. First flight: 20 December 1973 with V. S. Ilyushin at the controls. Manufactured 1974–1977, entered service in 1975.
- Su-17M2D
- Test-fit of the Tumansky/Khatchaturov R-29BS-300 engine (shared with some MiG-23s), with 112.7 kN (25,335 lbf) afterburning thrust, in a bulged rear fuselage. Due to lack of performance advantage and decreased range due to higher fuel consumption, it was decided to offer this engine as an export version only. First flight: 31 January 1975 with A. N. Isakov at the controls. The export variant was designated Su-22 (factory code S-32M2K, NATO "Fitter-F"), manufactured 1977–1978.
- Su-17UM (S-52U, "Fitter-E")
- First two-seat trainer version, based on the Su-17M2, but with a different, deeper fuselage with windscreen moved forward; same length as the original Su-17M. Internal fuel capacity reduced and port cannon deleted, but retained full avionics and armament. First flight: 15 August 1975 with V. A. Krechetov at the controls. Test flights revealed longitudinal instability at high angles of attack which was remedied by enlarging the tail fin. Export version with the R-29 engine was designated Su-22U. Manufactured 1976–1978, entered service in 1976.
- Su-17M3 (S-52, "Fitter-H")
- Based on the revised airframe of the Su-17UM, but with an avionics bay and an additional fuel tank in place of the rear cockpit, increasing the internal fuel capacity to 4850 l (1,280 U.S. gal). Doppler radar moved internally, removing the fairing. "Klen-P" laser rangefinder/target designator. A launch rail for K-13 (AA-2 "Atoll") or R-60 (AA-8 "Aphid") was added between the two existing pylons on each wing. First flight: 30 June 1976 with V. A. Krechetov at the controls. Export version with the R-29 engine and downgraded avionics (equivalent to Su-17M2) was designated Su-22M (factory designation S-52K, NATO "Fitter-J") and first flew on 24 May 1977 with E. S. Soloviev at the controls. An export version with Su-17M3 avionics was designated Su-22M3 (factory S-52MK). Su-17 manufactured 1976–1981, Su-22Ms were manufactured 1978–1984. Su-17M/Su-22M/Su-22M3 was the most numerous variant with almost 1,000 built.
- Su-17UM (S-52UM)
- The initial trainer version with the same avionics suite as the Su-17M.The export version was designated Su-22UM3 with R-29 engine, and Su-22UM3K with the AL-21 engine. Manufactured 1978–1982.
- Su-17UM3 (S-52UM3, "Fitter-G")
- Revised trainer with the same avionics suite as the Su-17M3. First flight: 21 September 1978 with Yu. A. Yegorov at the controls. The export version was designated Su-22UM3 with R-29 engine, and Su-22UM3K with the AL-21 engine. Manufactured 1978–1982.

Polish Su-22M4 in markings of 7th Tactical Sqn.
- Su-17M4 (S-54, "Fitter-K")
- Final production version with considerably upgraded avionics, including RSDN navigation (similar to LORAN), beacon navigation, inertial navigation, a more powerful (Klyon) "Kлён-54" laser rangefinder, radio compass, and SPO-15LE ("Sirena") radar-warning system. Additional fuselage inlets (including ram-air inlet at the base of the fin) to improve engine cooling airflow, fixed air intake shock cone. Many aircraft were equipped for the use of TV-guided missiles and BA-58 Vjuga pod for anti-radiation missiles. AL-21F-3 engine. Export version was designated Su-22M4 (factory S-54K). First flight: 19 June 1980 with Yu. A. Yegorov at the controls. Su-17M4 was manufactured 1981–1988, Su-22M4 was manufactured 1983–1990.
- Su-20
- The initial export version of the Su-17M, (S-32MK).
- Su-22M5
- A Russian-French upgrade package offered for existing aircraft with modernized cockpit, HOTAS, improved avionic systems. Deletes the laser rangefinder in favor of Phazotron/Thomson-CSF 'Phathom' radar.
- Su-22U
- The S-52U two-seat combat-trainer, export version of the Su-17UM, with a completely re-designed nose housing the tandem cockpits for student and instructor.
- Gun pods such as the GSh-23 based UPK-23 and SPPU-22 were utilized by the Su-17, Su-20, and Su-22. The SPPU-22 ground attack variant featured 30 degrees of traverse.
- An experimental version of the Su-20 was built with fixed wings attached to an Su-17M fuselage, in an effort to increase Payload/range performance by eliminating the weight of the wing sweep system. Good results were obtained in flight tests in 1973 but further development was cancelled.
- Tactical Reconnaissance versions of all variants could be made by fitting the KKR (Kombinirovanny Konteiner Razvedy – combined reconnaissance pod) on the centre-line pylon.
In-house OKB designations
- S-22I
- The first prototype "Variable-Geometry" Su-7, converted form a production Su-7BM, first flown on 2 August 1966.
- S-32
- The initial production version, dubbed Su-17 by the VVS (Voyenno-Vozdooshnyye Seely – Soviet air force).
- S-32M
- The Su-17 with the Lyul'ka AL-21F engine and re-structured fuselage plus several smaller modifications, resulting in a greater fuel capacity and more weapons stations.
- S-32MK
- The Su-20 export version with revised armament options, and less sophisticated avionics. First flight: 15 December 1972.
- S-32MK Hybrid
- Single aircraft (f/n 9500) built with fuselage of S-32MK and fixed wings of Su-7BMK. Offered to customers as cheaper/less complex alternative to Su-20, but no production.
- S-32M2
- The Su-17M with improved flying controls and weapon-aiming equipment. Production carried out from 1975 to 1977
- S-32M2K
- The Su-22 export version of the Su-17M2 with a Tumansky R-29BS-300 engine.
- S-32M2D
- An Su-17 tested with ski landing gear, similar to that used on the S-26 (Su-7), used for [very] rough field landing and takeoff tests.
- Su-52U
- The Su-17UM/Su-22U two-seat combat-trainer version with a completely re-designed nose housing the tandem cockpits for student and instructor.
- S-52
- In a reverse development the trainer modifications were adapted for a new Attack variant, the Su-17M3.
- S-52K
- An export variant of the S-52, given the designation Su-22M.
- S-52M3K
- Series production Su-22M3 aircraft with laser range-finder and avionics mods.
- S-52UK
- The trainer variant with all the S-32M2k structural modifications and a reduced weapons portfolio.
- S-52UM3
- The Su-17UM3 for the VVS with avionics and aero-dynamic changes.
- S-52UM3K
- The export version of the Su-17UM3.
- S-52R
- Tactical Reconnaissance Su-17M3R with a KKR (Kombinirovanny Konteiner Razvedy – combined reconnaissance pod) on the centre-line pylon
- S-54
- Production Su-17M4 fighter-bombers.
- S-54K
- Export Su-17M4s, designated Su-22M4.
- S-54R
- Tactical reconnaissance Su-17M4R with a KKR (Kombinirovanny Konteiner Razvedy – combined reconnaissance pod) on the centre-line pylon.
Operators
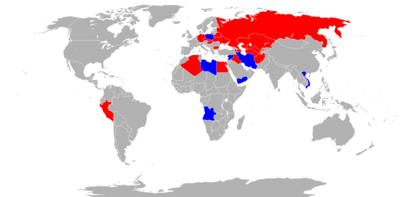 | |
| Blue = Current | Red = Former |
|---|---|
 Angola
Angola
- The People's Air and Air Defence Force of Angola operates 14 Su-22 variants.

Polish Su-22M4
 Iran
Iran
Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force. The Iranian Air Force received 40 Su-20/22s from Iraq in 1991.[53] While non-operational for several years, in 2013, Iran started an overhauling program.[54] In March 2015, it seems that some of the Iranian Air Force Su-22 were transferred to the Syrian Arab Air Force to fight in the ongoing Civil War.[55] Iran currently possesses 30 operational Su-22s. In July 2018 Iranian military technical experts successfully overhauled and modernized 10 Su-22s, giving them the ability to carry smart bombs, fire precision-guided munitions, transfer data from UAVs, and in the near future the system necessary to utilize air-launched cruise missiles with a range of 1500 km will be installed on them. [56]
 Libya
Libya
- 2 Su-22 in service.[57]
 Poland
Poland
- The Polish Air Force currently operates 12 Su-22M4 and 6 Su-22UM3K aircraft of 110 delivered. Poland operated 27 Su-20 since 1974 until the 1990s.
 Syria
Syria
- 28 Su-22 aircraft served with the Syrian Air Force prior to the Syrian civil war.
 Vietnam
Vietnam
- 36 Su-22 aircraft served with the Vietnam People's Air Force.[58]
Former operators
 Democratic Republic of Afghanistan
Democratic Republic of Afghanistan
Afghan Air Force. More than 70 were sent to the Afghan Air Force from 1982, including 45 Su-22M4 delivered from 1984.
 Armenia
Armenia
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan
- The Azerbaijan Air Force
 Belarus
Belarus
Belarus Air Force. The Belarusian Air Force inherited Su-17s from the Soviet Air Force, but none remain in service.
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgarian Air Force. The Bulgarian Air Force operated 18 Su-22M4 and five Su-22UM aircraft. All are retired.

Czech Air Force Su-22M4
 Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovak Air Force. The Czechoslovak Air Force's Su-22 (49 Su-22M4 and 8 Su-22UM3K in 1992) inventory was split between the Czech Republic and Slovakia in 1993. They were passed on to the Czech Air Force.
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic
Czech Air Force. The Czech Air Force inherited 31 Su-22M4 and five Su-22UM3K. All were retired in 2002.[59]
 East Germany
East Germany
Air Forces of the National People's Army. The East Germany operated 48 Su-22M4 and 8 Su-22UM-3K until unification, when they were passed on to the Luftwaffe.
Volksmarine. The East German Navy operated eight Su-22M-4Ks and two Su-22UM-3K aircraft.
 Egypt
Egypt
Egyptian Air Force. The Egyptian Air Force operated 48 of Su-20/22 aircraft, although all have been withdrawn, being replaced by the F-4 Phantom II and General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcons in their role.
 Germany
Germany
Luftwaffe. A number of Su-22 aircraft were inherited from East Germany, although these did not serve in the Luftwaffe, but some of them were painted with a Luftwaffe color scheme for test and evaluation. All of them have been decommissioned.
German Navy. Ex-Volksmarine aircraft.

Hungarian Su-22M3
 Hungary
Hungary
Hungarian Air Force. The Hungarian Air Force maintained 12 Su-22M3 and three Su-22UM3 aircraft from 1983. Two single seat and one training aircraft crashed. Withdrawn from service in 1997.
 Iraq
Iraq
Iraqi Air Force. The Iraqi Air Force received a large number of Su-22 models, of which 40 were impounded by Iran after having escaped coalition air campaign in 1991.[60] None survived the 2003 invasion of Iraq by the United States.
No. 1 Squadron IqAF - "as of September 1980, the Iraqi air force’s No. 1 Squadron was still equipped with 16 out of 18 Sukhoi Su-20s Iraq acquired in 1973."[61]
No. 44 Squadron IqAF - flying Su-20/22s in September 1980.[61]
 Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
- Su-17 aircraft were inherited by the Armed Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan, but never put into service.

Former LARAF Sukhoi Su-22M Fitter-H
 Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- The Libyan Air Force operated as many as 90 Su-22 aircraft, with around 40 Su-22M3 and Su-22UM3K aircraft in service at the beginning of 2011 when the Libyan uprising started. During the Libyan Civil War, the Gaddafi regime used Su-22s in combat operations.
 North Yemen
North Yemen
- North Yemen Air Force

Su-22UM Fitter J Peruvian Air Force
 Peru
Peru
Peruvian Air Force. The Peruvian Air Force acquired 32 Sukhoi Su-22A Fitter F, 4 Su-22U Fitter E, 16 Su-22M Fitter J and 3 Su-22UM Fitter G aircraft between 1977 and 1980. Retired in 2006, 11 remain in reserve status.
 Russia
Russia
Russian Air Force. The Russian Air Force inherited Soviet Su-17 aircraft, but has withdrawn the type from service. At least one example remains flying as a chase aircraft operated by Sukhoi at their KnAAPO facility.
- Russian Naval Aviation

Retired Slovak Su-22M4
 Slovakia
Slovakia
Slovak Air Force. The Slovak Air and Air Defense Forces inherited 18 Su-22M4 and three Su-22UM3K aircraft from Czechoslovakia in 1993. In 1999, six Su-22M4 and in 2001, four Su-22M4 and one Su-22UM3K aircraft were sold to Angola while rest of the fleet was grounded and is being used as museum exhibits and as teaching aid in flight schools.[62][63]
 South Yemen
South Yemen
- South Yemen Air Force
 Soviet Union
Soviet Union
- Soviet Union Su-17s were split between post-USSR countries.
- Soviet Air Force
- Soviet Naval Aviation
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
- A number of Su-17 aircraft were inherited by the Military of Turkmenistan, but they were never put into service.
 Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukrainian Air Force. A total of 40 Su-17 aircraft were inherited from the Soviet Union and most of them now retired from service, but a few are stored.
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
- A number of Su-17 aircraft were inherited by the Military of Uzbekistan, now all are retired and stored at Chirchiq.
 Yemen
Yemen
- Up to 23 Su-22 served with the Yemen Air Force prior to the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen. Many Su-22's were destroyed on the ground.
Specifications (Su-17M4)

Orthographic projection of the Su-17M4 "Fitter K", with plan view of wings swept and spread

EAF Su-20 armed with four 250 kg bombs, two rocket pods, and fitted with two external fuel tanks.
Data from Sukhoi,[64] Wilson,[65] deagel.com[66]
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 19.02 m (62 ft 5 in)
Wingspan:
With wings spread: 13.68 m (44 ft 11 in)
With wings swept: 10.02 m (32 ft 10 in)
Height: 5.12 m (16 ft 10 in)
Wing area:
With wings spread: 38.5 m² (414 ft²)
With wings swept: 34.5 m² (370 ft²)
Empty weight: 12,160 kg (26,810 lb)
Loaded weight: 16,400 kg (36,155 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: 19,430 kg (42,835 lb)
Fuel capacity: 3,770 kg (8,310 lb)
Powerplant: 1 × Lyulka AL-21F-3 afterburning turbojet
Dry thrust: 76.4 kN (17,185 lbf)
Thrust with afterburner: 109.8 kN (24,675 lbf)
Performance
Maximum speed:
At sea level: Mach 1.13 (1,400 km/h; 870 mph)
At altitude: Mach 1.51 (1,860 km/h; 1,156 mph)
Combat range: 1,150 km (715 mi; 620 nmi) in hi-lo-hi attack with 2,000 kg (4,400 lb) warload
Ferry range: 2,300 km (1,430 mi; 1,240 nmi)
Service ceiling: 14,200 m (46,590 ft)
Rate of climb: 230 m/s (45,275 ft/min)
Wing loading: 443 kg/m² (90.77 lb/ft²)
Thrust/weight: 0.68
Maximum g-load: 7 g
Armament
Guns:- 2 × 30 mm Nudelman-Rikhter NR-30 autocannons (80 rounds per gun, 160 rounds total)
UPK-23 or SPPU-22 gun pods for 2 × Gryazev-Shipunov GSh-23L autocannons
Hardpoints: 12 hardpoints with a capacity of up to 4,000 kg (8,800 lb) of stores and provisions to carry combinations of:
Missiles:
Air-to-air missiles:
- K-13
- R-60
- R-73
Air-to-surface missiles:
- Kh-23 Grom
Kh-25ML
Kh-29L/T/D
Anti-radiation missiles:
- Kh-58
Kh-27PS- Kh-28
Bombs: drop bombs, laser-guided bombs, electro-optical bombs, napalm bombs, drag chute bombs and cluster bombs
Air-to-surface rockets including the S-5 rocket, S-8 (rocket) & S-13 rocket systems.
See also
Related development
- Sukhoi Su-7
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- A-7 Corsair II
- IAR 93
- SEPECAT Jaguar
- Soko J-22 Orao
- Nanchang Q-5
Related lists
- Iranian aerial victories during the Iran–Iraq war
- Iraqi aerial victories during the Iran–Iraq war
- List of military aircraft of the Soviet Union and the CIS
- List of fighter aircraft
References
Notes
^ Green and Swanborough 2001.
^ abcdef "Sukhoi Su-17." Sukhoi Company Museum. Retrieved: 15 April 2007.[dead link]
^ abcd Markovskiy, Viktor. "Жаркое Небо Афганистана" (in Russian). Техника – Молодежи, 2000.
^ ab Goebel, Greg. "[2.0] Sukhoi Su-17 / 20 / 22." AirVectors, 1 November 2014. Retrieved: 11 April 2015.
^ Cooper, Tom. "African MiGs- Part 1." acig.info, 9 February 2008. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ http://www.deagel.com/equipment/r2c0007raw.htm[permanent dead link]
^ "The Year 1994." Archived 2018-01-07 at the Wayback Machine. ejection-history.org. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "ASN Wikibase Occurrence # 58437." aviation-safety.net, 20 March 2011. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ Cooper and Bishop, 2004, pp. 85–88.
^ http://www.cieldegloire.com/as_45_00_victoires.php#zandi Archived 2013-10-17 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Iraqi Perspectives Project Phase II. Um Al-Ma'arik (The Mother of All Battles): Operational and Strategic Insights from an Iraqi Perspective, Volume 1 (Revised May 2008)
^ http://www.rjlee.org/air/ds-aakill/
^ https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/ops/provide_comfort_2.htm
^ "Libyan Wars, 1980–1989, Part 6". Retrieved 14 November 2014..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Report: Libyan aircraft crashes after troops refuse bombing orders." CNN, 23 February 2011.
^ "UPDAT 1-Libya crew abort bombing mission on Benghazi: Report." Reuters, 23 February 2011.
^ "Simpson under fire as rebels forced back in Libya." BBC News, 7 March 2011. Retrieved: 9 March 2011.
^ "Libya Live Blog – March 11." Al Jazeera. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ G1 – Imagens mostram ataque de caça belga a aeronave na Líbia – notícias em Revolta Árabe Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "Aircraft Downed During the Cold War and Thereafter". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
^ "Drogas y Democracia – "Air Bridge Denial": El éxito de un fracaso". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
^ "El Ecuador 1972–1999. La Guerra del Cenepa" (in Spanish). Official Web Site of the Ecuadorian Armed Forces (www.fuerzasarmadasecuador.org). Archived from the original on 18 May 2006. Retrieved 20 June 2006. External link in|publisher=(help)
^ Cooper, Tom. "Peru vs. Ecuador. Alto-Cenepa War, 1995". Air Combat Information Group (www.acig.org). Retrieved 20 June 2006. External link in|publisher=(help)
^ ACIG Team. "Central & South American Air-to-Air Victories". Air Combat Information Group (www.acig.org). Retrieved 20 June 2006. External link in|publisher=(help)
^ Klaus, Erich. "Ecuador Air Force". Aeroflight (www.aeroflight.co.uk). Retrieved 20 June 2006. External link in|publisher=(help)
^ Diario "El Mundo", edición N° 114 del 4–5 de Marzo de 1995, p. 2
^ Cruz, Cesar. "Peruvian Fitters Unveiled". Air Forces Monthly, August 2003.
^ Warnes, Alex and Cesar Cruz. "Tiger Sukhois Frogfoots & Fitters in Peru". Air Forces Monthly, March 2006, p.48.
^ "Tiger Sukhois Frogfoots & Fitters in Peru". Air Forces Monthly Review, March 2006, p. 48.
^ Dastych, David M. "Poland's Black Wednesday." canadafreepress.com, 25 January 2008. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "Poland to Replace Su-22 Bombers with UCAV." Archived 2012-08-17 at the Wayback Machine. ria.ru, 14 August 2008. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ http://www.senat.gov.pl/gfx/senat/userfiles/_public/k8/dokumenty/stenogram/oswiadczenia/preiss/4001.pdf
^ ab Pacholski, Łukasz. Kolejnych dziesięć lat Su-22 in: „Wojsko i Technika” 1/2015. P. 130-132 (in Polish)
^ Fabulous Fitters January 12, 2017 Combat Aircraft Monthly Retrieved January 27, 2017
^ Kołobrzeg - Museum of Polish Arms Airport Retrieved January 27, 2017
^ "Syria." Archived 2010-12-15 at the Wayback Machine. Ejection history. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
^ Control of the Air: The Enduring Requirement (PDF), Aus air power, archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2012, retrieved 18 November 2012.
^ "Su-22 fires rockets", The Avionist (video), May 20, 2014.
^ " معرة النعمان: قصف وكر للإرهابيين والمخابرات التركية" (in Arabic) YouTube, 11 October 2012. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
^ Ranter, Harro. "ASN Aircraft accident 14-FEB-2013 Sukhoi Su-22M". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
^ "US coalition downs first Syria government jet." Retrieved 19 June 2017.
^ "A U.S. aircraft has shot down a Syrian government jet over northern Syria, Pentagon says." Retrieved 18 June 2017.
^ Report: Navy Pilot Breaks Silence About Shooting Down Syrian Fighter - Military.com, 31 July 2017
^ Israel fires Patriot missiles against Syrian jet in Golan Heights - The Jerusalem Post, 24 July 2018
^ https://www.almasdarnews.com/article/isis-releases-first-photos-of-syrian-aircraft-shot-down-by-israel/
^ "In Yemen, Houthis 'shoot down' army jet." presstv.ir. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "Middle East: Yemen denies warplane shot down." Al Jazeera English, 2 October 2009. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "Yemen rebels 'down fighter jet'." BBC News, 9 November 2009. Retrieved: 24 May 2010.
^ "Yemeni tribesmen shoot down army warplane." The Daily Telegraph (London), 28 September 2011.
^ "Sukhoi Su 22 Fighter Jet Shot Down by Anti-Saleh Fighters- Yemen." liveleak.com. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ Phelan, Jessica. "Yemen Fighter Plane Crashes in Sanaa, killing at least 12". Globalpost.com.
^ "Yemen army pilot killed in Sanaa jet crash " Middle East Online Retrieved: 13 May 2013.
^ https://www.mycity-military.com/slika.php?slika=143473_46214310_01IRIAF%20Su-22%20Fitter1.jpg
^ Boring, War Is (2013-12-18). "This Is How Iran Maintains Its Bizarre Air Force". War Is Boring. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
^ "Warplanes: Iran Gives Syria Ten Iraqi Su-22s". www.strategypage.com. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
^ https://en.mehrnews.com/news/136065/IRGC-overhauls-upgrades-10-Sukhoi-SU-22-fighter-jets
^ "World Air Forces 2017". Flightglobal Insight. 2017. Retrieved 4 July 2017.
^ "About the FlightGlobal Group | AirSpace Announcement | flightglobal.com". Flightglobal.com. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
^ "Info about Czech Air Force." Archived 2007-02-10 at the Wayback Machine. scramble.nl. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ https://www.mycity-military.com/slika.php?slika=143473_46214310_01IRIAF%20Su-22%20Fitter1.jpg
^ ab Tom Cooper. "The Tomcat's First Phoenix Kill". War is Boring. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
^ "Independent report about weapon export from Slovakia by SFPA." Archived 2008-12-30 at the Wayback Machine. security-studies.sk. Retrieved: 18 November 2012.
^ "Survival of the Fitter". AIRheads↑FLY. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
^ "Su-22M4." Sukhoi. Retrieved: 15 April 2007.
^ Wilson 2000, p. 130.
^ [1]
Bibliography
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
- Cooper, Tom and Farzad Bishop. Iranian F-14 Tomcat Units in Combat. Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, 2004.
ISBN 1-84176-787-5. - Green, William and F. Gordon Swanborough. The Great book of Fighters. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing, 2001.
ISBN 0-7603-1194-3. - Wilson, Stewart. Combat Aircraft since 1945. Fyshwick, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 2000.
ISBN 1-875671-50-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sukhoi Su-17. |
- from FAS
- List of all Su-17 (Su-20 and Su-22) fighters used by Polish Air Force
- from Russian Military Analysis
- Su-22M4 in panoramic view
- Su-22 Fitter in high-quality photos
