Mexican Cession

Area Mexico ceded to the United States in 1848, minus Texan claims. The Mexican Cession consisted of present-day U.S. states of California, Nevada, Utah, most of Arizona, about half of New Mexico, about a quarter of Colorado, and a small section of Wyoming.
The Mexican Cession is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico ceded to the U.S. in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande which had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, though the Texas annexation resolution two years earlier had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new State of Texas. The Mexican Cession (529,000 sq. miles) was the third largest acquisition of territory in US history. The largest was the Louisiana Purchase, with some 827,000 sq. miles (including land from fifteen present U.S. states and two Canadian provinces), followed by the acquisition of Alaska (about 586,000 sq. miles).
Most of the area had been the Mexican territory of Alta California, while a southeastern strip on the Rio Grande had been part of Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico, most of whose area and population were east of the Rio Grande on land that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas since 1835, but never controlled or even approached aside from the Texan Santa Fe Expedition. Mexico controlled the territory later known as the Mexican Cession, with considerable local autonomy punctuated by several revolts and few troops sent from central Mexico, in the period from 1821–22 after independence from Spain up through 1846 when U.S. military forces seized control of California and New Mexico on the outbreak of the Mexican–American War. The northern boundary of the 42nd parallel north was set by the Adams–Onís Treaty signed by the United States and Spain in 1821 and ratified by Mexico in 1831 in the Treaty of Limits (Mexico-United States). The eastern boundary of the Mexican Cession was the Texas claim at the Rio Grande and extending north from the headwaters of the Rio Grande, not corresponding to Mexican territorial boundaries. The southern boundary was set by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which followed the Mexican boundaries between Alta California (to the north) and Baja California and Sonora (to the south). The United States paid Mexico $15 million for the land which became known as the Mexican Cession.
Contents
1 Mexican–American War
2 Subsequent organization and the North-South conflict
3 Gadsden Purchase
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Mexican–American War
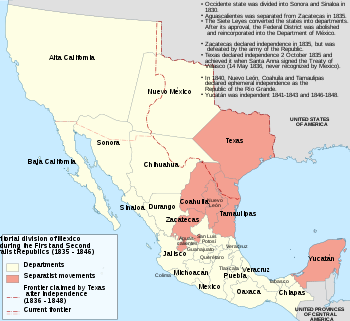
A map of Mexico, 1835–1846, with separatist movements highlighted
Alta California and Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico were captured soon after the start of the war and the last resistance there was subdued in January 1847, but Mexico would not accept the loss of territory. Therefore, during 1847, troops from the United States invaded central Mexico and occupied the Mexican capital of Mexico City, but still no Mexican government was willing to ratify transfer of the northern territories to the U.S. It was uncertain whether any treaty could be reached. There was even an All of Mexico Movement proposing complete annexation of Mexico among Eastern Democrats, but opposed by Southerners like John C. Calhoun who wanted additional territory for their crops but not the large population of central Mexico.
Eventually Nicholas Trist forced the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, explicitly redefining the border between Mexico and the United States in early 1848 after President Polk had already attempted to recall him from Mexico as a failure. Although Mexico did not overtly cede any land under the treaty, the redefined border had the effect of transferring Alta California and Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico to the control of the United States. Equally important, the new border also acknowledged Mexico's loss of Texas, both the core eastern portion and the western claims, neither of which had been formally recognized by Mexico until that time.
The U.S. Senate approved the treaty, rejecting amendments from both Jefferson Davis to also annex most of northeastern Mexico and Daniel Webster not to take even Alta California and Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico.[1] The United States also paid $15,000,000 ($482 million in 2016 dollars) for the land, and agreed to assume $3.25 million in debts to US citizens.[2] While technically the territory was purchased by the United States, the $15 million payment was simply credited against Mexico's debt to the U.S. at that time.
The Mexican Cession as ordinarily understood (i.e. excluding lands claimed by Texas) amounted to 525,000 square miles (1,400,000 km2), or 14.9% of the total area of the current United States. If the disputed western Texas claims are also included, that amounts to a total of 750,000 square miles (1,900,000 km2). If all of Texas had been seized, since Mexico had not previously acknowledged the loss of any part of Texas, the total area ceded under this treaty comes to 915,000 square miles (2,400,000 km2).
Considering the seizures, including all of Texas, Mexico lost 54% of its pre-1836 territory in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo.[3] For only fifteen years from 1821 (when Mexican independence was secured) and the Texan Revolt in 1836, the Mexican Cession (excluding Texas) formed approximately 42% of the country of Mexico; prior to that, it had been a part of the Spanish colony of New Spain for some three centuries. Beginning in the early seventeenth century, a chain of Roman Catholic missions and settlements extended into the New Mexico region, mostly following the course of the Rio Grande from the El Paso area to Santa Fe.
Subsequent organization and the North-South conflict
Soon after the war started and long before negotiation of the new Mexico–United States border, the question of slavery in the territories to be acquired polarized the Northern and Southern United States in the bitterest sectional conflict up to this time, which lasted for a deadlock of four years during which the Second Party System broke up, Mormon pioneers settled Utah, the California Gold Rush settled California, and New Mexico under a federal military U.S government turned back Texas's attempt to assert control over territory Texas claimed as far west as the Rio Grande. Eventually the Compromise of 1850 preserved the Union, but only for another decade. Proposals included:
- The Wilmot Proviso, which was created by Congressman David Wilmot, banning slavery in any new territory to be acquired from Mexico, not including Texas which had been annexed the previous year. Passed by the United States House of Representatives in August 1846 and February 1847 but not the Senate. Later an effort to attach the proviso to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo also failed.
- Failed amendments to the Wilmot Proviso by William W. Wick and then Stephen Douglas extending the Missouri Compromise line (36°30' parallel north) west to the Pacific, allowing slavery in most of present-day New Mexico and Arizona, Las Vegas, Nevada, and Southern California, as well as any other territories that might be acquired from Mexico. The line was again proposed by the Nashville Convention of June 1850.
Popular sovereignty, developed by Lewis Cass and Douglas as the eventual Democratic Party position, letting each territory decide whether to allow slavery.
William L. Yancey's "Alabama Platform," endorsed by the Alabama and Georgia legislatures and by Democratic state conventions in Florida and Virginia, called for no restrictions on slavery in the territories either by the federal government or by territorial governments before statehood, opposition to any candidates supporting either the Wilmot Proviso or popular sovereignty, and federal legislation overruling Mexican anti-slavery laws.- General Zachary Taylor, who became the Whig candidate in 1848 and then President from March 1849 to July 1850, proposed after becoming President that the entire area become two free states, called California and New Mexico but much larger than the eventual ones. None of the area would be left as an unorganized or organized territory, avoiding the question of slavery in the territories.
- The Mormons' proposal for a State of Deseret seizing areas from portions of the Mexican Cession but excluding the largest populations in Northern California and central New Mexico was considered unlikely to succeed in Congress, but nevertheless in 1849 President Taylor sent his agent John Wilson westward with a proposal to combine California and Deseret as a single state, decreasing the number of new free states and the erosion of Southern parity in the Senate, while legitimizing The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
- Senator Thomas Hart Benton in December 1849 or January 1850: Texas's western and northern boundaries would be the 102nd meridian west and 34th parallel north.
- Senator John Bell (with assent of Texas) in February 1850: New Mexico would get all Texas land north of the 34th parallel north (including today's Texas Panhandle), and the area to the south (including the southeastern part of today's New Mexico) would be divided at the Colorado River (Texas) into two slave states, balancing the admission of California and New Mexico as free states.[4]
- First draft of the compromise of 1850: Texas's northwestern boundary would be a straight diagonal line from the Rio Grande 20 miles (30 km) north of El Paso to the Red River of the South at the 100th meridian west (the southwestern corner of today's Oklahoma).
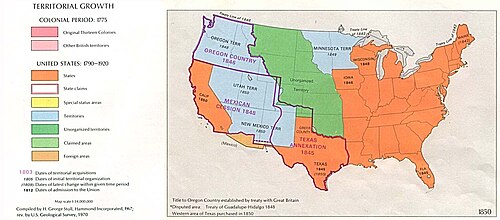
- The Compromise of 1850, proposed by Henry Clay in January 1850, guided to passage by Douglas over Northern Whig and Southern Democrat opposition, and enacted September 1850, admitted California as a free state including Southern California and organized Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory with slavery to be decided by popular sovereignty. Texas dropped its claim to the disputed northwestern areas in return for debt relief, and the areas were divided between the two new territories and unorganized territory. El Paso where Texas had successfully established county government was left in Texas. No southern territory dominated by Southerners (like the later short-lived Confederate Territory of Arizona) was created. Also, the slave trade was abolished in Washington, D.C. (but not slavery itself), and the Fugitive Slave Act was strengthened.
Gadsden Purchase
It quickly became apparent that the Mexican Cession did not include a feasible route for a transcontinental railroad connecting to a southern port. The topography of the New Mexico Territory included mountains that naturally directed any railroad extending from the southern Pacific coast northward, to Kansas City, St. Louis, or Chicago. Southerners, anxious for the business such a railroad would bring (and hoping to establish a slave-state beachhead on the Pacific coast[5]), agitated for the acquisition of railroad-friendly land at the expense of Mexico, thus bringing about the Gadsden Purchase of 1853.
See also
- The Zimmermann Telegram, which partly offered Imperial German assistance to Mexico in returning a sizable portion of the Mexican Cession's southern territory, as well as the U.S. state of Texas to Mexico in 1917.
References
^ George Lockhart Rives. The United States and Mexico, 1821-1848. pp. 634–636..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Articles XII-XV
^ Table 1.1 Acquisition of the Public Domain 1781-1867 Archived September 29, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
^ google.com/books Quarterly of the Texas State Historical Association, January 1904
^ Richards, The California Gold Rush and the Coming of the Civil War, p. 126 (2007).
External links
A Continent Divided: The U.S.-Mexico War, Center for Greater Southwestern Studies, the University of Texas at Arlington

