Laws of the Game (association football)
The Laws of the Game[1] (LOTG) are the codified rules that help define association football. They are the only rules of association football subscribed to by FIFA. The laws mention the number of players a team should have, the game length, the size of the field and ball, the type and nature of fouls that referees may penalise, the frequently misinterpreted offside law, and many other laws that define the sport. During a match, it is the task of the referee to interpret and enforce the Laws of the Game.
There were various attempts to codify the rules of football in England in the mid-19th century. The extant Laws date back to 1863 where a ruleset was formally adopted by the newly formed Football Association. The original Laws were heavily influenced by the Cambridge rules and their early development saw substantial influence from the Sheffield Rules. Over time, the Laws have been amended, and since 1886 they have been maintained by the International Football Association Board.
Contents
1 Current Laws of the Game
1.1 Laws
1.2 Presentation and interpretation
1.3 Jurisdiction and change management
2 History
2.1 Pre-1863
2.2 1863 rules
2.3 IFAB created
2.4 FIFA adoption
2.5 Notable amendments
3 Notes
4 References
5 External links
Current Laws of the Game
Laws
The current Laws of the Game (LOTG) consist of seventeen individual laws, each law containing several rules and directions:[1]
- Law 1: The Field of Play
- Law 2: The Ball
- Law 3: The Players
- Law 4: The Players' Equipment
- Law 5: The Referee
- Law 6: The Other Match Officials
- Law 7: The Duration of the Match
- Law 8: The start and restart of play
- Law 9: Ball in and out of play
- Law 10: Determining the outcome of a match
- Law 11: Offside
- Law 12: Fouls and Misconduct
- Law 13: Free kicks (direct and indirect)
- Law 14: The Penalty Kick
- Law 15: The Throw-in
- Law 16: The Goal Kick
- Law 17: The Corner Kick
Presentation and interpretation
In 1997, a major revision dropped whole paragraphs and clarified many sections to simplify and strengthen the principles. These laws are written in English Common Law style and are meant to be guidelines and goals of principle that are then clarified through practice, tradition, and enforcement by the referees.
The actual law book had long contained 50 pages more of material, organized in numerous sections, that included many diagrams but were not officially part of the main 17 laws. In 2007, many of these additional sections along with much of the material from the FIFA Questions and Answers (Q&A), were restructured and put into a new "Additional Instructions and Guidelines for the Referee" section. In the 2016/2017 revision of the Laws, the material from this section was folded into the Laws themselves.
Referees are expected to use their judgement and common sense in applying the laws; this is colloquially known as "Law 18".[2]
Jurisdiction and change management
The laws are administered by the International Football Association Board (IFAB). They meet at least once a year to debate and decide any changes to the text as it exists at that time. The meeting in winter generally leads to an update to the laws on 1 July of each year that take effect immediately. The laws govern all international matches and national matches of member organizations.[3] A minimum of six of the eight seat IFAB board needs to vote to accept a rule change. Four seats are held by FIFA to represent their 200+ member Nations, with the other four going to each of the British associations (the FA representing England, the SFA representing Scotland, FAW representing Wales and the IFA representing Northern Ireland), meaning that no change can be made without FIFA's approval, but FIFA cannot change the Laws without the approval of at least two of the British governing bodies.[3]
History
Pre-1863
In the nineteenth century, the word "football" could signify a wide variety of games in which players attempted to move a ball into an opponent's goal. The first published rules of "football" were those of Rugby School (1845), which permitted extensive handling, quickly followed by the Eton field game (1847), which was much more restrictive of handling the ball. In 1848, rules were created for use at Cambridge University — but they were not published at the time, and have subsequently been lost. The first detailed sets of rules published by football clubs (rather than a school or university) were those of Sheffield FC (written 1858, published 1859) which codified a game played for 20 years until being discontinued in favour of the Football Association code, and those of Melbourne FC (1859) which are the origins of Australian rules football. By the time the Football Association met in late 1863, many different sets of rules had been published, varying widely on such questions as the extent to which the ball could be handled, the treatment of offside, the amount of physical contact allowed with opponents, and the height at which a goal could be scored.
1863 rules
Wikisource has original text related to this article: 1863 Laws of the Game |
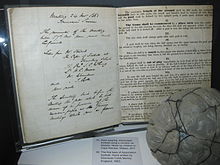
An early draft of the original hand-written 'Laws of the Game' drawn up on behalf of The Football Association by Ebenezer Cobb Morley in 1863 on display at the National Football Museum, Manchester.
The first draft of the Football Association's laws, drawn up by FA's secretary Ebenezer Cobb Morley, contained many features that would today be considered closer to rugby than association football: it permitted running while holding the ball, throwing the ball to a team-mate, and "hacking" (kicking an opponent on the shin). During the Association's deliberations, however, a new version of the Cambridge rules was published that was much more restrictive of handling and physical contact.[4] Morley and Charles W. Alcock were strongly influenced by the new Cambridge rules, making extensive changes in the final draft that was published on 5 December in Bell's Life in London and approved by the FA's members on 8 December 1863. These changes caused a split within the nascent FA, with some clubs such as Blackheath FC (which played a rugby-style game) strongly objecting to them. This led to the split between association football and rugby football which culminated in the formation of the Rugby Football Union in 1871.[5]
Some notable differences between the 1863 laws and the modern game are listed below:
- There was no crossbar. Goals could be scored at any height (as today in Australian rules football).
- While most forms of handling were forbidden, players were allowed to catch the ball (provided they did not run with it or throw it). A fair catch was rewarded with a free kick (a feature that today survives in various forms in Australian rules football, rugby union and American football).
- There was a strict offside rule, under which any player ahead of the kicker was in an offside position (similar to today's offside rule in rugby union). The only exception was when the ball was kicked from behind the goal line.
- The throw-in was awarded to the first player (on either team) to touch the ball after it went out of play. The ball had to be thrown in at right-angles to the touchline (as today in rugby union).
- There was no corner-kick. When the ball went behind the goal-line, there was a situation somewhat similar to rugby: if an attacking player first touched the ball after it went out of play, then the attacking team had an opportunity to take a free kick at goal from a point fifteen yards behind the point where the ball was touched (somewhat similar to a conversion in rugby). If a defender first touched the ball, then the defending team kicked the ball out from on or behind the goal line (equivalent to the goal-kick).
- Teams changed ends every time a goal was scored.
- The rules made no provision for a goal-keeper, match officials, punishments for infringements of the rules, duration of the match, half-time, number of players, or pitch-markings (other than flags to mark the boundary of the playing area).
At its meeting on 8 December 1863, the FA agreed that, as reported in Bell's Life in London, John Lillywhite would publish the Laws.[6] The first game to be played under the new rules was a 0-0 draw between Barnes and Richmond.[6]
Adoption of the laws was not universal among English football clubs. The Sheffield Rules continued to be used by many. Additionally, in preference of a more physical game with greater emphasis on handling of the ball, several decided against being part of the FA in its early years and would later form the Rugby Football Union.
IFAB created
Minor variations between the rules used in England (the jurisdiction of the Football Association) and the other Home Nations of the United Kingdom, Scotland, Wales and Ireland, led to the creation of the International Football Association Board to oversee the rules for all the home nations. Their first meeting was in 1886.[7] Before this, teams from different countries had to agree to which country's rules were used before playing.
FIFA adoption
When the international football body on the continent FIFA was founded in Paris in 1904, it immediately declared that FIFA would adhere to the rules laid down by the IFAB. The growing popularity of the international game led to the admittance of FIFA representatives to the IFAB in 1913. Up until 1958, it was still possible for the British associations to vote together to impose changes against the wishes of FIFA. This changed with the adoption of the current voting system whereby FIFA's support is necessary, but not sufficient, for any amendment to pass.[3]
Notable amendments
Wikisource has text of early versions of the Laws of Game from 1863 to 1923: Laws of the Game |
Notable amendments to the rules include:[8][5]
1866 – The strict rugby-style offside rule is relaxed: a player is onside as long as there are three opponents between the player and the opposing goal. The award of a free kick for a fair catch (still seen in other football codes) is eliminated. A tape (corresponding to the modern crossbar) is added to the goals; previously goals could be scored at any height (as today in Australian rules football).[a]
1867 – The situation when the ball goes behind the goal-line is simplified: all rugby-like elements are removed, with the defending team being awarded a goal-kick regardless of which team touched the ball.[b]

From 1866 to 1883, the laws provided for a tape between the goalposts
1870 – All handling of the ball is forbidden (previously, players had been allowed to catch the ball). Teams change ends at half-time, but only if no goals were scored in the first half.[b]
1871 – Introduction of the specific position of goalkeeper, who is allowed to handle the ball "for the protection of his goal".
1872 – The indirect free kick is introduced as a punishment for a handball, the first mention of a punitive action for contravening the rules. The corner kick is introduced. Teams do not change ends after goals scored during the second half.[b]
1873 – The throw-in is awarded against the team who kicked the ball into touch (previously it was awarded to the first player from either team to touch the ball after it went out of play).[b] The goalkeeper may not "carry" the ball.
1874 – The indirect free kick, previously used only to punish handball, is extended to cover foul play and offside. The first reference to a match official (the "umpire"). Previously, team captains had generally been expected to enforce the laws.[b]
1875 – A goal may not be directly scored from a corner-kick or from the kick-off. Teams change ends at half-time only. The goal may have either a crossbar or tape.[b]
1877 – The throw-in may go in any direction (previously it had to be thrown in at right-angles to the touchline, as today in rugby union).[b] As a result of this change, the clubs of the Sheffield Football Association agreed to abandon their own distinctive "Sheffield Rules" and adopt the FA laws.
1878 – A player can be offside from a throw-in.
1881 – The referee is introduced, to decide disputes between the umpires. The caution (for "ungentlemanly behaviour") and the sending-off (for violent conduct) appear in the laws for the first time.
1883 – An "international conference" between the English, Scottish, Irish and Welsh football associations, held in December 1882, resulted in the unification of the rules across the home nations, which entailed several changes to the FA's laws the following year. The throw-in finally reaches its modern form, with players required to throw the ball from above the head using two hands. A player cannot be offside from a corner kick. The goalkeeper may take up to two steps while holding the ball. The goal must have a crossbar (the option of using tape is removed). The kick-off must be kicked forwards. The touch-line is introduced (previously, the boundary of the field of play had been marked by flags).
1887 – The goalkeeper may not handle the ball in the opposition's half.
1888 – The drop ball is introduced as a means of restarting play after it has been suspended by the referee.
1889 – A player may be sent off for repeated cautionable behaviour.
1890 – A goal may not be scored directly from a goal kick.

When first introduced in 1891, the penalty was awarded for offences within 12 yards of the goal-line.
1891 – The penalty kick is introduced, for handball or foul play within 12 yards of the goal line. The umpires are replaced by linesmen. Pitch markings are introduced for the goal area, penalty area, centre spot and centre circle.
1897 – The laws specify, for the first time, the number of players on each team (11) and the duration of each match (90 minutes, unless agreed otherwise). The half-way line is introduced. The maximum length of the ground is reduced from 200 yards to 130 yards.
1901 – Goalkeepers may handle the ball for any purpose (previously the goalkeeper was permitted to handle the ball only "in defence of his goal").
1902 – The goal area and penalty area assume their modern dimensions, extending six yards and eighteen yards respectively from the goal posts. The penalty spot is introduced.
1903 – A goal may be scored directly from a free kick awarded for handball or foul play (previously all free-kicks awarded for infringements of the laws, other than penalty kicks, had been indirect). A referee may refrain from awarding a free kick or penalty in order to give advantage to the attacking team. A player may be sent off for "bad or violent language to a Referee".
1907 – Players cannot be offside when in their own half.
1912 – The goalkeeper may handle the ball only in the penalty area.
1920 – A player cannot be offside from a throw-in.
1924 – A goal may be scored directly from a corner kick.
1925 – The offside rule is relaxed further: a player is onside as long as there are two opponents between the player and the oppponents' goal-line (previously, three opponents had been required).
1931 – The goalkeeper may take four steps (rather than two) while carrying the ball.
1937 – The "D" is added to the pitch markings, to ensure that players do not encroach within 10 yards of the player taking a penalty kick.
1938 – The laws are completely rewritten by Stanley Rous. A player may be sent off for "serious foul play".
1970 – Introduction of red and yellow cards.
1990 – A further relaxation of the offside rule: a player level with the second-last opponent is considered onside (previously, such a player would have been considered offside). A player may be sent off for an offence that denies opponents a "clear goalscoring opportunity".
1992 – Introduction of the back-pass rule: the goalkeeper may not handle the ball after it has been deliberately kicked to him/her by a teammate.
1997 – The rules are completely rewritten, for the first time since 1938.[9] A goal may be scored directly from the kick-off or from the goal kick. The goalkeeper may not handle the ball after receiving it directly from a team-mate's throw-in.
2000 – The four-step restriction on the goalkeeper handling the ball is repealed and replaced by the "six-second rule": the goalkeeper may not handle the ball for more than six seconds. The goalkeeper may no longer be charged while holding the ball.
2012 – Goal-line technology permitted (but not required).
2016 – The kick-off may be kicked in any direction.
2018 – Video assistant referees permitted (but not required). A fourth substitution is permitted in extra time.[10]
Notes
^ Adopted from Cambridge rules
^ abcdefg Adopted from Sheffield rules
References
^ ab IFAB (18 May 2017). "Laws of the Game". theifab.com. Zurich: International Football Association Board. Retrieved 27 August 2017..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ United States Soccer Federation Inc.,; Michael Lewis (2000). Soccer for dummies. Foster City, CA: IDG Books Worldwide. ISBN 1118053575. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
^ abc "The IFAB: How it works". FIFA. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
^ "Cambridge... the birthplace of football?!". BBC. 22 September 2009. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
^ ab "FIFA – History – the Laws – From 1863 to the Present Day". FIFA. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
^ ab "The History of The FA". The Football Association. Retrieved 6 June 2014.
^ "The International FA Board (IFAB)". FIFA. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
^ FIFA. "FIFA History of Football". Retrieved 8 December 2011.
^ https://www.fifa.com/news/y=1997/m=5/news=the-new-laws-the-game-70248.html
^ "International Football Association Board | IFAB". International Football Association Board | IFAB. 3 March 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2018.
The Rules of Association Football, 1863: The First FA Rule Book Bodleian Library (2006)
External links
- The current Laws of the Game (FIFA Site)
- Rules & Governance (The FA website)
The formation of the Football Association and the First FA Rules from the Association of Football Statisticians at the Wayback Machine (archived 21 June 2006)- Q&A Laws of the Game (AskTheRef.com)
Archives of the IFAB from Soccer South Bay Referee Association; includes minutes of meetings deciding on changes to the Laws of the Game
