Hauts-de-France
This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (July 2016) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Hauts-de-France | |
|---|---|
Region | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Prefecture | Lille |
| Departments | 5
|
| Government | |
| • President | Xavier Bertrand (DVD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 31,813 km2 (12,283 sq mi) |
| Population (2012) | |
| • Total | 5,973,098 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | FR-HDF |
| NUTS Region | FRE |
| Website | www.regionhautsdefrance.fr |
Hauts-de-France[1] (French pronunciation: [o d(ə) fʁɑ̃s], meaning "Upper France"), is a region of France created by the territorial reform of French Regions in 2014, from a merger of Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy. Its capital is Lille. The new region came into existence on 1 January 2016, after the regional elections in December 2015.[2] France's Conseil d'État approved Hauts-de-France as the name of the region on 28 September 2016, effective 30 September 2016.[3]
With 6,009,976 inhabitants (as of January 1, 2015), and a population of 189 inhabitants/km2, it represents the 3rd most populous region in France and the 2nd most densely populated in metropolitan France after Île-de-France.
The region covers an area of more than 31,813 km2 (12,283 sq mi). It borders Normandy, Grand Est, Île-de-France, Belgium (Flemish Region and Wallonia) and the United Kingdom via the English Channel.
Contents
1 Toponymy
2 Geography
2.1 Departments
2.2 Major communities
3 French sartorial heritage
4 See also
5 References
6 External links
Toponymy
The region's interim name Nord-Pas-de-Calais-Picardie was a hyphenated placename, created by hyphenating the merged regions' names—Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardie—in alphabetical order.[4]
On 14 March 2016, well ahead of the 1 July deadline, the Regional council decided on Hauts-de-France as the region's permanent name.[1][4] The provisional name of the region was retired on 30 September 2016, when the new name of the region, Hauts-de-France, took effect.[3]
Geography
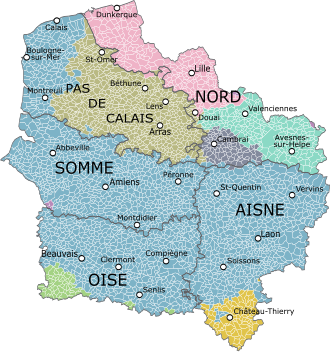
Map of the new region with its five départements, colored according to the historical provinces as they existed until 1790.
Picardy
Île-de-France
Artois
French Flanders
French Hainaut
Cambrai
Champagne
Other
The region borders Belgium (Flanders and Wallonia) to the northeast, the English Channel to the northwest, as well as the French regions of Grand Est to the southeast, Île-de-France to the south, and Normandy to the southwest. It is connected to the United Kingdom (England) via the Channel Tunnel.
Departments
Hauts-de-France comprises five departments: Aisne, Nord, Oise, Pas-de-Calais, and Somme.
Major communities

Lille

Amiens

View of England from Cap Gris Nez, France
Lille (227,560; region prefecture; surrounding area is home to over 1.5 million inhabitants)
Amiens (133,448)
Roubaix (94,713)
Tourcoing (91,923)
Dunkirk (90,995)
Calais (72,589)
Villeneuve-d'Ascq (62,308)
Saint-Quentin (55,978)
Beauvais (54,289)
Valenciennes (42,691)
French sartorial heritage
The region was a pivotal center of mulquinerie
See also
- Nord-Pas-de-Calais
- Picardy
- Regions of France
- Canadian National Vimy Memorial
- Battle of Vimy Ridge
References
^ ab "La Région a voté et s'appelle désormais Hauts-de-France" [The region has voted and is now called Hauts-de-France]. La Voix du Nord (in French). Lille. 15 March 2016. Retrieved 15 March 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "La carte à 13 régions définitivement adoptée" [The 13-region map finally adopted]. Le Monde (in French). Agence France-Presse. 17 December 2014. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
^ ab Décret n° 2016-1265 du 28 septembre 2016 portant fixation du nom et du chef-lieu de la région Hauts-de-France (in French)
^ ab Loi n° 2015-29 du 16 janvier 2015 relative à la délimitation des régions, aux élections régionales et départementales et modifiant le calendrier électoral (in French)
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Hauts-de-France. |
Official website (in French)
(in French)
- Merger of the regions - France 3
Coordinates: 49°55′14″N 2°42′11″E / 49.9206°N 2.7030°E / 49.9206; 2.7030
