Arizona Territory
This article includes a list of references, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. (April 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Territory of Arizona | |||||
Organized incorporated territory of the United States | |||||
| |||||
 Flag Flag | |||||
 | |||||
Capital | Fort Whipple (1863–64) Prescott (1864–67) Tucson (1867–77) Prescott (1877–89) Phoenix (1889– ) | ||||
Government | Organized incorporated territory | ||||
Governor | |||||
| • | 1863–1866 | John Noble Goodwin | |||
| • | 1909–1912 | Richard Elihu Sloan | |||
Legislature | Arizona Territorial Legislature | ||||
History | |||||
| • | Arizona Organic Act | February 24, 1863 | |||
| • | Statehood of Arizona | February 14, 1912 | |||
The Territory of Arizona (also known as Arizona Territory) was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863 until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Arizona. It was created from the western half of the New Mexico Territory during the American Civil War.
Contents
1 History
2 Capital
3 Boundary
4 Statehood
5 Territorial proclamation
6 See also
7 Notes
8 References
9 External links
History
Following the expansion of the New Mexico Territory in 1853, as a result of the Gadsden Purchase, several proposals for a division of the territory and the organization of a separate Territory of Arizona in the southern half of the territory were advanced as early as 1856. These proposals arose from concerns about the ability of the territorial government in Santa Fe to effectively administer the newly acquired southern portions of the territory.[1]


Gadsden Purchase 1853
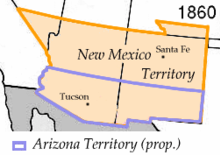
The first proposal dates from a conference held in Tucson that convened on August 29, 1856. The conference issued a petition to the U.S. Congress, signed by 256 people, requesting organization of the territory and elected Nathan P. Cook as the territorial delegate to Congress. In January 1857, the bill for the organization of the territory was introduced into the House of Representatives, but the proposal was defeated on the grounds that the population of the proposed territory was yet too small. Later a similar proposal was defeated in the Senate. The proposal for creation of the territory was controversial in part because of the perception that the New Mexico Territory was under the influence of southern sympathizers who were highly desirous of expanding slavery into the southwest.
In February 1858, the New Mexico territorial legislature adopted a resolution in favor of the creation of the Arizona territory, but with a north-south border along the 109th meridian, with the additional stipulation that all the Indians of New Mexico would be removed to northern Arizona.
In April 1860, impatient for Congress to act, a convention of 31 delegates met in Tucson and adopted a constitution for a provisional territorial government of the area south of 34 degrees north. The delegates elected Dr. Lewis S. Owings as provisional governor.
At the outbreak of the Civil War, sentiment in the territory was in favor of the Confederacy. Territorial secession conventions were called at Mesilla and Tucson in March 1861 that adopted an ordinance of secession, established a provisional Arizona Territory with Owings as its governor, and petitioned the Confederate Congress for admission.
The Confederacy regarded the territory as a valuable route for possible access to the Pacific Ocean, with the specific intention of capturing California. In July 1861, a small Confederate force of Texans under the command of Lieutenant Colonel John R. Baylor assaulted Fort Fillmore at Mesilla in the eastern part of the territory. After the fort was abandoned by the Union garrison, Baylor's force cut off the fleeing Union troops and forced them to surrender. On August 1, Baylor issued a "Proclamation to the People of the Territory of Arizona", taking possession of the territory for the Confederacy, with Mesilla as the capital and himself as the governor. Baylor's subsequent dismantling of the existing Union forts in the territory left the white settlers at the mercy of the Apache, who quickly gained control of the area and forced many of the white settlers to seek refuge in Tucson.[2]
On August 28, a convention met again in Tucson and declared that the territory formed the previous year was part of the Confederacy. Granville H. Oury was elected as delegate to the Confederate Congress. Oury drafted legislation authorizing the organization of the Confederate Territory of Arizona. The legislation passed on January 13, 1862, and the territory was officially created by proclamation of President Jefferson Davis on February 14.
The following month, in March 1862, the U.S. House of Representatives, now devoid of the southern delegates and controlled by Republicans, passed a bill to create the United States Arizona Territory using the north-south border of the 107th meridian. The use of a north-south border rather than an east-west one had the effect of denying a de facto ratification of the Confederate Arizona Territory. The house bill stipulated that Tucson was to be the capital. The final bill passed the Senate in February 1863 without the Tucson-as-capital stipulation, and was signed into law by President Abraham Lincoln on February 24, the date of the official organization of the US Arizona Territory.
Capital
The first capital was established in 1864 at Prescott, in the northern Union-controlled area. The capital was moved to Tucson in 1868, and back to Prescott in 1877.[3] The capital was finally moved to Phoenix on February 4, 1889.[4][5]
Boundary
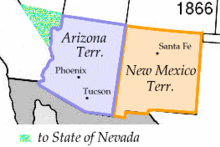
The boundaries for the original territory, if they had kept their same size, would have made present-day Las Vegas part of Arizona. However, in 1867, Congress transferred the Arizona Territory's northwestern corner, specifically most of its land west of the Colorado River, to the state of Nevada.[6] This reduced the territory to its current area.
Statehood
The territory was admitted to the Union as the 48th state on February 14, 1912.
Territorial proclamation
Proclamation to the People of Arizona.[7]
| “ | I, John N. Goodwin, having been appointed by the President of the United States, and duly qualified, as Governor of the TERRITORY OF ARIZONA, do hereby announce that by virtue of the powers with which I was invested by an act of the Congress of the United States, providing a temporary government for the Territory. I shall this day proceed to organize said government. The provisions of the act, and all laws and enactments established thereby, will be enforced by the proper Territorial officers from and after this date. A preliminary census will forthwith be taken, and thereafter the Judicial Districts will be formed, and an election of members of the Legislative Assembly, and the other officers provided by the Act be ordered. I invoke the aid and cooperation of all Citizens of the Territory in my efforts to establish a government whereby the security of life and property will be maintained throughout its limits, and its varied resources be rapidly and successfully developed. The Seat of Government will, for the present, be at or near Fort Whipple. Signed at Navajo Springs, Arizona | ” |
— By the Governor: Richard C. McCormick, Secretary of the Territory | ||
See also
American Civil War, 1861–1865
Territory of Arizona (Confederate States), 1861–1862
Apache Wars, 1851–1886
Gadsden Purchase, 1853- Governors of the Territory of Arizona
- History of Arizona
James Reavis, The "Baron of Arizona"
Mexican–American War, 1846–1848
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, 1848
Navajo Wars, 1846–1865- Territorial evolution of the United States
Notes
^ Paul Bisceglia, Arizona's Role in the Civil War, University of San Diego. History 173 - U.S. Civil War from http://history.sandiego.edu accessed September 29, 2018.
^ Colton, Ray C.: The Civil War..., pp. 15-19.
^ Wagoner, Jay J. (1970). Arizona Territory 1863-1912: A Political history. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. p. 113. ISBN 0-8165-0176-9..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Wagoner, Jay J. (1970). Arizona Territory 1863-1912: A Political history. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. p. 245. ISBN 0-8165-0176-9.
^ Kathleen Garcia, ed. (2008). Early Phoenix. Arcadia Publishing. p. 18. ISBN 0738548391.
^ "History". Lincoln County Nevada. Retrieved December 28, 2018.
^ Wagoner p. 32–33 & front piece
References
- Cheek, Lawrence W. (1995). Arizona. Oakland, CA: Compass American Guides.
ISBN 1-878867-72-5.
Colton, Ray C. (1984) [1959]. The Civil War in the Western Territories. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-1902-0.
Cunniff, M.G. (January 1906). "The Last of the Territories". The World's Work: A History of Our Time. XI: 7108–7119. Retrieved 2009-07-10.
- Sheridan, Thomas E. (1995). Arizona: A History. Tucson, AZ: The University of Arizona Press.
ISBN 0-8165-1515-8.
Wagoner, Jay J. (1970). Arizona Territory 1863–1912: A Political history. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0-8165-0176-9.
External links
- Compiled Laws And Revised Statutes Of Arizona Territory
Coordinates: 34°03′N 111°05′W / 34.05°N 111.09°W / 34.05; -111.09

