Rahul Dravid
 Rahul Dravid at GQ Men of the Year 2012 Awards | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full name | Rahul Sharad Dravid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | (1973-01-11) 11 January 1973 Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nickname | The Wall, The Great Wall, Jammy, Mr. Dependable[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 5 ft 11 in (1.80 m) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Batting | Right-handed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bowling | Right arm off spin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | Batsman, occasional wicketkeeper, Coach | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www.rahuldravid.com | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National side |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test debut (cap 207) | 20 June 1996 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Test | 24 January 2012 v Australia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ODI debut (cap 95) | 3 April 1996 v Sri Lanka | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last ODI | 16 September 2011 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ODI shirt no. | 19 (prev. 5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Only T20I (cap 38) | 31 August 2011 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| T20I shirt no. | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domestic team information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years | Team | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1990–2012 | Karnataka | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2000 | Kent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2003 | Scottish Saltires | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008–2010 | Royal Challengers Bangalore (squad no. 19) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011–2013 | Rajasthan Royals (squad no. 19) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | Marylebone Cricket Club | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Career statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: ESPNcricinfo, 30 January 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rahul Sharad Dravid (/ˌrəhuːl drəvɪd/ (![]() listen); born 11 January 1973) is a former Indian cricketer and captain, widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen in the history of cricket.[2][3][4] He is the current Overseas Batting Consultant for the Indian team, and also the head coach for the Under-19 and 'A' teams.[5] Dravid scored nearly 25000 runs in international cricket.[6] He is colloquially known as Dependable or Mr. Dependable, and often referred to as The Great Wall or The Wall by Indian cricket followers.[7]
listen); born 11 January 1973) is a former Indian cricketer and captain, widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen in the history of cricket.[2][3][4] He is the current Overseas Batting Consultant for the Indian team, and also the head coach for the Under-19 and 'A' teams.[5] Dravid scored nearly 25000 runs in international cricket.[6] He is colloquially known as Dependable or Mr. Dependable, and often referred to as The Great Wall or The Wall by Indian cricket followers.[7]
Born in a Marathi family and brought up in Bangalore, he started playing cricket at the age of 12 and later represented Karnataka at the under-15, under-17 and under-19 levels. Hailed as The Wall, Dravid was named one of the best five cricketers of the year by Wisden Cricketers' Almanack in 2000 and received the Player of the Year and the Test Player of the Year awards at the inaugural ICC awards ceremony in 2004.[8][9] In December 2011, he became the first non-Australian cricketer to deliver the Bradman Oration in Canberra.[10]
As of December 2016, Dravid is the fourth-highest run scorer in Test cricket, after Sachin Tendulkar, Ricky Ponting and Jacques Kallis.[11][12] In 2004, after completing his century against Bangladesh in Chittagong, he became the first and the only player till date to score a century in all the ten Test-playing countries.[13] As of October 2012, he holds the record for the most number of catches taken by a player (non-wicket-keeper) in Test cricket, with 210.[14] Dravid holds a unique record of never getting out for a Golden duck in the 286 Test innings which he has played. He has faced 31258 balls, which is the highest number of balls faced by any player in test cricket. He has also spent 44152 minutes at the crease, which is the highest time spent on crease by any player in test cricket.[15]
In August 2011, after receiving a surprise recall in the ODI series against England, Dravid declared his retirement from ODIs as well as Twenty20 International (T20I), and in March 2012, he announced his retirement from international and first-class cricket. He appeared in the 2012 Indian Premier League as captain of the Rajasthan Royals.[16]
Rahul Dravid, along with Glenn McGrath were honoured during the seventh annual Bradman Awards function in Sydney on 1 November 2012.[17] Dravid has also been honoured with the Padma Shri and the Padma Bhushan award, India's fourth and third highest civilian awards respectively.[18][19]
In 2014, Rahul Dravid joined the GoSports Foundation, Bangalore as a member of their board of advisors. In collaboration with GoSports Foundation he is mentoring India's future Olympians and Paralympians as part of the Rahul Dravid Athlete Mentorship Programme.[20]Indian badminton player Prannoy Kumar, Para-swimmer Sharath Gayakwad and young Golfer S. Chikkarangappa was part of the initial group of athletes to be mentored by Rahul Dravid. In July 2018, Dravid became the fifth Indian cricketer to be inducted into ICC Hall of Fame.[21]
Contents
1 Early life
2 Formative years and domestic career
3 International career
3.1 Early career
3.2 (1996–98) — a tale of two formats
3.3 Success in Test cricket
3.4 Struggle in ODIs
3.5 Debut World Cup success
3.6 Rise through the ranks
3.7 History at Eden
3.8 Peak years (2002–2006)
3.9 India tour of England, 2002
3.10 2003 Cricket World Cup
3.11 2011 Tour of England
3.12 Retirement
4 County stint
5 Indian Premier League and Champions League
6 Playing style
7 Controversies
7.1 Ball-tampering incident
7.2 Captaincy
8 Achievements and awards
8.1 National honours
8.2 Other honours
9 Personal life
9.1 Family
9.2 Commercial endorsements
9.3 Social commitments
10 Biographies
10.1 Books
11 References
12 External links
Early life
Dravid was born in a Marathi Deshastha Brahmin family[22] in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.[23] His family later moved to Bangalore, Karnataka, where he was raised.[24] His mother tongue is Marathi.[25] Dravid's father Sharad Dravid worked for a company that makes jams and preserves, giving rise to the later nickname Jammy. His mother, Pushpa, was a professor of Architecture at the University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering (UVCE), Bangalore.[26] Dravid has a younger brother named Vijay.[27] He did his schooling at St. Joseph's Boys High School, Bangalore and earned a degree in commerce from St. Joseph's College of Commerce, Bangalore.[27] He was selected to India national cricket team while studying MBA in St Joseph's College of Business Administration. He is fluent in several languages, Marathi, Kannada, English and Hindi.
Formative years and domestic career
Dravid started playing cricket at the age of 12, and represented Karnataka at the under-15, the under-17 and the under-19 levels.[28] Former cricketer Keki Tarapore first noticed Dravid's talent while coaching at a summer camp in the Chinnaswamy Stadium.[29] Dravid scored a century for his school team.[30] He also played as wicket-keeper.[27]
Dravid made his Ranji Trophy debut in February 1991, while still attending college.[31] Playing alongside future India teammates Anil Kumble and Javagal Srinath against Maharashtra in Pune, he scored 82 runs in the match, which ended in a draw.[32] He followed it up with a century against Bengal and three successive centuries after.[33] However, Dravid's first full season was in 1991–92, when he scored two centuries and finished up with 380 runs at an average of 63.30,[34] getting selected for the South Zone cricket team in the Duleep Trophy.[35] Dravid's caught the national team selectors' eye with his good performances for India A in the home series against England A in 1994–95.[33]
International career
Early career
Dravid, who had been knocking at the doors of Indian national cricket team for quite a while with his consistent performance in domestic cricket, received his first national call in October 1994, for the last two matches of the Wills World Series. However, he could not break into the playing eleven. He went back to the domestic circuit and kept knocking harder.[36] So much so, that when the selectors announced the Indian team for the 1996 World Cup sans Dravid, an Indian daily newspaper carried a headline – "Rahul Dravid gets a raw deal".[37][38] However, they could not ignore him any longer after the World Cup. Dravid made his international debut on 3 April 1996 in an ODI against Sri Lanka in the Singer Cup held in Singapore immediately after the 1996 World Cup, replacing Vinod Kambli.[39][40] He wasn't particularly impressive with the bat, scoring just three runs before being dismissed by Muttiah Muralitharan, but took two catches in the match.[41] He followed it up with another failure in the next game scoring just four runs before getting run out against Pakistan.[41]
In contrast to his ODI debut, his Test debut was rather successful one. Dravid was selected for the Indian squad touring England on the backdrop of a consistent performance in domestic cricket for five years.[42][43] Fine performances in the tour games including fifties against Gloucestershire and Leicestershire failed to earn him a place in the team for the First Test.[41][44] He finally made his Test debut at Lord's on 20 June 1996 against England in the Second Test of the series at the expense of injured senior batsman Sanjay Manjrekar.[39] Manjrekar, who was suffering from an ankle injury, was to undergo a fitness test on the morning of the Second Test. Dravid had already been informed that he would play if Manjrekar fails the test. As fate would have it, Manjrekar failed the fitness test. Ten minutes before the toss, Sandeep Patil, the then Indian coach, went up to Dravid to inform him that he was indeed going to make his debut that day. Patil recalled years later:[45]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
I told him he will be playing. His face lit up. I cannot forget that moment.
Coming in to bat at no. 7,[46] he forged important partnerships, first with another debutante Sourav Ganguly and then with Indian lower order, securing a vital first innings lead for his team.[47] Batting for more than six hours, he scored 95 runs before getting out to the bowling of Chris Lewis. Dravid was just five runs short of a landmark debut hundred when he nicked a Lewis delivery to the keeper and walked even before umpire's decision. When asked about the walk, he quipped, "Everybody at the ground had heard the nick".[48] He also took his first catch in Test cricket in this match to dismiss Nasser Hussain off the bowling of Srinath.[49][50] In the next tour game against British Universities, Dravid scored a hundred.[41] He scored another fifty in the first innings of the Third Test.[41] Dravid concluded a successful debut series with an impressive average of 62.33 from two Test matches.[51]
.mw-parser-output .quotebox{background-color:#F9F9F9;border:1px solid #aaa;box-sizing:border-box;padding:10px;font-size:88%}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft{margin:0.5em 1.4em 0.8em 0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright{margin:0.5em 0 0.8em 1.4em}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.centered{margin:0.5em auto 0.8em auto}.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatleft p,.mw-parser-output .quotebox.floatright p{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-title{background-color:#F9F9F9;text-align:center;font-size:larger;font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:before{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" “ ";vertical-align:-45%;line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox-quote.quoted:after{font-family:"Times New Roman",serif;font-weight:bold;font-size:large;color:gray;content:" ” ";line-height:0}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .left-aligned{text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .right-aligned{text-align:right}.mw-parser-output .quotebox .center-aligned{text-align:center}.mw-parser-output .quotebox cite{display:block;font-style:normal}@media screen and (max-width:360px){.mw-parser-output .quotebox{min-width:100%;margin:0 0 0.8em!important;float:none!important}}
Rahul Dravid, reflecting back on his Test debut 15 years later, during India tour of England, 2011.[52]
(1996–98) — a tale of two formats
Dravid's early years in international cricket mirrored his international debut. While he straightaway made a name for himself in Test cricket, he had to struggle quite a bit to make a mark in ODIs.[53]
Success in Test cricket
After a successful Test debut in England, Dravid played in the one-off Test against Australia in Delhi – his first Test in India. Batting at no. 6, he scored 40 runs in the first innings.[46] Dravid batted at no. 3 position for the first time in the First Test of the three-match home series against South Africa in Ahmedabad in November 1996. He didn't do too well in the series scoring just 175 runs at an average of 29.16.[54]
Two weeks later, India toured South Africa for a three–match Test series. Chasing a target of 395 runs in the First Test, Indian team bundled out meekly for 66 runs on the Durban pitch that provided excessive bounce and seam movement.[55] Dravid, batting at no. 6, was the only Indian batsman who reached double figures in the innings scoring 27 not out.[56] He was promoted to the no. 3 slot again in the second innings of the Second Test however, it was his breakthrough performance in the Third Test that secured his position as India's quintessential no. 3 batsman. He almost won the match for India with his maiden test hundred in the first innings scoring 148 runs and another 81 runs in the second innings at Wanderers before the thunderstorms, dim light and Cullinan's hundred saved the day for South Africa enabling them to draw the match.[46][57] Dravid's performance in this Test earned him his first Man of the Match award in Test cricket.[58] He top scored for India in the series with 277 runs at an average of 55.40.[59]
Dravid carried his good form from South Africa to the West Indies where he once again top scored for India in the five–match Test series that India lost 0–1. He scored 360 runs at an average of 72.00 including four fifties.[60][61] 92 runs scored in the first innings of the fifth match in Georgetown earned him a joint Man of the Match award along with Shivnarine Chanderpaul.[62] With this series, Dravid concluded a successful 1996/97 Test season, topping the international runs chart with 852 runs from 12 matches at an average of 50.11 with six fifties and one hundred.[63]
Dravid continued his good run in the following season scoring seven fifties in eight Tests that included fifties in six consecutive innings (three each against Sri Lanka and Australia), becoming only the second Indian to do so after Gundappa Vishwanath.[64] By the end of 1997/98 Test season, he had scored 15 fifties in 22 Tests which included four scores of nineties but just a solitary hundred.[65]
The century drought came to an end in the ensuing season when he further raised the bar of his performance scoring 752 runs in seven Tests at an average of 62.66 that included four hundreds and one fifty and in the process topping the runs chart for India for the 1998/99 Test season.[66] The first of those four hundreds came on the Zimbabwe tour. Dravid top scored in both the innings against Zimbabwe scoring 118 and 44 runs respectively however, India lost the one-off Test.[67]
The Zimbabwe tour was followed by a tour to New Zealand. First Test having been abandoned without a ball being bowled,[68] the series started for Dravid with the first duck of his Test career in the first innings of the Second Test and ended with hundreds in both the innings of the Third Test in Hamilton. He scored 190 and 103 not out in the first and the second innings respectively, becoming only the third Indian batsman, after Vijay Hazare and Sunil Gavaskar, to score a century in both innings of a Test match.[41][69] Dravid topped the runs table for the series with 321 runs from two matches at an average of 107.00 but could not prevent India from losing the series 0–1.[70][71]
Later that month, India played a two Test home series against Pakistan. Dravid didn't contribute much with the bat. India lost the First Test but won the Second Test in Delhi riding on Kumble's historic 10-wicket haul. Dravid played his part in the 10-wicket haul by taking a catch to dismiss Mushtaq Ahmed who was Kumble's eighth victim of the innings.[72][73] The Indo-Pak Test series was followed by the 1998–99 Asian Test Championship. Dravid couldn't do much with the bat as India went on to lose the riot-affected First Test of the championship against Pakistan at the Eden Gardens.[74] India went to Sri Lanka to play the Second Test of the championship. Dravid scored his fourth hundred of the season at Colombo in the first innings of the match. He also effected a brilliant run out of Russel Arnold during Sri Lankan innings fielding at short leg.[75] On the fourth morning, Dravid got injured while fielding at the same position when the ball from Jayawardene's pull shot hit him below his left eye through the helmet grill. He didn't come out to bat in the second innings due to the injury.[76] The match ended in a draw as India failed to qualify for the Finals of the championship.[77]
Struggle in ODIs
In a stark contrast to his Test career, Dravid had to struggle a lot to make a mark in the ODIs.[53] Between his ODI debut in April 1996 and the end of 1998 calendar year, Dravid regularly found himself in and out of the ODI team.[78]
Despite his initial struggle in ODIs, there were quite a few highlights as well.[38] Dravid tasted first success of his ODI career in the 1996 'Friendship' Cup against Pakistan in the tough conditions of Toronto.[79] He emerged as the highest scorer of the series with 220 runs in five matches at an average of 44.00 and a strike rate of 68.53.[80] He won his first ODI Man of the Match award for the 46 runs scored in the low scoring third game of the series.[81] He top scored for India in the Standard Bank International One-Day Series 1996/97 in South Africa with 280 runs from eight games at an average of 35.00 and a strike rate of 60.73,[82] the highlight being a Man of the Match award-winning performance (84 runs, one catch) in the Final of the series that came in a losing cause.[83] He was the second highest run scorer for India in the four-match bilateral ODI series in the West Indies in 1996/97 with 121 runs at an average of 40.33 and a strike rate of 57.61.[84]
Dravid's maiden ODI hundred came in a losing cause in the 1997 Pepsi Independence Cup against Pakistan in Chennai.[85][86] Dravid top scored for India in the quadrangular event with 189 runs from three games at an average of 94.50 and a strike rate of 75.60 however, India failed to qualify for the Final of the series.[87][88]
However, Dravid's achievements in the ODIs were dwarfed by his failures in the shorter format of the game.[38] 14 runs from two games in the 1996 Pepsi Sharjah Cup; 20 runs from two innings in the Singer World Series; 65 runs from four innings in the 1997 'Friendship' Cup; 88 runs from four games in the 1998 Coca-Cola Triangular Series including a 22-ball five runs and a 21-ball one run innings, both coming against Bangladesh; 32 runs from four games in the 1998 'Friendship' Cup;[89] a slew of such poor performances often forced him to the sidelines of the India ODI squad.[78] By the end of 1998, Dravid had scored 1709 runs in 65 ODIs at a humble average of 31.64 with a poor strike rate of 63.48.[90]
By now, Dravid had been branded as a Test specialist. While he continued to score heavily in Test cricket, his poor strike rate in ODIs came under scanner. He drew criticism for not being able to adjust his style of play to the needs of ODI cricket, his lack of attacking capability and play big strokes. However, Dravid worked hard and re-tooled his game by increasing his range of strokes and adapting his batting style to suit the requirements of ODI cricket. He learned to pace his innings cleverly without going for the slogs.[38][53][79]
Dravid's ODI renaissance began on the 1998/99 New Zealand tour. He carried his form from the Hamilton Test, where he had scored twin centuries, into the bilateral ODI series and scored a run-a-ball hundred in the First ODI that earned him his third Man of the Match award.[38][41][81] The hundred came in a losing cause.[91] However, his effort of 51 runs from 71 balls in the Fourth ODI came in India's victory and earned him his second Man of the Match award of the series.[81][92] He ended as the top scorer of the series with 309 runs from five games at an average of 77.25 and a strike rate of 84.65.[93] Dravid scored a hundred against Sri Lanka in 1998/99 Pepsi Cup at Nagpur adding a record 236 runs for the 2nd wicket with Ganguly, who also scored a hundred in the match. Uncharacteristically, Dravid was the faster of the two scoring 116 of 118 deliveries.[94] In the next match against Pakistan, he bowled four overs and took the wicket of Saeed Anwar, out caught behind by wicket-keeper Nayan Mongia.[95] This was his first wicket in international cricket.[41]
Dravid warmed up for his debut World Cup with two fifties in the 1998–99 Coca-Cola Cup in Sharjah, one each against England and Pakistan.[96] Standing-in as the substitute wicket-keeper in the third match of the series for Nayan Mongia, who got injured during keeping, Dravid effected two dismissals. He first stumped Graeme Hick off Sunil Joshi's bowling, who became Dravid's first victim as a wicket-keeper, and then caught Neil Fairbrother off Ajay Jadeja's bowling.[97][98][99] He top scored for India in the tournament,[100] though his last ODI innings before the World Cup was a golden duck against Pakistan, in the Final of the series.[96]
Before Indian team departed for England to participate in the 1999 World Cup, they played a friendly game with 1983 World Cup winning team. Although Dravid scored just 20 runs, he took two wickets dismissing Dilip Vengsarkar and Roger Binny.[101]
Debut World Cup success
Dravid announced his form in England hitting consecutive fifties against Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire in the warm-up games.[41]
He made his World Cup debut against South Africa at Hove striking a half century, but scored just 13 in the next game against Zimbabwe.[102] India lost both the games.[103] Having lost the first two games, India needed to win the remaining three games of the first round to have any chance of advancing into the Super Six stage.[104] Dravid put up a partnership of 237 runs with Sachin Tendulkar against Kenya at Bristol – a World Cup record – and in the process hit his maiden World Cup hundred, helping India to a 94-run victory.[105] India's designated keeper Mongia left the field at the end of 9th over during Kenyan innings, forcing Dravid to keep the wickets for the rest of the innings.[106] In the absence of injured Nayan Mongia, Dravid played his first ODI as a designated keeper against Sri Lanka at Taunton.[107][108] Dravid once again staged a record breaking partnership worth 318 runs – the first ever three hundred run partnership in ODI history – but this time with Sourav Ganguly, guiding India to a 157-run win.[109] Dravid scored 145 runs from 129 balls with 17 fours and a six, becoming the second batsman in World Cup history to hit back-to-back hundreds.[108] Dravid struck a fine fifty in the last group match as India defeated England to advance into the Super Six stage.[110] Dravid scored 2, 61 & 29 in the three Super Six matches against Australia, Pakistan & New Zealand respectively.[102] India failed to qualify for the semi-finals having lost to Australia and New Zealand but achieved a consolation victory against Pakistan in a tense game, what with the military conflict going on between the two countries in Kashmir at the same time.[111][112] Dravid emerged as the top scorer of the tournament with 461 runs from 8 games at an average of 65.85 and a strike rate of 85.52.[113] He capped a successful World Cup outing on personal front with a commentary stint during the World Cup Final which resulted in him getting reprimanded by the BCCI for appearing on television without board's permission. He received CEAT Cricketer of the World Cup award, later that year.[114]
Dravid's post-World Cup campaign started on a poor note with just 40 runs coming in 4 games of Aiwa Cup in August 1999.[41] He soon came into his own, top-scoring for India in two consecutive limited-overs series – the Singapore Challenge, the highlight being a hundred in the Final coming in a lost cause,[115][116] and the DMC Cup, the highlight being a match winning effort (77 runs, 4 catches) in the series decider for which he received man-of-the-match award.[117][118] By now, Dravid had started to keep wickets on an infrequent basis with India fielding him as designated wicket-keeper in five out of 10 ODIs played in the three events.[41][107] Dravid had a quiet time in the LG Cup where he scored 81 runs in 4 games.[41]
Dravid kick-started his post World Cup Test season with a decent outing against New Zealand in the 3-match home series. His best effort of the series came in the second innings of the First test at Mohali scoring 144, helping India salvage a draw after being bowled out for 83 runs in the First innings.[119] Before this innings, Dravid had five test hundreds to his name from 29 tests, all of which came in away tests, this being his first test hundred on Indian soil.[46] Dravid did well in the 3–2 series win against New Zealand in the bilateral ODI series, scoring 240 runs in 5 games at an average of 60 and a strike rate of 83.62, ending as the second highest scorer in the series.[120][121] His career best effort in ODIs came in this series in the second game at Hyderabad where he scored run-a-ball 153 runs which included 15 fours and two sixes.[96] He featured in a 331-run partnership with Tendulkar, which was the highest partnership in ODI cricket history, a record that stood for 15 years until it was broken in 2015.[122] With this series, Dravid ended an eventful year, as far as his ODI career was concerned, on a high note. In 1999, Dravid scored 1761 runs in 43 ODIs at an average of 46.34 and a strike rate of 75.16 including 6 hundreds and 8 fifties and featured in two 300+ partnerships.[122][123]
India toured Australia in December 1999 for a 3-match test series and a triangular ODI tournament. Although Dravid scored a hundred against Tasmania in the practice match, he failed miserably with the bat in the Test series as India slumped to a 0–3 whitewash. He did reasonably well in the 1999–2000 Carlton & United Series scoring 3 fifties in the triangular event however, India failed to qualify for the Final of the tournament.[41][124]
Dravid's poor form in Tests continued as India suffered a 0–2 whitewash against South Africa in a home series.[41] He had moderate success in the bilateral ODI series against South Africa. He contributed to India's 3–2 series win with 208 runs at an average of 41.60 which included 2 fifties and three wickets at an average of 22.66 topping the bowling average chart for the series.[41][125] His career best bowling figure of 2/43 from nine overs in the First ODI at Kochi, was also the best bowling figure by any bowler in that particular match.[41][126] India next played a tri-nation series in Sharjah but failed to qualify for the Finals.[127] Such was the collective failure of Indian batting, that Dravid, with a mediocre returns of 89 runs from 4 matches at an average of 22.25, was still the 2nd best Indian batsman in the series.[128]
Rise through the ranks
In February 2000, Tendulkar tendered his resignation from captaincy amidst much speculations resulting in the promotion of Ganguly, the vice-captain then, as the new captain of the Indian team.[129][130] In May 2000, while Dravid was busy playing county cricket in England, Indian team was announced for the Asia cup and he was handed the vice-captaincy of the team. The newly appointed vice-captain had to leave the county championship temporarily, missing two championship games and two one day games, to fulfill his national commitment.[131] Indian team, Dravid included, fared poorly in the Asia cup and failed to qualify for the Final. Subsequently, Dravid returned to England to resume his county sojourn with Kent.[41][132]
As the new international season commenced, the first and foremost challenge for the newly appointed captain and vice-captain, Ganguly and Dravid respectively, was to pull the team out of the shadows of the match fixing scandal. Indian team played 2000 ICC KnockOut Trophy with vigour and showed a lot of character beating Kenya, Australia and South Africa in consecutive matches to reach the Finals. Although India lost to New Zealand in the Finals, their spirited performance in the tournament helped restoring public faith back in Indian cricket.[133] Dravid played his part scoring 157 runs in 4 matches at an average of 52.33, including 2 fifties.[134] Dravid scored 85 runs in the second match of 2000–01 Coca-Cola Champions Trophy against Zimbabwe while opening the innings but was forced to miss the rest of the tournament because of an injury. India went on to reach the Final where they got bowled out for a paltry score of 54 losing to Sri Lanka by 245 runs.[133]
India kick started the new Test season with a 9-wicket win against Bangladesh. Dravid played a brisk knock of 41 runs from 49 balls, including 5 fours and a six, while chasing a target of 63 runs.[135] Dravid's next assignment was a test series against Zimbabwe which was John Wright's first series as Indian coach.[133] Dravid had recommended Wright's name as the new national team coach having had the first hand experience of Wright's coaching skills during his county stint.[136] The Indian vice-captain welcomed the new coach with his maiden double hundred. He scored 200 not out in the first inning and 70 not out in the second, guiding India to a comfortable 9-wicket victory against Zimbabwe. He scored 162 in the drawn Second test to end the series with an average of 432.00 – highest batting average by an Indian in a Test series.[41][137]
Dravid had a modest outing with the bat against Zimbabwe in the bilateral ODI series.[41] He captained the Indian team for the first time in the fifth match of the series in the absence of the regular captain Ganguly who was serving one match suspension.[138] Riding on Agarkar's all-round performance, Dravid led India to a 39-run victory in his maiden ODI as Indian captain.[139]
History at Eden
The Australian team toured India in February 2001 for what was being billed as the "Final Frontier" for Steve Waugh's all conquering men, who were coming on the back of 15 consecutive Test wins.[140] Dravid failed in the first innings of the First Test but displayed strong resilience in Tendulkar's company in the second innings. Dravid's 196 ball long resistance finally ended when he got out bowled to Warne for 39 runs. Despite their efforts, they could not stop the Australians from extending their winning streak to 16 consecutive Test wins as they beat India convincingly by 10 wickets inside three days.[141][142]
The Australian juggernaut seemed unstoppable as they looked on course for their 17th consecutive victory in the Second Test at the Eden Gardens, when they bowled India out for meagre 171 in the first innings and enforced a follow-on after securing a massive lead of 274 runs. In the second innings, Laxman, who had scored a fine fifty in the first innings, was promoted to no. 3 position which had been Dravid's usual spot for quite sometime now, while Dravid, who had gotten out bowled to Warne for second time in a row in the first innings for just 25 runs, was relegated to no. 6 position. When Dravid joined Laxman in the middle on the third day of the Test, with scoreboard reading 232/4 and India still needing 42 runs to avoid an innings defeat, another convincing win for Australia looked inevitable. However, what transpired etched the names of Laxman and Dravid as the architects of one the greatest fightbacks in the cricketing history.[140][143]
Dravid and Laxman played the remaining time on the third day and whole of the fourth day, denying Australia a single wicket on Day 4.[140] Steve Waugh used nine different bowlers but could not break the Laxman-Dravid partnership who completely dominated the Australian bowlers adding 335 runs on Day 4.[144] Dravid, who was disappointed, both with the severe criticism for his own recent failures in the series as well as the flak received by the team in the media, celebrated his hundred in an uncharacteristic fashion gesturing at the press box.[140][145] Eventually, Laxman got out on the fifth morning bringing the 376-runs partnership to an end. Dravid soon perished getting run out for 180 while trying to force the pace.[140] Captain Ganguly declared the innings at 657/7 setting Australia a target of 384 runs with 75 overs left in the match.[146][147] An inspired team India bowled superbly to dismiss Australia for 212 in 68.3 overs.[145][148] India won the match by 171 runs. This was only the third instance of a team winning a Test after following-on and India became the 2nd team to do so.[146]
Dravid scored 81 runs in the first innings of the Third Test and took 4 catches in the match as India defeated Australia at Chennai in a nail biting finish to clinch the series 2–1. Dravid scored 80 in the first of the 5-match ODI series at his home ground as India won the match by 60 runs. He didn't do too well in the remaining 4 ODIs as Australia won the series 3–2.[41][149] Dravid topped the averages for the 2000/01 Test season with 839 runs from six matches at an average of 104.87.[150]
Dravid had a decent outing in Zimbabwe, scoring 137 runs from 134 balls in the First Tour game and aggregating 138 runs at an average of 69.00 from the drawn Test series.[151][152] In the ensuing triangular ODI series, he aggregated 121 runs from 5 matches at an average of 40.33 and a strike rate of 101.68, the highlight being an unbeaten 72 off 64 balls,[153] while chasing a target of 235 against Zimbabwe in the 3rd match of the series, guiding India to a 4-wicket win with four balls to spare. He was adjudged man of the match for his match winning knock.[154]
On the next tour to Sri Lanka, India lost the first three matches of the triangular event. In the absence of suspended Ganguly, Dravid captained the side in the 4th match and led them to their first win in the series. India won the next two matches to qualify for the Final, which they went on to lose to Sri Lanka.[155] Dravid played crucial innings in all the three victories including a fifty in the last match. He top scored for India in the series with 259 runs from seven matches at an average of 51.80 and a strike rate of 59.81.[156] Dravid, who had been relegated to no. 6 position during the Test series against Australia few months back, regained his usual no. 3 spot during the ensuing 3-Test series in Sri Lanka, in the absence of Laxman. Batting at no. 3, Dravid scored a crucial 75 in the tough fourth innings chase of the Second Test.[155] The young leaders of the team, Ganguly and Dravid, ensured India's first Test win in Sri Lanka since 1993, through some stunning display of batting in the fourth innings of the Second Test, despite the absence of key players like Tendulkar, Laxman, Srinath and Kumble.[157] However, India lost the First and the Third Test to lose the series 1–2.[155] Dravid top scored for India in the series with 235 runs at an average of 47.00.[158]
Dravid had decent success in Standard Bank tri-series on South Africa tour, scoring 214 runs (including 3 fifties) at an average of 53.50 and a strike rate of 71.81.[159] He also kept wickets in the final two ODIs of the series effecting 3 stumpings.[107] Dravid opened the innings in the first test of the ensuing Test series but failed to make a mark as India lost the match. India, having failed to last hundred overs in any of the previous three innings in the series, needed to bat out four sessions in the Second Test to save the match. They started on a poor note losing their first wicket in the first over with zero runs on the scoreboard. However, Dravid forged an important partnership of 171 runs with Dasgupta. More importantly, the partnership lasted for 83.2 overs taking India to the brink of safety. Poor weather too helped India salvage a draw as only 96.2 overs could be bowled in the innings.[160][161][162] Dravid captained the team in the 'unofficial' Third test in the absence of injured Ganguly, which India lost by an innings margin.[163][164]
By the end of the South African tour, Dravid had started experiencing problem in his right shoulder. Although he played the ensuing home test series against England, he pulled out of the six-match bilateral ODI series to undergo shoulder rehabilitation program in South Africa. He returned for the Zimbabwe's tour of India but performed below par, scoring a fifty each in the Test series and the bilateral ODI series.[164][41]
Peak years (2002–2006)
Overall, Dravid had a disappointing 2001/02 season, scoring 296 runs from seven Tests at an average of 29.60. However, Dravid struck form in the ensuing season. For the next four years, Dravid outclassed every Indian batsman by a mile to establish himself as India's most prolific run-machine. During this four-year period, Dravid was the top scorer for India in both the formats of the game. Between 2002-06, Dravid scored 4,697 runs for India in 48 Tests at an average of 70.10, almost 18 runs more than the next best batsman, Virender Sehwag, who averaged 52.48 in the same period. He scored fourteen hundreds during the period, including four double hundreds.
India toured West Indies in April 2002. Dravid scored an unbeaten hundred, his tenth overall and 6th outside India, against West Indies at Georgetown in the first test match. Batting with a swollen jaw after being hit by a Mervyn Dillon bouncer, Dravid scored 144 not out saving the day for India as they avoided a follow-on. The match ended in a draw. India beat West Indies by 37 runs in the second test at Port of Spain. Dravid contributed to the win with a fifty and 4 catches. He scored 91 runs in the 4th drawn test at St. John's. He also took the wicket of Ridley Jacobs who was batting on 118 – Dravid's only wicket in Test cricket. India lost the 5-match test series 1–2. Dravid was the 2nd highest scorer for India aggregating 404 runs at an average of 57.71. He fared poorly with the bat in the bilateral ODI series. He also doubled up as the wicket-keeper in the series effecting 2 dismissals (1 catch and 1 stumping).
India tour of England, 2002
India's next international assignment was the England tour in June 2002, six years after the previous tour when Dravid had made his Test debut. It was on this tour where Dravid hit the peak form of his career. The tour started with a triangular ODI series involving India, England and Sri Lanka. Dravid continued his keeping job in the series. In the first ODI at Lord's, he effected three dismissals (two catches and a stumping) and then scored an unbeaten 73 guiding India to a six-wicket victory against England in the company of Yuvraj Singh. In the 4th ODI against Sri Lanka, he scored a fifty that won him a man of the match award as India won the match by 4 wickets. India eventually pulled off a remarkable chase to win the tournament beating England in the final by two wickets. Dravid's aggregated 245 runs in the tournament at an average of 49.
Dravid warmed up for the four-match Test series with a fifty against Hampshire in the tour game. He scored 46 and 63 in the First Test at Lord's as India lost the match by 170 runs. He failed in the first innings of the Second Test at Nottingham as India scored 357 runs. England, riding on Vaughn's hundred, piled up a mammoth 617 runs, taking a first innings lead of 260 runs. Indian team was in a state of bother as they were reduced to 11/2 in the second innings, still trailing by 249 runs however, a match saving hundred by Dravid along with the fifties from Tendulkar and Ganguly enabled India to draw the match.
The Third Test was played at Headingley, traditionally known to be conducive for seam bowling. Ganguly won the toss and took a bold decision to bat first on a gloomy overcast morning. Nasser Hussain had studded his bowling line-up with four seamers including Hoggard, Flintoff, Tudor and Caddick. To make the matters worse, India lost Sehwag in the seventh over of the match. However, Dravid came in and joined forces with Bangar. Together the two batsmen weathered the storm. They applied themselves, took body blows but never gave the English bowlers any chance. Dravid and Bangar starred in a match defining partnership of 170 runs. By the time Bangar got out after a commendable fifty, the sun was out and batting had become easier. Tendulkar joined Dravid as Dravid went on to complete his 12th Test hundred. Dravid and Tendulkar put on 150 runs together before a battered and bruised Dravid finally got out stumped to Giles for 148 runs, but not before playing out the difficult morning session of the second day. As the conditions got easier to bat, Ganguly and Tendulkar piled on England's misery bringing up their individual hundreds in the process. India declared the innings on 628/8 and then bowled England out twice to win the match by an innings and 46 runs – India's first overseas victory by an innings margin since 1977/78. Such was the impact of Dravid's seven-hour-long fighting knock that, despite Sachin outscoring him by 45 runs (he scored 193 runs), Dravid was adjudged the man of the match for his 148 runs. Dravid backed up his two consecutive hundreds in the series with another one at The Oval, this time scoring a double hundred. After England scored 515 runs in the first innings of the fourth Test, Dravid scored 217 runs to take India to 505. The test and the series ended in a draw. Dravid was adjudged man of the match for second consecutive match. Dravid amassed 602 runs in the series at an average of 100.33, including three hundreds and a fifty and was adjudged joint man of the series along with Vaughan.
Dravid became the first Indian batsman to score hundreds in four consecutive Test innings when he scored 100 not out against West Indies in the first of the three match home series at Wankhede. Severe cramps and dehydration forced Dravid to leave his inning midway soon after he completed his hundred as he retired hurt on 100 to get drips administered to himself. India won the test by innings and 112 runs. Dravid didn't do too well in the remaining two tests ending with a modest series aggregate of 148 runs at an average of 49.33. Dravid did well in the subsequent bilateral 7-match ODI series. He topped Indian averages for the series scoring 300 runs at an average of 75 and a strike rate of 89.82 including one hundred and two fifties. He also effected 7 dismissals (6 catches, 1 stumping) – most by a wicketkeeper in the series. In the 4th ODI, West Indies set India an improbable target of 325 runs to win the match. Dravid scored a solid hundred and forged an unbeaten partnership with Bangar as India won the match by 5 wickets levelling the series 2–2. He once again scored an important fifty in the 6th match when India were down in the series 2–3, helping India win the match and level the series 3–3. India, however, lost the last match to lose the series 3–4.
India's preparation for 2003 World Cup didn't go as well as they'd have hoped for. Their last overseas tour before the World Cup turned out to be a disaster. Indians suffered a whitewash in the 2 match Test series in New Zealand and lost the ODI series 2–5. Although Dravid top scored for India in the Test series and was the 3rd best batsman for India in the ODIs, his performances were far from satisfactory.
2003 Cricket World Cup
He was appointed the vice-captain during 2003 World Cup, in which India reached the finals, playing as a wicket-keeper batsman to accommodate an additional batsman, a strategy that worked out well. Dravid was appointed the captain for the Indian team for 2007 World Cup, where India had an unsuccessful campaign.

Dravid fielding during a Test match against Sri Lanka in Galle in 2008.
In 2003–2004 season, Dravid scored three double centuries: one each against New Zealand, Australia and Pakistan. In the first innings of the second Test against Australia at Adelaide, India reached 85–4 in reply to Australia's 556, when Dravid and Laxman made 303 for the fifth wicket. Laxman was dismissed for 148 and Dravid went on make 233, at that time the highest score by an Indian batsman outside India. He made 72 not out in the second innings, and India won.[165] Dravid scored 619 runs in the four-match series against Australia with an average of 103.16, winning the man of the series award. During the later part of the season, in Ganguly's absence, Dravid led India to its first test victory over Pakistan at their home[166] in the first test match at Multan Cricket Stadium. At Rawalpindi, in the third and final match of the series, Dravid made 270 runs, helping India to win the series.[167] During India's unsuccessful tour of England in 2011, in which their 4–0 loss cost them the top rank in Test cricket, Dravid made three centuries.

Dravid batting against Australia at the MCG
2011 Tour of England
Having regained his form on the tour to West Indies, where he scored a match-winning hundred in Sabina park, Jamaica, Dravid then toured England in what was billed as the series which would decide the World No. 1 ranking in tests. It would later be hailed as one of his greatest series performances by experts.
In the first test at Lord's, in reply to England's 474, Dravid scored an unbeaten 103, his first hundred at the ground where he debuted in 1996. He received scant support from his teammates as India were bowled out for 286 and lost the test.[168] The 2nd test at Trentbridge, Nottingham again saw Dravid in brilliant form. Sent out to open the batting in place of an injured Gautam Gambhir, he scored his second successive hundred. His 117 though, again came in a losing cause, as a collapse of 6 wickets for 21 runs in the first innings led to a massive defeat by 319 runs.[169] Dravid failed in both innings in the third test at Birmingham, as India lost by an innings and 242 runs, one of the heaviest defeats in their history.[170] However, he came back brilliantly in the fourth and final match at The Oval. Again opening the batting in place of Gambhir, he scored an unbeaten 146 out of India's total of 300, carrying his bat through the innings. Once again, though, his efforts were in vain as India lost the match, completing a 0–4 whitewash.[171]
In all, he scored 461 runs in the four matches at an average of 76.83 with three hundreds. He accounted for over 26% of India's runs in the series and was named India's man of the series by England coach Andy Flower. His performance in the series was met with widespread admiration and was hailed by some as one of his finest ever series[172][173]
Retirement
Rahul Dravid was dropped from the ODI team in 2009, but was selected again for an ODI series in England in 2011, surprising even Dravid himself since, although he had not officially retired from ODI cricket, he had not expected to be recalled.[174][175][176] After being selected, he announced that he would retire from ODI cricket after the series.[174] He played his last ODI innings against England at Sophia Gardens, Cardiff, on 16 September 2011, scoring 69 runs from 79 balls before being bowled by Graeme Swann.[177] His last limited-overs international match was his debut T20I match; he announced his retirement before playing his first T20I match.[178]
Dravid announced his retirement from Test and domestic cricket on 9 March 2012, after the 2011–12 tour of Australia, but he said that he would captain the Rajasthan Royals in the 2012 Indian Premier League. He was the second-highest run scorer and had taken the highest number of catches in Test cricket at the time of his retirement.[179]
In July 2014, he played for the MCC side in the Bicentenary Celebration match at Lord's.[180]
County stint
Dravid had always been keen on further honing his batting skills in testing English conditions by playing in county cricket. He had discussed about the prospects regarding the same with John Wright, the former New Zealand cricketer and incumbent Kent coach, during India's 1998–99 tour of New Zealand. Wright was particularly impressed with Dravid's performance on that tour, especially his twin hundreds at Hamilton. The talks finally materialized and Dravid made his county debut for Kent in April 2000. His co-debutante Ganguly made his county debuted in the same match, albeit for the opposite team.[132]
Kent offer had come as a welcome change for Dravid. There was too much negativity surrounding Indian cricket marred by match fixing controversy. Dravid himself had been struggling to score runs in Tests for quite some time now.[41] The county stint gave him a chance to "get away to a new environment" and "relax". The wide variety of pitches and weather conditions in England and a full season of intense county cricket against professional cricketers gave him a chance to further his cricketing education and learn things about his game.[132]
Dravid made the most of this opportunity. In his 2nd game for Kent, Dravid scored a fluid 182 propelling them to an innings and 163 runs victory over the touring Zimbabwe side. Out of 7 first class tour games that Zimbabwe played on that tour, Kent was the only team that managed to beat them. Dravid hit another fifty in a draw against Surrey. In June 2000, Dravid had to miss a county match for Kent in order to perform his national duties.
In July 2000, Kent's away match against Hampshire at Portsmouth was billed as a showdown between two great cricketers- Warne and Dravid. Dravid came out on top. On a dustbowl, tailor made to suit home team spinners, Warne took 4 wickets but could not take the all important wicket of Dravid. Coming in to bat at 15/2, Dravid faced 295 balls scoring 137 runs – his maiden hundred in county championships. Dravid scored 73 not out in the 2nd innings guiding Kent to a six wicket victory as Warne went wicketless.
In their last county game of the season, Kent needed one bonus point to prevent themselves from being relegated to the Second Division. Dravid made sure they stay put in the First Division by fetching that one bonus point with an inning of 77 runs.
Dravid concluded a successful stint with Kent aggregating 1221 runs from 16 first class matches(15 county games and 1 tour game against Zimbabwe) at an average of 55.50 including 2 hundreds and 8 fifties. He shouldered Kent's batting single-handedly as the second best Kent batsman during the same period, Paul Nixon, scored just 567 runs at an average of 33.35 in 17 matches. Dravid contributed to Kent's county campaign not just with the bat but also with his fielding and bowling taking 14 catches and 4 wickets at an average of 32.00.
Indian Premier League and Champions League
RS Dravid's record in Twenty20 matches[181] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| League | Matches | Runs | HS | 100s | 50s | Avg. |
T20I[182] | 1 | 31 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 31.00 |
IPL[183] | 89 | 2174 | 75* | 0 | 11 | 28.23 |
CLT20[184] | 15 | 282 | 71 | 0 | 1 | 23.50 |
Rahul Dravid played for Royal Challengers Bangalore in IPL 2008, 2009 and 2010. Later he played for Rajasthan Royals and led it to finals of Champions League T20 in 2013, and play-offs of Indian Premier League in 2013. Dravid announced retirement from Twenty20 after playing the 2013 Champions League Twenty20 in Sept.-Oct 2013.[185][186]
Playing style
Dravid is known for his technique, and had been one of the best batsmen for the Indian cricket team. In the beginning, he was known as a defensive batsman who should be confined to Test cricket, and was dropped from the ODI squad due to a low strike rate. However, in a period of his career, he began consistently scoring runs in ODIs as well, earning him the ICC Player of the year award. His nickname of 'The Wall' in Reebok advertisements is now used as his nickname. Dravid has scored 36 centuries in Test cricket at an average of 53.19; this included five double centuries. In one-dayers, he has an average of 39.49, and a strike rate of 71.22. He is one of the few Indians whose Test average is better at away than at home, averaging almost five runs more in foreign pitches.[187] As of 23 September 2010, Dravid's Test average in abroad is 55.53, and his Test average at home is 50.76;[187] his ODI average abroad is 37.93[188] and his ODI average at home is 43.11.[189] Taking those matches in consideration that were won by India, Dravid averages 66.34 runs in Tests[190] and 50.69 runs in ODIs.[191]
Dravid's sole Test wicket was of Ridley Jacobs in the fourth Test match against the West Indies during the 2001–2002 series. While he has no pretensions to being a bowler, Dravid often kept wicket for India in ODIs. Dravid is now a specialist batsman, averaging 63.51 in matches played since 1 January 2000.
Dravid was involved in two of the largest partnerships in ODIs: a 318-run partnership with Sourav Ganguly, the first pair to combine for a 300-run partnership, and then a 331-run partnership with Sachin Tendulkar, which is a world record. He also holds the record for the greatest number of innings played since debut before being dismissed for a duck. His highest scores in ODIs and Tests are 153 and 270 respectively. Each of his five double centuries in Tests was a higher score than his previous double century (200*, 217, 222, 233, 270).
Also, Dravid is the current world record holder for the highest percentage of runs scored in matches won under a single captain, where the captain has won more than 20 Tests.[192] In the 21 Test matches India won under Ganguly's captaincy, Dravid scored at a record average of 102.84 runs; scoring 2571 runs, with nine hundreds, three of them being double-centuries, and ten fifties in 32 innings. He contributed nearly 23% of the total runs scored by India in those 21 matches, which is almost one run out of every four runs the team scored.
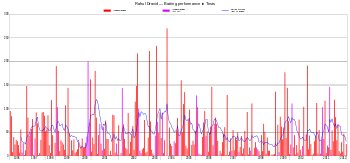
An innings-by-innings breakdown of Dravid's Test match batting career, showing runs scored (red bars with purple bars for not out) and the average of the last ten innings (blue line).
He was named one of the Wisden cricketers of the year in 2000. Though primarily a defensive batsman, Dravid scored 50 runs not out in 22 balls (a strike rate of 227.27) against New Zealand in Hyderabad on 15 November 2003, the second fastest 50 among Indian batsmen. Only Ajit Agarkar's 67 runs off 21 balls is faster than that of Dravid.
In 2004, Dravid was awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India. On 7 September 2004, he was awarded the inaugural Player of the year award and the Test player of the year award by the International Cricket Council (ICC). On 18 March 2006, Dravid played his 100th Test against England in Mumbai.
In 2006, it was announced that he would remain captain of the Indian team up to the 2007 World Cup in the West Indies.
However, after the series against England, he stepped down as the Indian captain due to personal reasons. MS Dhoni took over as ODI captain, whereas Anil Kumble replaced him in test matches.
In 2007, he was dropped from the Indian ODI Squad following poor series against Australia. Dravid went back to play for Karnataka in the Ranji Trophy, scoring 218 runs against Mumbai.
In 2008, he made 93 runs in the first innings of the Perth test, the highest score of the match, to help India win and make the series 1–2. However, he was ignored by selectors for the subsequent one-day tri-series.
After a barren run in Test matches in 2008, Dravid came under increasing media pressure to retire or be dropped. In the Second Test against England in Mohali, he scored 136 runs, putting on a triple-century stand with Gautam Gambhir.
After reaching 10,000 test runs milestone, he said,"It's a proud moment for sure. For me, growing up, I dreamt of playing for India. When I look back, I probably exceeded my expectations with what I have done over the last 10 to 12 years. I never had an ambition to do it because I never believed – it is just a reflection of my longevity in the game."[193]
Dravid is also one of the two batsmen to score 10,000 runs at a single batting position and is the fourth highest run scorer in Test Cricket, behind Tendulkar, Ponting and Kallis.
Controversies
Ball-tampering incident
In January 2004, Dravid was found guilty of ball tampering during an ODI with Zimbabwe. Match referee Clive Lloyd adjudged the application of an energy sweet to the ball as a deliberate offence, although Dravid himself denied this was his intent.[194] Lloyd emphasised that television footage caught Dravid putting a lozenge on the ball during the Zimbabwean innings on Tuesday night at the Gabba.[194] According to the ICC's Code of Conduct, players are not allowed to apply substances to the ball other than sweat and saliva.[194] Dravid was fined half of his match fee.[194]
Indian coach John Wright came out in defence of Dravid, stating that "It was an innocent mistake". Wright argued that Dravid had been trying to apply saliva to the ball when parts of a losenge he had been chewing stuck to the ball; Dravid then tried to wipe it off.[195] ICC regulations prevented Dravid from commenting about the issue, but former Indian captain Sourav Ganguly also stated that Dravid's act was "just an accident".[195]
Captaincy
Rahul Dravid has had a mixed record when leading India in Tests.
One of Dravid's most debated decisions was taken in March 2004, when he was standing in as the captain for injured Sourav Ganguly. India's first innings was declared at a point when Sachin Tendulkar was at 194 runs not out with 16 overs remaining on Day 2. In this test match Sehwag scored triple century first time. He became the first Indian to score triple century in test with a score of 309.[196]
In March 2006, India lost the Mumbai Test, giving England its first Test victory in India since 1985, enabling it to draw the series 1–1. The defeat in Mumbai was arguably the result of Dravid's decision to bowl first on a flat dry pitch, which later deteriorated and ended with an Indian collapse in the run chase. Coincidentally, it was Dravid's 100th test match in which the Indians were all out for 100 runs in the second innings.
After India failed to qualify for the final of the DLF Cup, Dravid, the skipper, was criticised by former all-rounder Ravi Shastri who said that he was not assertive enough and let Greg Chappell make too many decisions.[197] When asked for a response, Dravid said that Shastri, while a 'fair critic', was 'not privy' to the internal decision-making process of the team.[198]
He was criticised by Vijay Mallya for not picking the team with right balance after his then IPL team Royal Challengers Bangalore finished seventh out of the eight teams that participated in the 2008 season.[199]
Achievements and awards
National honours
- 1998 - Arjuna Award recipient for achievements in cricket[200]
- 2004 -
 Padma Shri – India's fourth highest civilian award[201]
Padma Shri – India's fourth highest civilian award[201]
- 2013 -
 Padma Bhushan – India's third highest civilian award
Padma Bhushan – India's third highest civilian award
Other honours
- 1999 - CEAT International Cricketer of the World Cup[202]
- 2000 - Dravid was one of the five cricketers selected as Wisden Cricketer of the Year.[203]
- 2004 - ICC Cricketer of the year – Highest award in the ICC listings[204]
- 2004 - ICC Test Player of The Year, ICC Cricketer of The Year [204]MTV Youth Icon of the Year for 2004
- 2006 - Captain of the ICC's Test Team[205]
- 2011 - NDTV Indian of the Year's Lifetime Achievement Award with Dev Anand[206]
- 2012 - Don Bradman Award with Glenn McGrath[207]
- 2015 - Wisden India's Highest Impact Test Batsman[208]
- 2018 - ICC Hall of Fame
Personal life
Family
On 4 May 2003 he married Vijeta Pendharkar, a surgeon from Nagpur.[209] They have two children: Samit, born in 2005,[210] and Anvay, born in 2009.[211] Dravid is fluent in Marathi, Hindi, Kannada and English.
Commercial endorsements
Rahul Dravid has been sponsored by several brands throughout his career including Reebok (1996 – present),[212]Pepsi (1997 present),[213] Kissan (Unknown),[214]Castrol (2001 – present),[215]Hutch
(2003),[216][217] Karnataka Tourism (2004),[218]Max Life (2005 – present),[219]Bank of Baroda (2005 – present),[220]Citizen (2006 – present),[221] Skyline Construction (2006 – present),[222]Sansui (2007),[223]Gillette (2007 – present),[224]Samsung (2002[225] – 2004[226]), World Trade Center Noida (2013– present),[227].
Social commitments
- Children's Movement for Civic Awareness (CMCA)[228][229]
- UNICEF Supporter and AIDS Awareness Campaign[230]
Biographies
Books
Two biographies have been written on Rahul Dravid and his career:
Rahul Dravid – A Biography written by Vedam Jaishankar (.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 978-81-7476-481-2). Publisher: UBSPD Publications. Date: January 2004[231]
The Nice Guy Who Finished First written by Devendra Prabhudesai. Publisher: Rupa Publications. Date: November 2005[232]
- A collection of articles, testimonials and interviews related to Dravid was released by ESPNcricinfo following his retirement. The book was titled Rahul Dravid: Timeless Steel.
References
^ Jammy: Advertisers' Mr Dependable. The Hindu Businessline. Retrieved 10 March 2010.
^ "Is Rahul Dravid the greatest middle-order batsman of all time?". bbc.co.uk. 9 March 2012. Archived from the original on 11 March 2012.
^ "The greatness of Rahul Dravid". bbc.co.uk. 9 March 2012. Archived from the original on 11 June 2012.
^ "'The best No. 3 batsman in the world'". rediff.com. 28 March 2012. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013.
^ ESPNcricinfo (2017-07-15), Run Order: Is the Indian team a little too coach heavy?, retrieved 2017-08-08
^ Rahul Dravid's investment tip: Govt bonds, mutual funds and FDs
^ 9 Instances That Prove 'The Wall' Rahul Dravid Is A National Treasure
^ "Cricketer of the Year, 2000 – Rahul Dravid". Content.cricinfo.com. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "ICC Awards: Look no further Dravid". Espnstar.com. 5 September 2008. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Dravid, gentleman and thinking cricketer: Report". The Economic Times. PTI. 10 March 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2012.
^ "Superb in overseas conditions". Archived from the original on 27 November 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
^ "Test matches / Batting records". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2012.
^ "They came, they played, they conquered". Archived from the original on 25 April 2009. Retrieved 11 May 2009.
^ "Indian Dravid claims Test catch record". CNN. 6 April 2009. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "This day that year: Rahul Dravid faced his first ball in Test on June 22, 1996". India Today. Retrieved 3 July 2017.
^ "Rahul Dravid announces retirement from international cricket". Times of India. Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
^ "Bradman Awards honour for Dravid, McGrath". Wisden India. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
^ "Padma Awards" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2014. Retrieved July 21, 2015.
^ "Padma Vibhushan for Yash Pal, Roddam, S.H. Raza, Mohapatra". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2013.
^ "Rahul Dravid to mentor India's potential Olympians – Latest News & Updates at Daily News & Analysis". 27 January 2014. Archived from the original on 6 February 2014.
^ "Ponting, Dravid, Claire Taylor inducted into ICC Hall of Fame". ESPNcricinfo. 2 July 2018.
^ "Meet Rahul Sharad Dravid". Times of India. Retrieved 24 February 2007.
^ "Meet Rahul Dravid". The Times of India. 24 February 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Cricinfo – Players and Officials – Rahul Dravid". Archived from the original on 27 April 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "The Hindu : Keeping the windows".
^ "People | The Great Wall of India". Verveonline.com. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ abc "Dravid's personal choices". Dravidthewall. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
^ "webindia123-Indian personalities-sports-RAHUL DRAVID". Archived from the original on 10 August 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "Cricinfo – Coach Keki Tarapore reflects on pupil Rahul Dravid". Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid". Triposo. Archived from the original on 22 October 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
^ "Rahul Dravid Ranji debut". 40to40. Archived from the original on 23 October 2013. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
^ "Maharashtra v Karnataka at Pune, 02-05 Feb 1991". Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ ab Jaishankar, Vedam (19 January 1997). "Dravid: taming the Goliaths of pace". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 22 April 1997. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
^ "Batting – Most Runs (Ranji trophy 1991–92)". Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "South Zone squad 1991–92". Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Taking Guard". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. p. 5. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ Somani, Saurabh (22 May 2012). "Stranger, Legend, Martyr – Champion". WisdenIndia. Archived from the original on 14 January 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
^ abcde Somani, Saurabh (16 September 2011). "The Rahul Dravid journey in ODIs". Cricbuzz. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
^ ab "Timeline: Rahul Dravid". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
^ "Rahul Dravid Profile@Firstpost". Firstpost. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2017.
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuv "Player Oracle: Rahul Dravid". CricketArchive. Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
^ Guyer, Julian (20 July 2011). "Lord's feels like home, says Dravid". Cricketcountry. Archived from the original on 18 August 2015. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Taking Guard". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 2–8. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 13–17. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Hero at Headquarters". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. p. 18. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ abcd "Dravid's Test career: Innings by innings list". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
^ Sethuraman, Gautham (20 June 2013). "Golden debuts on this day: Sourav Ganguly and Rahul Dravid at Lord's". Khelnama. Archived from the original on 22 August 2015. Retrieved 22 August 2015.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Hero at Headquarters". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 20–22. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ "Test fielding innings list: Rahul Dravid". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
^ "Scorecard: India tour of England, 1996 – 2nd Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Hero at Headquarters". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. p. 26. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ Gollapudi, Nagraj (19 July 2011). "Dravid returns to where it all began". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 27 August 2015. Retrieved 27 August 2015.
^ abc Gollapudi, Nagraj (15 September 2011). "Just another day in Dravid's life". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 April 2016. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: South Africa in India Test series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
^ "Match report: India tour of South Africa 1996/97, First Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
^ "Scorecard: India tour of South Africa 1996/97, First Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
^ "Match Report: India tour of South Africa, 1996/97, Third Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
^ "Match awards in Tests for Rahul Dravid". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 17 October 2015. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
^ "Most runs: India in South Africa Test series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
^ "Results: India in West Indies, Test series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 26 January 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
^ "Most runs: India in West Indies, Test series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 17 October 2015. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
^ "Scorecard: India tour of West Indies, 1996/97, Fifth Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
^ "Most runs: 1996/97 Test season". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
^ "Most fifties in consecutive Test innings". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 31 October 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
^ "Dravid in Tests till 1997/98 Test season". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 31 October 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
^ "Indian batting in 1998/99 Test season". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 August 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
^ "Scorecard: India in Zimbabwe, 1998/99, Only Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 May 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
^ "Scorecard: India in New Zealand, 1998/99, First Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
^ "Match Report: India in New Zealand, 1998/99, Third Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 24 August 2016.
^ "Most runs: India in New Zealand, Test series, 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 19 August 2017.
^ "Results: India in New Zealand, 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 1 August 2017. Retrieved 19 August 2017.
^ "Scorecard: Pakistan in India, 1998/99, First Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 March 2016. Retrieved 25 August 2016.
^ "Scorecard: Pakistan in India, 1998/99, Second Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 2 May 2016. Retrieved 25 August 2016.
^ "Match Report: Asian Test Championship 1998/99, First Test, Ind vs Pak". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
^ Sa'adi Thawfeeq. "Match report: Asian Test Championship 1998/99, Second Test, SL vs Ind". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
^ S Jagadish; Rick Eyre. "Match Report: Asian Test Championship 1998/99, Second Test, SL vs Ind". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
^ "Results: Asian Test Championship 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
^ ab Gupta, Rajneesh (17 October 2007). "When poor form ruled Dravid out". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2008. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
^ ab S Rajesh (16 September 2011). "An unlikely star of the 50-over format". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
^ "Top scorers: Sahara 'Friendship' Cup 1996". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
^ abc "Dravid's match/series awards in ODIs". Howstat. Archived from the original on 29 August 2016. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: Standard Bank International One Day series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: Final, Standard Bank International One Day series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 17 April 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: India in West Indies ODI series, 1996/97". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 6th match, Pepsi Independence Cup 1997, IND vs PAK". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 February 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 6th match, Pepsi Independence Cup 1997, IND vs PAK". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 September 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: Pepsi Independence Cup 1997". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 1 November 2014. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
^ "Result summary: Pepsi Independence Cup 1997". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 November 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
^ "Dravid's ODI career: Series averages". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
^ "Dravid in ODIs: Debut-1998". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 1st match, India in New Zealand ODI series, 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 4th match, India in New Zealand ODI series, 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: India in New Zealand ODI series, 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 2nd match, Pepsi Cup 1998/99, Ind vs SL". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 19 July 2015. Retrieved 18 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 3rd match, Pepsi Cup 1998/99, Ind vs Pak". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
^ abc "Dravid's ODI career: Innings by innings list". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
^ "Dravid's ODI fielding analysis: Innings by innings list". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 19 January 2017. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 3rd match, Coca-cola Cup 1998/99, Eng vs Ind". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 16 August 2015. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 3rd match, Coca-Cola Cup 1998/99, Eng vs Ind". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
^ "Most runs: Coca-Cola Cup 1998/99". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 November 2016. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: Good Luck India Match (Ind 1983 vs Ind 1999)". CricketArchive. Archived from the original on 12 February 2012. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
^ ab "Dravid's performance in ICC World Cup 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 21 January 2017. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
^ "Result summary: ICC World Cup 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 November 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
^ "Indians throw thriller away". BBC News. Archived from the original on 21 January 2017. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 9th Group A match, ICC World Cup 1999, Ind vs Ken". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: 15th match, ICC World Cup 1999, Ind vs Ken". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
^ abc "Dravid's appearances as designated keeper in ODIs". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ ab "Indian record-breakers crush holders". BBC News. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ "Dravid & Ganguly partner to World Cup best in '99". icc-cricket.com. Archived from the original on 4 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ "England crash out". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ "India triumph in Pakistan Cup clash". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 January 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ "Kiwis charge into semi-finals". BBC News. Archived from the original on 28 January 2017. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: ICC World Cup, 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 November 2016. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
^ Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "On The Roller-Coaster". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. p. 73. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ "Most runs: Coca-Cola Singapore Challenge, 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 6 October 2013. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
^ "Scorecard: Final, Coca-Cola Singapore Challenge 1999, Ind vs WI". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 16 December 2016. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: DMC Cup, 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 23 January 2017. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
^ Siddiqui, Latafat Ali. "India defeat West Indies to win series". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 April 2016. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 1st Test, New Zeland in India Test series, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 12 March 2015. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
^ "Match report: 5th match, New Zealand in India ODI series, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 3 February 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
^ "Most runs: New Zealand in India ODI series, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 January 2017. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
^ ab "Highest partnerships for any wicket in ODIs". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
^ "Dravid in ODIs in the year 1999". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 January 2017. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
^ "Result Summary: India tour of Australia, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2017.
^ "Bowling statistics: South Africa in India, ODI series, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 24 October 2017. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: South Africa in India, 1999/00, First ODI". ESPNcricinfo. 9 March 2000. Archived from the original on 29 August 2018. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ "Results: Coca-cola Cup, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 18 February 2018. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ "Most runs: Coca-cola Cup, 1999/00". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ Vasu, Anand (20 February 2000). "Tendulkar to step down, mystery shrouds decision". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 10 September 2018. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ Ramchand, Partab (26 February 2000). "Ganguly captain for one dayers, Indian team for second Test". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ Weaver, Paul (24 May 2000). "Kent cry foul as Dravid leads Indian exodus". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 9 May 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
^ abc Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Kent, And The Coliseum". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 81–84. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ abc Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Kent, And The Coliseum". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 84–88. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ "Most runs: ICC Knockout Tournament, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: Only Test, India in Bangladesh, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ Mustafi, Suvajit (6 March 2018). "Sourav Ganguly credits Rahul Dravid for John Wright's appointment as India's coach". CricketCountry. Archived from the original on 10 March 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ Verma, Devarchit (15 July 2014). "Naman Ojha narrowly misses out on beating Rahul Dravid's feat during India A's tour of Australia 2014". CricketCountry. Archived from the original on 19 April 2015. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ Mittra, Sakyasen (13 December 2000). "Bengal players rush to Ganguly's defence". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: 5th ODI, Zimbabwe in India, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. 14 December 2000. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ abcde Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "Kent, And The Coliseum". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 90–96. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ Sethuraman, Mahesh (27 February 2013). "Mumbai '01 - An underrated classic". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: First Test, Australia in India, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 July 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ Burnett, Adam (29 May 2018). "The Best Of VVS Laxman". Archived from the original on 29 July 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "No wickets in a full day's play". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 3 February 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ ab "We took it session by session, say the day's heroes". ESPNcricinfo. 14 March 2001. Archived from the original on 12 December 2011. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ ab Chughtai, Arshad (18 March 2001). "Forced to follow-on yet won". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 4 February 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ Bhattacharya, Rahul (30 August 2018). "India beating Australia in Kolkata". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: Second Test, Australia in India, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 30 August 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Results summary: Australia in India, 2000/01". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Batting averages: 2000/01 Test season". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: First Tour game, India in Zimbabwe, 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Most runs: India in Zimbabwe, Test series, 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 21 January 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Most runs: Coca-cola Cup, India in Zimbabwe, 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 21 January 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: 3rd match, Zim vs Ind, Coca-Cola Cup, 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ abc Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "One For A Crisis". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 98–102. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ "Most runs: Coca-Cola Cup (in Sri Lanka), 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ Ugra, Sharda (10 September 2001). "Unlikely friendship between Sourav Ganguly, Rahul Dravid holds key to Team India's future". India Today. Archived from the original on 14 September 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Most runs: Test series, India in Sri Lanka, 2001". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 5 January 2018. Retrieved 14 September 2018.
^ "Most runs: Standard Bank Triangular Tournament, 2001/02". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 19 February 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: First Test, India in South Africa, 2001/02". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 March 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: Second Test, India in South Africa, 2001/02". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 6 March 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
^ Premachandran, Dileep (1 December 2001). "The gleam of bone". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 15 September 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
^ "Scorecard: 'Unoffical' Third Test, India in South Africa, 2001/02". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 7 March 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
^ ab Prabhudesai, Devendra (December 2005). "One For A Crisis". The Nice Guy Who Finished First: A Biography Of Rahul Dravid. New Delhi, Ind: Rupa Publications. pp. 102–7. ISBN 978-81-291-16505.
^ "Cricinfo – 2nd Test: Australia v India at Adelaide, Dec 12–16, 2003". Content-ind.cricinfo.com. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Multan Test, Statistical Highlights". Rediff. 2 April 2004. Archived from the original on 26 March 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2013.
^ "Cricinfo – 3rd Test: Pakistan v India at Rawalpindi, Apr 13–16, 2004". Content-ind.cricinfo.com. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ 1st Test: England v India at Lord's, Jul 21–25, 2011 | Cricket Scorecard Archived 13 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine.. ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ 2nd Test: England v India at Nottingham, Jul 29 – Aug 1, 2011 | Cricket Scorecard Archived 13 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine.. ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ 3rd Test: England v India at Birmingham, Aug 10–13, 2011 | Cricket Scorecard Archived 13 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine.. ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ 4th Test: England v India at The Oval, Aug 18–22, 2011 | Cricket Scorecard Archived 22 January 2015 at the Wayback Machine.. ESPN Cricinfo. Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ England v India: Rahul Dravid deserves our respect after frustrating England Archived 28 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine.. Telegraph. Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ http://www.telegraphindia.com/1110822/jsp/.../story_14407797.jsp. Retrieved 23 December 2013. Missing or empty|title=(help)
[dead link]
^ ab "Dravid says no more ODIs after England series". The Indian Express. 7 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
[permanent dead link]
^ "I had a satisfying ODI career: Rahul Dravid". The Times of India. 16 September 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
^ "Rahul Dravid says thanks but no thanks". Daily News and Analysis. 7 August 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
^ Davies, Will. "Rahul Dravid Bows Out in Style".
^ "Dravid retires from T20I". Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 31 August 2011.
^ "Rahul Dravid announces retirement from international cricket". The Times of India. 9 March 2012. Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 9 March 2012.
^ "MCC v Rest of the World – 5 July". Lord's. 5 July 2014. Archived from the original on 7 July 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
^ "Statistics / Statsguru / RS Dravid /One-Day Internationals". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 February 2016. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ "List of Test victories". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ "IPL Records-Most Runs". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 3 February 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ "CLT20 Records-Most Runs". Cricinfo. Archived from the original on 1 October 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
^ Never thought I'd play T20 cricket for so long, an emotional Dravid bids farewell : Featured, News – India Today Archived 30 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine.. Indiatoday.intoday.in (2013-10-07). Retrieved on 2013-12-23.
^ "Rahul Dravid leaves greater T20 legacy than Sachin Tendulkar – Firstpost". 8 October 2013. Archived from the original on 10 October 2013.
^ ab Rahul Dravid- Analysis of Performances at Home and Away Archived 24 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine.. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
^ "Rahul Dravid away batting stats in ODI". Retrieved 23 November 2010.
^ "Rahul Dravid home batting stats in ODI". Archived from the original on 7 August 2013. Retrieved 23 November 2010.
^ "Rahul Dravid Test analysis in matches won". Retrieved 23 November 2010.
^ "Rahul Dravid ODI analysis in matches won". Retrieved 23 November 2010.
^ "Cricinfo – The Man Fridays". Content-usa.cricinfo.com. Archived from the original on 23 January 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Dravid reaches Test runs landmark". BBC News. 29 March 2008. Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ abcd "Ball tampering was deliberate, says Lloyd". Sydney Morning Herald. 22 January 2004. Archived from the original on 6 November 2012. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
^ ab "Wright defends Dravid in ball-tampering case". cricinfo.com. ESPN cricinfo. Archived from the original on 3 March 2010. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
^ "Multan declaration was a mistake: Ganguly". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 30 April 2004. Archived from the original on 1 September 2005.
^ "Shastri criticises Dravid". The Hindu. Chennai, India. 25 September 2006. Archived from the original on 19 October 2007.
^ "Pathan's destiny is in his own hands: Dravid". Zee News. 9 October 2006. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Cricinfo – Dravid regrets top-order failure". Content-ind.cricinfo.com. Archived from the original on 23 August 2007. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Dravid receives Arjuna Award". Tribuneindia. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
^ "Rahul Dravid awarded Padma Shri". Deccan Herald. 1 July 2004. Archived from the original on September 7, 2006. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
^ "Dravid bags ceat cricketer of the world cup award". Businesswireindia.com. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
^ "Rahul Dravid – Wisden Cricketer of the Year". Wisden Almanack. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
^ ab "Dravid walks away with honours". Chennai, India: The Hindu. 9 September 2004. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
^ "ICC Test Team Captain 2006". Rediff. 3 November 2006. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
^ "NDTV Indian of the Year 2011". ndtv.com. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
^ "Bradman Awards honour for Dravid, McGrath". Wisden India. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
^ "HISTORY-CHANGING COLOSSUS". Wisden India Impact Index. Retrieved 2 January 2016.
^ "Dravid weds Vijeta Pendharkar". Archived from the original on 2 April 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "Dravid blessed with a baby boy". Archived from the original on 29 March 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2007.
^ "Dravid becomes a dad again". Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2009.
^ "3 more ambassadors for Reebok". The Hindu Business Line. 7 May 2004. Archived from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Pepsi". Rediff. 10 June 1997. Archived from the original on 21 October 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of". The Tribune. India. 12 May 2002. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Castrol". The Hindu Business Line. 16 February 2001. Archived from the original on 21 October 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ Kujnish Vashisht (2005). A Practical Approach to Marketing Management. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. p. 308.Hutch in its another campaign uses Rahul Dravid (Mr. Dependable)
^ Argenti (2007). Strategic Corporate Communication. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 71.You might know that Sachin Tendulkar, a star Cricketer, is a brand ambassador for Airtel and Rahul Dravid, another star cricketer, is brand ambassador for Hutch.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the honorary brand ambassador of Karnataka Tourism". The Times of India. India. 23 February 2004. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Max Life Insurance". Sify. 27 April 2005. Archived from the original on 1 September 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Bank of Baroda". The Hindu Business Line. 7 June 2005. Archived from the original on 2 January 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Citizen Watches". The Hindu Business Line. 9 May 2006. Archived from the original on 9 February 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Rahul Dravid to be the brand ambassador of Skyline Construction". Rediff. 10 November 2006. Archived from the original on 6 December 2006. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ Tuesday, 27 March 2007 at 0005 hrs IST (27 March 2007). "Videocon, Sansui declare Dhoni, Dravid out of ads". The Financial Express. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ Mehta, Mona (15 September 2007). "India Inc stands behind 'The Wall'". The Financial Express. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
^ "Samsung to spend Rs 20–25 crore between Jan–March 2003 on cricket > afaqs! news & features". Afaqs.com. 11 December 2002. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ Sydenham, Richard (28 March 2004). "Pakistan-India Cricket Series Spurs $40 million Marketing Boon". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
^ "Rahul Dravid is the Brand Ambassador of World Trade Center Noida". Biharprabha News. Archived from the original on 18 November 2013. Retrieved 15 November 2013.
^ "The Great Wall of India". Children's Movement for Civic Awareness. September 2004. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
^ "Testimonials". Children's Movement for Civic Awareness. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
^ "Rahul Dravid leads AIDS Awareness Campaign". Indian Television.com. 16 July 2004. Archived from the original on 23 November 2008. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Book Review – Rahul Dravid, A Biography". Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
^ "Book Launch:The Nice Guy Who Finished First". Rediff. 2005-11-17. Archived from the original on 22 October 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2007.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rahul Dravid. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Rahul Dravid |
- Official website
Rahul Dravid at ESPNcricinfo
Rahul Dravid at CricketArchive (subscription required)
Rahul Dravid at Yahoo! Cricket
| Preceded by Sourav Ganguly | Indian Test captains 2005–2007 | Succeeded by Anil Kumble |
| Preceded by Sourav Ganguly | Indian One-Day captains 2005–2007 | Succeeded by Mahendra Singh Dhoni |
| Preceded by First | Sir Garfield Sobers Trophy 2004 | Succeeded by Andrew Flintoff & Jacques Kallis |
| Preceded by Position started | Royal Challengers Bangalore captain 2008 | Succeeded by Kevin Pietersen |
| Preceded by Shane Warne | Rajasthan Royals captain 2011–2013 | Succeeded by Shane Watson |
