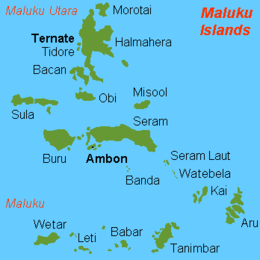
Morotai
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | South East Asia |
| Coordinates | 2°19′N 128°28′E / 2.317°N 128.467°E / 2.317; 128.467Coordinates: 2°19′N 128°28′E / 2.317°N 128.467°E / 2.317; 128.467 |
| Archipelago | Maluku Islands |
| Area | 2,476 km2 (956 sq mi) |
| Length | 80 km (50 mi) |
| Width | 42 km (26.1 mi) |
| Administration | |
Indonesia | |
| Province | North Maluku |
| Largest settlement | Daruba |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 52697 (2010 Census) |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone |
|
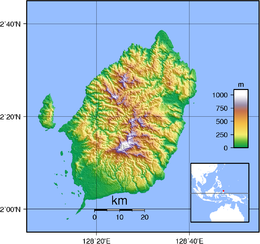
Morotai Island (Indonesian: Pulau Morotai) is an island in the Halmahera group of eastern Indonesia's Maluku Islands (Moluccas). It is one of Indonesia's northernmost islands.
Morotai is a rugged, forested island lying to the north of Halmahera. It has an area of some 2,476 square kilometres (956 sq mi), stretching 80 kilometres (50 mi) north-south and no more than 42 kilometres (26 mi) wide. The island's largest town is Daruba, on the islands south coast. Almost all of Morotai's numerous villages are coastal settlements; a paved road linking those on the east coast starts from Daruba and will eventually reach Berebere, the principal town on Morotai's east coast, 68 kilometres (42 mi) from Daruba.[citation needed] Between Halmahera and the islets and reefs of the west coast of Morotai is the Morotai Strait, which is about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) wide.[1]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Second World War
1.2 Permesta rebellion
2 Notable people
3 See also
4 References
5 Sources
6 External links
History
Morotai was part of the Ternate Sultanate, which was a vassal of the Dutch East India Company by the end of the 17th century.
Second World War
The Empire of Japan invaded Morotai early in 1942 as part of its Dutch East Indies Campaign. US forces and their allies launched the Battle of Morotai in 1944; bombing the island in August and invading it in September. Imperial Japanese forces on Morotai held out until 1945 but failed to expel the Allied invaders. In the latter part of 1944, 61,000 personnel landed on Morotai.[2] Two thirds of them were engineers, who rapidly established facilities including harbors and two airstrips[2] plus extensive fuel stores.
The formal surrender of the Second Japanese Army took place at Morotai on 9 September 1945.
The last Japanese holdout from the war, Private Teruo Nakamura (Amis: Attun Palalin), was discovered by the Indonesian Air Force on Morotai, and surrendered to a search patrol on December 18, 1974.[3]
Permesta rebellion
The Dutch Empire withdrew in the Indonesian National Revolution in the late 1940s, after which the new Indonesian Air Force (AURI) kept one of the Allied-built airstrips in use.[2] During the Permesta rebellion in 1958, AURI North American B-25 Mitchell bomber aircraft used the airstrip in transit on their way to attack the rebel centre at Manado in North Sulawesi.[4] Permesta had its own "Revolutionary Air Force", AUREV, whose aircraft, munitions and pilots were supplied by the CIA. AUREV aircraft attacked Morotai on April 21[4] and again early on April 26.[5] The second air raid was immediately followed by an amphibious Permesta landing force that quickly captured the island.[6] Within hours a Douglas C-47 Skytrain transport aircraft landed on the now captured airstrip, carrying senior Permesta representative and two Americans.[6] One was a USAF officer who inspected the runway and pronounced that Boeing B-29 Superfortress heavy bomber aircraft could use it.[6]
In May 1958 Indonesian National Armed Forces started to gather amphibious forces to retake both Morotai and the rebel-held town of Jailolo on the neighbouring island of Halmahera.[7] By May 16 the assault fleet started to gather in Ambon harbour and on May 20 its troops landed on Morotai while élite Pasukan Gerak Tjepat (PGT or "Quick Reaction Force") troops parachuted onto the island.[8] The Permesta force's surrender was as quick as its capture of the island less than a month before.[8] It alarmed the Permesta rebels who had captured Jailolo, many of whom promptly fled back to North Sulawesi.[8] Thereafter the rebellion was largely confined to the Minahassa Peninsula of Sulawesi, where Permesta remnants waged a guerilla campaign until the last unit surrendered in January 1962.[9]
Notable people
Melky Goeslaw, singer and father of Melly Goeslaw
See also
- Battle of Morotai
- Islands of Indonesia
References
^ "Journals - BYU ScholarsArchive". ojs.lib.byu.edu..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 102.
^ "The Last Last Soldier?", Time, January 13, 1975.
^ ab Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 103.
^ Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 106.
^ abc Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 107.
^ Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 134.
^ abc Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 147.
^ Conboy & Morrison 1999, p. 161.
Sources
Conboy, Kenneth; Morrison, James (1999). Feet to the Fire CIA Covert Operations in Indonesia, 1957–1958. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1-55750-193-9.
Kahin, Audrey R; Kahin, George McT (1997) [1995]. Subversion as Foreign Policy The Secret Eisenhower and Dulles Debacle in Indonesia. Seattle and London: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-97618-7.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Morotai. |