East Asia
East Asia .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} 东亚/東亞 (in Chinese) 東アジア (in Japanese) 동아시아 (in Korean) Дорнод Ази (in Mongolian) | |
|---|---|
Subregion of Asia | |
 | |
State[note 1] |
|
| Major cities |
|
| Area [note 2] | |
| • Total | 11,839,074 km2 (4,571,092 sq mi) |
| Population (2016)[note 3] | |
| • Total | 1,641,908,531 |
| • Rank | 2nd (World) |
| Time zone |
|
| Languages and language families |
|
| East Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 东亚/东亚细亚 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 東亞/東亞細亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan | .mw-parser-output .uchen{font-family:"Qomolangma-Dunhuang","Qomolangma-Uchen Sarchen","Qomolangma-Uchen Sarchung","Qomolangma-Uchen Suring","Qomolangma-Uchen Sutung","Qomolangma-Title","Qomolangma-Subtitle","Qomolangma-Woodblock","DDC Uchen","DDC Rinzin",Kailash,"BabelStone Tibetan",Jomolhari,"TCRC Youtso Unicode","Tibetan Machine Uni",Wangdi29,"Noto Sans Tibetan","Microsoft Himalaya"}.mw-parser-output .ume{font-family:"Qomolangma-Betsu","Qomolangma-Chuyig","Qomolangma-Drutsa","Qomolangma-Edict","Qomolangma-Tsumachu","Qomolangma-Tsuring","Qomolangma-Tsutong","TibetanSambhotaYigchung","TibetanTsugRing","TibetanYigchung"} ཨེ་ཤ་ཡ་ཤར་མ་ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnamese alphabet | Đông Á | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chữ Hán | 東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hangul | 동아시아/동아세아/동아 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanja | 東아시아/東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian | Зүүн Ази .mw-parser-output .font-mong{font-family:"Menk Hawang Tig","Menk Qagan Tig","Menk Garqag Tig","Menk Har_a Tig","Menk Scnin Tig","Oyun Gurban Ulus Tig","Oyun Qagan Tig","Oyun Garqag Tig","Oyun Har_a Tig","Oyun Scnin Tig","Oyun Agula Tig","Mongolian BT","Mongolian Baiti","Noto Sans Mongolian","Mongol Usug","Mongolian White","MongolianScript","Code2000","Menksoft Qagan"}.mw-parser-output .font-mong-mnc,.mw-parser-output .font-mong:lang(mnc-Mong),.mw-parser-output .font-mong:lang(dta-Mong),.mw-parser-output .font-mong:lang(sjo-Mong){font-family:"Abkai Xanyan","Abkai Xanyan LA","Abkai Xanyan VT","Abkai Xanyan XX","Abkai Xanyan SC","Abkai Buleku","Daicing White","Oyun Gurban Ulus Tig","Oyun Qagan Tig","Oyun Garqag Tig","Oyun Har_a Tig","Oyun Scnin Tig","Oyun Agula Tig","Mongolian BT","Mongolian Baiti","Noto Sans Mongolian"} ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨ ᠠᠽᠢ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kana | ひがしアジア/とうあ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kyūjitai | 東亞細亞/東亞 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shinjitai | 東亜細亜(東アジア)/東亜 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur | .mw-parser-output .font-ugy{font-family:"UKIJ Tuz","UKIJ Nasq","UKIJ Basma","UKIJ_Mac Basma","UKIJ Zilwa","UKIJ Esliye","UKIJ Tuz Basma","UKIJ Tuz Kitab","UKIJ Tuz Gezit","UKIJ Tuz Qara","UKIJ Tuz Qara","UKIJ Tuz Tor","UKIJ Kesme","UKIJ Kesme Tuz","UKIJ Qara","UKIJ Basma Aq","UKIJ Basma Qara","UKIJ Basma Tuz","UKIJ Putuk","UKIJ Tuz Xet","UKIJ Tom Xet","UKIJ Tuz Jurnal","UKIJ Arabic","UKIJ CJK","UKIJ Ekran","UKIJ_Mac Ekran","UKIJ Teng","UKIJ Tor","UKIJ Tuz Tom","UKIJ Mono Keng","UKIJ Mono Tar","UKIJ Nokia","UKIJ SimSun","UKIJ Yanfon","UKIJ Qolyazma","UKIJ Saet","UKIJ Nasq Zilwa","UKIJ Sulus","UKIJ Sulus Tom","UKIJ 3D","UKIJ Diwani","UKIJ Diwani Yantu","UKIJ Diwani Tom","UKIJ Esliye Tom","UKIJ Esliye Qara","UKIJ Jelliy","UKIJ Kufi","UKIJ Kufi Tar","UKIJ Kufi Uz","UKIJ Kufi Yay","UKIJ Merdane","UKIJ Ruqi","UKIJ Mejnuntal","UKIJ Junun","UKIJ Moy Qelem","UKIJ Chiwer Kesme","UKIJ Orxun-Yensey","UKIJ Elipbe","UKIJ Qolyazma Tez","UKIJ Qolyazma Tuz","UKIJ Qolyazma Yantu","UKIJ Ruqi Tuz",FZWWBBOT_Unicode,FZWWHQHTOT_Unicode,Scheherazade,Lateef,LateefGR,"Noto Naskh Arabic","Microsoft Uighur";font-feature-settings:"cv50"1} شەرقىي ئاسىي | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russian | Восточная Азия | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Vostochnaja Azija | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

China, Korea, Japan and Vietnam are culturally East Asian
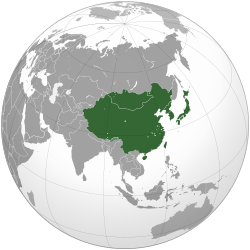
East Asia is the eastern subregion of Asia, which can be defined in either geographical[1] or ethno-cultural[2] terms.[3][4] Culturally, China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam are commonly seen as being encompassed by cultural East Asia (East Asian cultural sphere).[5] Geographically and geopolitically, the region constitutes China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea.[1][3][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13]
The region was the cradle of various ancient civilizations such as ancient China, ancient Japan, ancient Korea, and the Mongol Empire.[14][15] East Asia was one of the cradles of world civilization, with China, an ancient East Asian civilization being one of the earliest cradles of civilization in human history. For thousands of years, China largely influenced East Asia as it was principally the leading civilization in the region exerting its enormous prestige and influence on its neighbors.[16][17][18] Historically, societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. The Chinese calendar preserves traditional East Asian culture and serves as the root to which many other East Asian calendars are derived from. Major religions in East Asia include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana[note 4]), Confucianism and Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, Ancestral worship, and Chinese folk religion in Greater China, Buddhism and Shintoism in Japan, and Christianity, Buddhism, and Sindoism in Korea.[12]Shamanism is also prevalent among Mongols and other indigenous populations of northern East Asia such as the Manchus.[19][20]
East Asians comprise around 1.6 billion people, making up about 38% of the population in Continental Asia and 22% of the global population. The region is home to major world metropolises such as Beijing, Hong Kong, Seoul, Shanghai, Taipei, and Tokyo. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in Mongolia and Western China, both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the lowest population density of any sovereign state. The overall population density of the region is 133 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi), about three times the world average of 45/km2 (120/sq mi).
Contents
1 History
2 Definitions
2.1 Alternative definitions
3 Economy
4 Territorial and regional data
4.1 Etymology
4.2 Demographics
4.3 Ethnic groups
5 Culture
5.1 Overview
5.2 Religions
5.3 Festivals
6 Collaboration
6.1 East Asian Youth Games
6.2 Free trade agreements
6.3 Military alliances
7 Cities and towns
8 See also
9 Notes
10 References
11 External links
History
In comparison with the profound influence of the Ancient Greeks and Romans on Europe and the Western World, China would already possess an advanced civilization nearly half a millennia before Japan and Korea.[21] As Chinese civilization existed for about 1500 years before other East Asian civilizations emerged into history, Imperial China would exert much of its cultural, economic, technological, and political muscle onto its neighbors.[22][23][24] Succeeding Chinese dynasties exerted enormous influence across East Asia culturally, economically, politically, and militarily for over two millennia.[24][25] Imperial China's cultural preeminence not only led the country to become East Asia's first literate nation in the entire region, it also supplied Japan, Vietnam, and Korea with Chinese loanwords and linguistic influences rooted in their writing systems.[26] In addition, the Chinese Han dynasty hosted the largest unified population in East Asia, the most literate and urbanized as well as being the most technologically and culturally advanced civilization in the region.[27] Cultural and religious interaction between the Chinese and other regional East Asian dynasties and kingdoms occurred. China's impact and influence on Korea began with the Han dynasty's northeastern expansion in 108 BC when the Han Chinese conquered the northern part of the Korean peninsula and established a province called Lelang. Chinese influence would soon take root in Korea through the inclusion of the Chinese writing system, monetary system, rice culture, and Confucian political institutions.[28] Jōmon society in ancient Japan incorporated wet-rice cultivation and metallurgy through its contact with Korea. Vietnamese society was greatly impacted by Chinese influence, the northern part of Vietnam was occupied by Chinese empires and states for almost all of the period from 111 BC to 938 AD. In addition to administration, and making Chinese the language of administration, the long period of Chinese domination introduced Chinese techniques of dike construction, rice cultivation, and animal husbandry. Chinese culture, having been established among the elite mandarin class, remained the dominant current among that elite for most of the next 1,000 years (939-1870s) until the loss of independence under French Indochina. This cultural affiliation to China remained true even when militarily defending Vietnam against attempted invasion, such as against the Mongol Kublai Khan. The only significant exceptions to this were the 7 years of the strongly anti-Chinese Hồ dynasty which banned the use of Chinese (among other actions triggering the fourth Chinese invasion), but then after the expulsion of the Ming the rise in vernacular chữ nôm literature. Although 1,000 years of Chinese rule left many traces, the collective memory of the period reinforced Vietnam's cultural and later political independence. As full-fledged medieval East Asian states were established, Korea by the fourth century AD and Japan by the seventh century AD, Korea, Japan, and Vietnam actively began to incorporate Chinese influences such as Confucianism, the use of written Han characters, Chinese style architecture, state institutions, political philosophies, religion, urban planning, and various scientific and technological methods into their culture and society through direct contacts with succeeding Chinese dynasties.[29] For many centuries, most notably from the 7th to the 14th centuries, China stood as East Asia's most advanced civilization, commanding influence across the region up until the early modern period.[30] The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's history for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural influence over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.[31][32][23] The transmission of advanced Chinese cultural practices and ways of thinking greatly shaped the region up until the 19th century.[21]
As East Asia's connections with Europe and the Western world strengthened during the late 19th century, China's power began to decline. U.S. Commodore Matthew C. Perry would open Japan to Western ways, and the country would expand in earnest after the 1860s.[33][34] Around the same time, Japan with its rush to modernity transformed itself from an isolated feudal samurai state into East Asia's first industrialized nation.[35][11][34] The modern and powerful Japan would galvanize its position in the Orient as East Asia's greatest power with a global mission poised to advance to lead the entire world.[35] By the early 1900s, the Japanese empire succeeded in asserting itself as East Asia's first modern power. With its newly found international status, Japan would begin to inextricably take a more active position in East Asia and leading role in world affairs at large. Flexing its nascent political and military might, Japan soundly defeated the stagnant Qing dynasty during the First Sino-Japanese War as well as vanquishing imperial rival Russia in 1905; the first major military victory in the modern era of an East Asian power over a European one.[36][33] Its hegemony was the heart of an empire that would include Taiwan and Korea.[35] During World War II, Japanese expansionism with its imperialist aspirations through the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere would incorporate Korea, Taiwan, much of eastern China and Manchuria, Hong Kong, Vietnam, and Southeast Asia under its control establishing itself as a maritime colonial power in East Asia.[37] After a century of exploitation by the European and Japanese colonialists, post-colonial East Asia saw the defeat and occupation of Japan by the victorious Allies as well as the division of China and Korea during the Cold War. The Korean peninsula became independent but then it was divided into two rival states, while Taiwan became the main territory of de facto state Republic of China after the latter lost Mainland China to the People's Republic of China in the Chinese Civil War. During the latter half of the twentieth century, the region would see the post war economic miracle of Japan, the economic rise of South Korea and Taiwan, and the integration of Mainland China into the global economy through its entry in the World Trade Organization while enhancing its emerging international status as a potential world power.[6][38]
Culturally, China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam are commonly seen as being encompassed by cultural East Asia (East Asian cultural sphere).
Definitions
In common usage, the term East Asia typically refers to a region including Greater China, Japan, Korea and Mongolia.[39][40][41][42][43]
China, Japan, and Korea represent the three core countries and civilizations of traditional East Asia - as they once shared a common written language, culture, as well as sharing Confucian philosophical tenets and the Confucian societal value system once instituted by Imperial China.[44][45][45][46][47] Other usages define China, Hong Kong, Macau, Japan, South Korea, North Korea and Taiwan as countries that constitute East Asia based on their geographic proximity as well as historical and modern cultural and economic ties, particularly with Japan and Korea having strong cultural influences that originated from China.[47][48][49][3][50][51] Some scholars include Vietnam as part of East Asia as it has been considered part of the greater sphere of Chinese influence. Though Confucianism continues to play an important role in Vietnamese culture, Chinese characters are no longer used in its written language and many scholarly organizations classify Vietnam as a Southeast Asian country.[3][52] Mongolia is geographically north of China yet Confucianism and the Chinese writing system and culture had no impact in Mongolian society. Thus, Mongolia is sometimes grouped with Central Asian countries such as Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan.[3][52]
Broader and looser definitions by international organizations such as the World Bank refer to the "three major Northeast Asian economies, i.e. China, Japan, and South Korea", as well as Mongolia, North Korea, the Russian Far East and Siberia.[53] The Council on Foreign Relations includes the Russia Far East, Mongolia, and Nepal.[54] The World Bank also acknowledges the roles of sub-national or de facto states, such as Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. The Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia defines the region as "China, Japan, the Koreas, Nepal, Mongolia, and eastern regions of the Russian Federation".[55]

The countries of East Asia also form the core of Northeast Asia, which itself is a broader region.
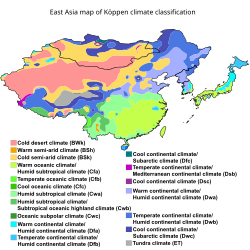
East Asia map of Köppen climate classification.
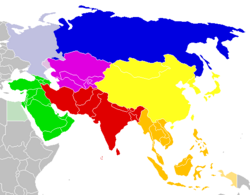
UNSD geoscheme for Asia based on statistic convenience rather than implying any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories:[56]
North Asia
Central Asia
Western Asia
South Asia
East Asia
Southeast Asia
The UNSD definition of East Asia is based on statistical convenience,[56] but also other common definitions of East Asia contain Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan, and Japan.[1][57]
Culturally, China, Japan, Korea and Vietnam are commonly seen as being encompassed by cultural East Asia (East Asian cultural sphere).[2][58][59][60]
Alternative definitions
There are mixed debates around the world whether these countries or regions should be considered in East Asia or not.
Vietnam (officially part of Southeast Asia geographically, although culturally it is a part of the East Asian cultural sphere, politically, it is related to both Southeast Asia and East Asia)
Far Eastern Federal District in Russia (often described as North Asia due to its location, although this part of Russia is often seen as more closely related to its East Asian neighbours)- Sovereignty issues exist over some territories in the South China Sea.
In business and economics, "East Asia" is sometimes used to refer to a wide geographical area covering ten Southeast Asian countries in ASEAN, Greater China, Japan and Korea. However, in this context, the term "Far East" is used by the Europeans to cover ASEAN countries and the countries in East Asia. However, being a Eurocentric term, Far East describes the region's geographical position in relation to Europe rather than its location within Asia. Alternatively, the term "Asia Pacific Region" is often used in describing East Asia, Southeast Asia as well as Oceania.
Observers preferring a broader definition of "East Asia" often use the term Northeast Asia to refer to the greater China area, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan, with Southeast Asia covering the ten ASEAN countries. This usage, which is seen in economic and diplomatic discussions, is at odds with the historical meanings of both "East Asia" and "Northeast Asia".[61][62][63] The Council on Foreign Relations defines Northeast Asia as Japan and Korea.[54]
Economy
| Country | GDP nominal billions of USD (2017)[64] | GDP nominal per capita USD (2017)[64] | GDP PPP billions of USD (2017)[64] | GDP PPP per capita USD (2017)[64] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12,014.610 | 8,643.107 | 23,159.107 | 16,660.269 | |
| 341.659 | 46,109.124 | 454.912 | 61,393.316 | |
| 49.802 | 77,451.287 | 71.778 | 111,629.024 | |
| 4,872.135 | 38,439.517 | 5,428.813 | 42,831.523 | |
| N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 1,538.030 | 29,891.255 | 2,029.032 | 39,433.779 | |
| 11.135 | 3,639.894 | 39.704 | 12,978.557 | |
| 579.302 | 24,576.665 | 1,185.480 | 50,293.541 |
Territorial and regional data
Etymology
| Flag | Common Name | Official Name | ISO 3166 Country Codes[67] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exonym | Endonym | Exonym | Endonym | ISO Short Name | Alpha-2 Code | Alpha-3 Code | Numeric | |
| China | 中国 | People’s Republic of China | 中华人民共和国 | China | CN | CHN | 156 | |
| Hong Kong | 香港 | Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People’s Republic of China | 中華人民共和國香港特別行政區 | Hong Kong | HK | HKG | 344 | |
| Macau | 澳門 | Macao Special Administrative Region of the People’s Republic of China | 中華人民共和國澳門特別行政區 Região Administrativa Especial de Macau da República Popular da China | Macao | MO | MAC | 446 | |
| Japan | 日本 | State of Japan | 日本国 | Japan | JP | JPN | 392 | |
| Mongolia | Монгол улс | Mongolia | Монгол Улс( ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ) | Mongolia | MG | MNG | 496 | |
| North Korea | 조선 | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea | 조선민주주의인민공화국 (朝鮮民主主義人民共和國) | Korea (the Democratic People's Republic of) | KP | PRK | 408 | |
| South Korea | 한국 | Republic of Korea | 대한민국 (大韓民國) | Korea (the Republic of) | KR | KOR | 410 | |
Taiwan[68] | 臺灣 / 台灣 | Republic of China | 中華民國 | Taiwan (Province of China)[69] | TW | TWN | 158 | |
Demographics
| State/Territory | Area km2 | Population[70] (2016) | Population density per km2 | HDI[71] | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9,640,011[note 6] | 1,403,500,365[note 7] | 138 | 0.752 | Beijing | |
| 1,104 | 7,302,843 | 6,390 | 0.933 | Hong Kong | |
| 30 | 612,167 | 18,662 | 0.909 | Macau | |
| 377,930 | 127,748,513 | 337 | 0.909 | Tokyo | |
| 120,538 | 25,368,620 | 198 | 0.733 | Pyongyang[72] | |
| 100,210 | 50,791,919 | 500 | 0.903 | Seoul | |
| 1,564,100 | 3,027,398 | 2 | 0.741 | Ulaanbaatar | |
| 36,188 | 23,556,706 | 639 | 0.885 | Taipei[73] |
Ethnic groups
| Ethnicity | Native name | Population | Language(s) | Writing system(s) | Major states/territories* | Physical appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Han/Chinese | 漢人 or 汉人, 漢族 or 汉族 | 1,260,000,000[74] | Chinese, Mandarin, Cantonese, Shanghainese, Hokkien, Hakka, Gan, Hsiang, etc. | Simplified Han characters, Traditional Han characters |  | |
Yamato/Japanese | 日本族 (にほんぞく) 大和民族 (やまとみんぞく) | 125,117,000[75] | Japanese | Han characters (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana |  | |
Joseon/Korean | 한민족 (韓民族) 조선족 (朝鮮族) | 79,432,225[citation needed] | Korean | Hangul, Han characters (Hanja) |  | |
Bai | 白族 | 1,858,063 | Bai, Southwestern Mandarin | Latin script, Simplified Han characters |  | |
Hui | 回族/回回 | 10,586,087[citation needed] | Northwestern Mandarin, other Chinese Dialects, Huihui language, etc. | Simplified Han characters |  | |
Mongols | Монголчууд/ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯᠴᠤᠳ Монгол/ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ | 8,942,528 | Mongolian | Mongol script, Cyrillic script |  | |
Zhuang | 壮族/Bouxcuengh | 18,000,000 | Zhuang, Southwestern Mandarin, etc. | Simplified Han characters, Latin script |  | |
Uyghurs | ئۇيغۇر | 15,000,000+[76] | Uighur | Arabic alphabet, Cyrillic script |  | |
Manchus | 满族/ ᠮᠠᠨᠵᡠ | 10,422,873[citation needed] | Northeastern Mandarin, Manchurian (endangered), etc. | Simplified Han characters, Mongol script |  | |
Hmong/Miao | Ghaob Xongb/Hmub/Mongb | 9,426,007[citation needed] | Hmong, Southwestern Mandarin | Latin script, Simplified Han characters |  | |
Tibetans | བོད་པ་ | 6,500,000 | Tibetan, Rgyal Rong, Rgu, etc. | Tibetan script |  | |
Yi | ꆈꌠ/彝族 | 8,714,393 | Various Loloish, Southwestern Mandarin | Yi script, Simplified Han characters |  | |
Tujia | 土家族 | 8,353,912 | Northern Tujia, Southern Tujia | Simplified Han characters |  | |
Kam | Gaeml | 2,879,974 | Gaeml | Simplified Han characters, Latin script |  | |
Tu | 土族/Monguor | 289,565 | Tu, Northwestern Mandarin | Simplified Han characters |  | |
Daur | 达斡尔族/ ᠳᠠᠭᠤᠷ | 131,992 | Daur, Northeastern Mandarin | Mongol script, Simplified Han characters |  | |
Taiwanese Aborigines | Pangcah, etc. | 533,600 | Austronesian languages (Amis, Yami), etc. | Latin script, Traditional Han characters |  | |
Ryukyuan | (琉球民族(りゅうきゅうみんぞく) 沖縄人 (おきなわじん) | 1,900,000 | Japanese Ryukyuan | Han characters (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana |  | |
Ainu | アイヌ | 200,000 | Japanese Ainu[77] | Han characters (Kanji), Katakana, Hiragana |  |
- Note: The order of states/territories follows the population ranking of each ethnicity, within East Asia only.
Culture
Overview
The culture of East Asia has largely been influenced by China, as it was the civilization that had the most dominant influence in the region throughout the ages that ultimately laid the foundation for East Asian civilization.[78] The vast knowledge and ingenuity of Chinese civilization and the classics of Chinese literature and culture were seen as the foundations for a civilized life in East Asia. Imperial China served as a vehicle through which the adoption of Confucian ethical philosophy, Chinese calendar system, political and legal systems, architectural style, diet, terminology, institutions, religious beliefs, imperial examinations that emphasized a knowledge of Chinese classics, political philosophy and cultural value systems, as well as historically sharing a common writing system reflected in the histories of Japan and Korea.[79][24][80][81][82][83][84][85][47] The Imperial Chinese tributary system was the bedrock of network of trade and foreign relations between China and its East Asian tributaries, which helped to shape much of East Asian affairs during the ancient and medieval eras. Through the tributary system, the various dynasties of Imperial China facilitated frequent economic and cultural exchange that influenced the cultures of Japan and Korea and drew them into a Chinese international order.[86][87] The Imperial Chinese tributary system shaped much of East Asia's foreign policy and trade for over two millennia due to Imperial China's economic and cultural dominance over the region, and thus played a huge role in the history of East Asia in particular.[32][87] The relationship between China and its cultural influence on East Asia has been compared to the historical influence of Greco-Roman civilization on Europe and the Western World.[83][81][87][79]
Religions
| Religion | Native name | Denomination | Major book | Type | Est. Followers | Ethnic groups | States/territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chinese religion | none, various classifications including 民間信仰, 神教/神道, etc. | Taoism, Confucianism, folk salvationist sects, Wuism, Nuo | Chinese classics, Huangdi Sijing, precious scrolls, etc. | Pantheism/polytheism | ~900,000,000[88][89] | Han, Hmong, Qiang, Tujia (worship of the same ancestor-gods) | |
Taoism | 道教 | Zhengyi, Quanzhen | Tao Te Ching | Pantheism/polytheism | ~20,000,000[89] | Han, Zhuang, Hmong, Yao, Qiang, Tujia | |
Confucianism | 儒教 | Cheng-Zhu, Lu-Wang | Four Books and Five Classics | Immanent transcendence/pantheism | N/A | Han, Korean, Yamato | |
East Asian Buddhism | 漢傳佛教 or 汉传佛教 | Mahayana | Diamond Sutra | Non-God | ~300,000,000 | Han, Korean, Yamato | |
Tibetan Buddhism | བོད་བརྒྱུད་ནང་བསྟན། | Mahayana | Anuttarayoga Tantra | Non-God | ~10,000,000 | Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols | |
Shamanism[note 8] and Bon, etc. | Бөө мөргөл, བོན | N/A | N/A | Polytheism/pantheism | N/A | Tibetans, Manchus, Mongols, Oroqen | |
Shintoism | 神道 | Shinto sects | Kojiki, Nihon Shoki | Polytheism/pantheism | N/A | Yamato | |
Sindo/Muism | 신도 or 무교 | Sindo sects | N/A | Polytheism/pantheism | N/A | Korean | |
Ryukyuan religion | 琉球神道 or ニライカナイ信仰 | N/A | N/A | Polytheism/pantheism | N/A | Ryukyuan |
Festivals
| Festival | Native Name | Other name | Calendar | Date | Gregorian date | Activity | Religious practices | Food | Major ethnicities | Major states/territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chinese New Year | 春節 or 春节 | Spring Festival | Chinese | Month 1 Day 1 | 21 Jan–20 Feb | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | Worship the King of Gods | Jiaozi | Han, Korean, Manchus etc. | |
New Year | 元旦 | Yuan Dan | Gregorian | 1 Jan | 1 Jan | Fireworks | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
Losar or Tsagaan Sar | ལོ་གསར་ or Цагаан сар | White Moon | Tibetan, Mongolian | Month 1 Day 1 | 25 Jan – 2 Mar | Family Reunion, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping, Fireworks | N/A | Chhaang or Buuz | Tibetans, Mongols, Tu etc. | |
Lantern Festival | 元宵節 or 元宵节 | Upper Yuan Festival (上元节) | Chinese | Month 1 Day 15 | 4 Feb – 6 Mar | Lanterns Expo, Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Sky-officer | Yuanxiao | Han, Korean, Yamato | |
Qingming Festival | 清明節 or 清明节 | Tomb Sweeping Day | Solar | 15th day since March equinox | 4–6 April | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Burning Hell money | Cold Food | Han, Korean, Mongols | |
Dragon Boat Festival | 端午節 or 端午节 | Duanwu Festival | Chinese | Month 5 Day 5 | Driving poisons & plague away, Dragon Boat Race, Wearing colored lines, Hanging felon herb on the front door. | Worship various Gods | Zongzi | Han, Korean, Yamato | ||
Ghost Festival | 中元節 or 中元节 | Mid Yuan Festival | Chinese | Month 7 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Earth-officer | Han, Korean, Yamato | |||
Mid-Autumn Festival | 中秋節 or 中秋节 | 中秋祭 | Chinese | Month 8 Day 15 | Family Reunion, Enjoying Moon view | Worship the Moon Goddess | Mooncake | Han, Korean, Yamato | ||
| Double Ninth Festival | 重陽節 or 重阳节 | Double Positive Festival | Chinese | Month 9 Day 09 | Climbing Mountain, Taking care of elderly, Wearing Cornus. | Worship various Gods | Han, Korean, Yamato | |||
| Lower Yuan Festival | 下元節 or 下元节 | N/A | Chinese | Month 10 Day 15 | Ancestors Worship, Tomb Sweeping | Birthdate of the God of Water-officer | Ciba | Han, Korean | ||
| Small New Year | 小年 | Jizao (祭灶) | Chinese | Month 12 Day 23 | Cleaning Houses | Worship the God of Hearth | tanggua | Han, Mongols | ||
| International Labor Day | N/A | N/A | Gregorian | 1 May | 1 May | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| International Women's Day | N/A | N/A | Gregorian | 8 Mar | 8 Mar | Taking care of women | N/A | N/A | N/A | All |
*Japan switched the date to the Gregorian calendar after the Meiji Restoration.
*Not always on that Gregorian date, sometimes April 4.
Collaboration
East Asian Youth Games
Formerly the East Asian Games is a multi-sport event organised by the East Asian Games Association (EAGA) and held every four years since 2019 among athletes from East Asian countries and territories of the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA), as well as the Pacific island of Guam, which is a member of the Oceania National Olympic Committees.
The East Asian Games is 1 of 5 Regional Games of the OCA. The others are the East Asian Games, the Central Asian Games, the South Asian Games, the Southeast Asian Games (SEA Games), and the West Asian Games.
Free trade agreements
| Name of agreement | Parties | Leaders at the time | Negotiation begins | Signing date | Starting time | Current status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Park Geun-hye | May, 2012 | Jun 01, 2015 | Dec 30, 2015 | Enforced | |
| China–Japan–South Korea FTA | Xi Jinping, Shinzō Abe, Park Geun-hye | Mar 26, 2013 | N/A | N/A | 10 round negotiation | |
| Japan-Mongolia EPA | Shinzō Abe, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | - | Feb 10, 2015 | - | Enforced | |
| China-Mongolia FTA | Xi Jinping, Tsakhiagiin Elbegdorj | N/A | N/A | N/A | Officially proposed | |
| China-HK CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Tung Chee-hwa | - | Jun 29, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| China-Macau CEPA | Jiang Zemin, Edmund Ho Hau-wah | - | Oct 18, 2003 | - | Enforced | |
| Hong Kong-Macau CEPA | Carrie Lam, Fernando Chui | Oct 09, 2015 | N/A | N/A | Negotiating | |
ECFA | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Jan 26, 2010 | Jun 29, 2010 | Aug 17, 2010 | Enforced | |
| CSSTA (Based on ECFA) | Xi Jinping, Ma Ying-jeou | Mar, 2011 | Jun 21, 2013 | N/A | Abolished | |
| CSGTA (Based on ECFA) | Hu Jintao, Ma Ying-jeou | Feb 22, 2011 | N/A | N/A | Suspended |
Military alliances
| Name | Abbr. | Parties within the region |
|---|---|---|
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation | SCO | |
| General Security of Military Information Agreement | GSOMIA | |
Sino-North Korean Mutual Aid and Cooperation Friendship Treaty | - | |
Treaty of Mutual Cooperation and Security between the United States and Japan | - | |
Mutual Defense Treaty Between the United States and the Republic of Korea | - | |
Taiwan Relations Act (Sino-American Mutual Defense Treaty before 1980) | TRA (SAMDT) | |
Major non-NATO ally (Global Partners of NATO) | - |
Cities and towns

Beijing is the capital of the People's Republic of China and the largest metropolis in northern China.

Shanghai is the largest city in China and one of the largest in the world, and is a global financial centre and transport hub with the world's busiest container port.

Guangzhou is one of the most important cities in southern China. It has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road and continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub today.

Xi'an or Chang'an is the oldest of the Four Great Ancient Capitals of China, having held the position under several of the most important dynasties. It has a significant cultural influence in East Asia.

Hong Kong is one of the world's leading global financial centres and is known as a cosmopolitan metropolis.

Taipei is the capital of the Republic of China and anchors a major high-tech industrial area in Taiwan.

Tokyo is the capital of Japan and one of the largest cities in the world, both in metropolitan population and economy.

Osaka is the second largest metropolitan area in Japan.

Kyoto was the Imperial capital of Japan for more than one thousand years.

Seoul is the capital of South Korea, one of the largest cities in the world and a leading global technology hub.

Pyongyang is the capital of North Korea, and is a significant metropolis on the Korean Peninsula.
Ulaanbaatar is the capital of Mongolia with a population of 1 million as of 2008.
 Play media
Play mediaPass of the ISS over Mongolia, looking out west towards the Pacific Ocean, China, and Japan. As the video progresses, you can see major cities along the coast and the Japanese islands on the Philippine Sea. The island of Guam can be seen further down the pass into the Philippine Sea, and the pass ends just to the east of New Zealand. A lightning storm can be seen as light pulses near the end of the video.
See also
- China–Japan–South Korea trilateral summit
- East Asia Summit
- East Asian Community
- East Asian languages
- East Asian studies
- Four Asian Tigers
- Northeast Asia
Notes
^ A state is a compulsory political organization with a centralized government that maintains a monopoly of the legitimate use of force within a certain geographical territory. Some states are sovereign. Some states are subject to external sovereignty or hegemony where ultimate sovereignty lies in another state.
^ The area figure is based on the combined areas of Greater China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea and Japan as listed at List of countries and outlying territories by total area.
^ The population figure is the combined populations of Greater China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Japan as listed at the 2017 revision of the World Population Prospects.
^ includes Tibetan Buddhism traditionally prevailing in Tibetan and Mongolian areas
^ Listed as "Taiwan Province of China" by the IMF
^ Includes all area which under PRC's government control (excluding "South Tibet" and disputed islands).
^ A note by the United Nations: "For statistical purposes, the data for China do not include Hong Kong and Macao, Special Administrative Regions (SAR) of China, and Taiwan Province of China."
^ almost Manchu, Mongolian
References
^ abc "East Asia". Encarta. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2008-01-12.the countries and regions of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Mongolia, South Korea, North Korea and Japan.
.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Columbia University – "East Asian cultural sphere" Archived 2008-02-27 at the Wayback Machine. "The East Asian cultural sphere evolves when Japan, Korea, and what is today Vietnam all share adapted elements of Chinese civilization of this period (that of the Tang dynasty), in particular Buddhism, Confucian social and political values, and literary Chinese and its writing system."
^ abcde Prescott, Anne (2015). East Asia in the World: An Introduction. Routledge. ISBN 978-0765643223.
^ Miller, David Y. (2007). Modern East Asia: An Introductory History. Routledge. pp. xxi–xxiv. ISBN 978-0765618221.
^ "Central Themes for a Unit on China | Central Themes and Key Points | Asia for Educators | Columbia University". afe.easia.columbia.edu. Retrieved 2018-12-01.
^ ab Kort, Michael (2005). The Handbook Of East Asia. Lerner Publishing Group. p. 7. ISBN 978-0761326724.
^ "Country Profiles: East Asia". Children and Armed Conflict Unit at the University of Essex.
^ "East Asia". Springer Netherlands.
^ "East Asia". Dictionary.com.
^ Seybolt, Peter J. "China, Korea and Japan: Forgiveness and Mourning". Center for Asian Studies. Center for Asian Studies.
^ ab Asian History Module Learning. Rex Bookstore Inc. 2002. p. 186. ISBN 978-9712331244.
^ ab Salkind, Neil J. (2008). Encyclopedia of Educational Psychology. Sage Publications. p. 56. ISBN 978-1412916882.
^ Holcombe, Charles (2010). A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century. Cambridge University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0521731645.
^ Association of Academies of Sciences in Asia (2012). Towards a Sustainable Asia: The Cultural Perspectives. Springer. p. 17. ISBN 978-3642166686.
^ Minahan, James B. (2014). Ethnic Groups of North, East, and Central Asia: An Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. pp. xx–xxvi. ISBN 978-1610690171.
^ Zaharna, R.S.; Arsenault, Amelia; Fisher, Ali (2013). Relational, Networked and Collaborative Approaches to Public Diplomacy: The Connective Mindshift (1st ed.). Routledge (published 2013-05-01). p. 93. ISBN 978-0415636070.
^ Holcombe, Charles (2017). A History of East Asia: From the Origins of Civilization to the Twenty-First Century. Cambridge University Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-1107544895.
^ Szonyi, Michael (2017). A Companion to Chinese History. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 90. ISBN 978-1118624609.
^ Chongho Kim, "Korean Shamanism", 2003 Ashgate Publishing
^ Andreas Anangguru Yewangoe, "Theologia crucis in Asia", 1987 Rodopi
^ ab Ellington, Lucien (2009). Japan (Nations in Focus). p. 21.
^ Walker, Hugh Dyson (2012). East Asia: A New History. AuthorHouse. p. 119.
^ ab Amy Chua; Jed Rubenfeld (2014). The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America. Penguin Press HC. p. 121. ISBN 978-1594205460.
^ abc Kang, David C. (2012). East Asia Before the West: Five Centuries of Trade and Tribute. Columbia University Press. pp. 33–34. ISBN 978-0231153195.
^ Goucher, Candice; Walton, Linda (2012). World History: Journeys from Past to Present. Routledge (published September 11, 2012). p. 232. ISBN 978-0415670029.
^ Norman, Jerry (1988). Chinese. Cambridge University Press. p. 17. ISBN 978-0521296533.
^ Chua, Amy (2009). Day of Empire: How Hyperpowers Rise to Global Dominance--and Why They Fall. Anchor. p. 62. ISBN 978-1400077410.
^ Tsai, Henry (2009-02-15). Maritime Taiwan: Historical Encounters with the East and the West. Routledge. p. 3. ISBN 978-0765623287.
^ Fagan, Brian M. (1999). The Oxford Companion to Archaeology. Oxford University Press. p. 362. ISBN 978-0195076189.
^ Brown, John (2006). China, Japan, Korea: Culture and Customs. Createspace Independent. p. 33. ISBN 978-1419648939.
^ Lone, Stewart (2007). Daily Lives of Civilians in Wartime Asia: From the Taiping Rebellion to the Vietnam War. Greenwood. p. 3. ISBN 978-0313336843.
^ ab Warren I. Cohen. East Asia at the Center : Four Thousand Years of Engagement with the World. (New York: Columbia University Press, 2000.
ISBN 0231101082
^ ab Tindall, George Brown; Shi, David E. (2009). America: A Narrative History (1st ed.). W. W. Norton & Company (published November 16, 2009). p. 926. ISBN 978-0393934083.
^ ab April, K.; Shockley, M. (2007). Diversity: New Realities in a Changing World. Palgrave Macmillan (published February 6, 2007). p. 163. ISBN 978-0230001336.
^ abc Batty, David (2005-01-17). Japan's War in Colour (documentary). TWI.CS1 maint: Date and year (link)
^ "The Japanese Economy". Walk Japan.
^ Tindall, George Brown; Shi, David E. (2009). America: A Narrative History (1st ed.). W. W. Norton & Company (published November 16, 2009). p. 1147. ISBN 978-0393934083.
^ Northrup, Cynthia Clark; Bentley, Jerry H.; Eckes Jr., Alfred E. (2004). Encyclopedia of World Trade: From Ancient Times to the Present. Routledge. p. 297. ISBN 978-0765680587.
^ Gilbet Rozman (2004), Northeast asia's stunted regionalism: bilateral distrust in the shadow of globalization. Cambridge University Press, pp. 3-4.
^ "Northeast Asia dominates patent filing growth." Retrieved on August 8, 2001.
^ "Paper: Economic Integration in Northeast Asia." Retrieved on August 8, 2011.
^ Spinosa, Ludovico (2007). Wastewater Sludge. Iwa Publishing. p. 57. ISBN 978-1843391425.
^ Kim, Johnny S. (2013). Solution-Focused Brief Therapy: A Multicultural Approach. Sage Publications. p. 55. ISBN 978-1452256672.
^ Ikeo, Aiko (1996). Economic Development in Twentieth-Century East Asia: The International Context. Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 978-0415149006.
^ ab Yoshimatsu, H. (2014). Comparing Institution-Building in East Asia: Power Politics, Governance, and Critical Junctures. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 1. ISBN 978-1137370549.
^ Kim, Mikyoung (2015). Routledge Handbook of Memory and Reconciliation in East Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-0415835138.
^ abc Hazen, Dan; Spohrer, James H. (2005). Building Area Studies Collections. Otto Harrassowitz (published 2005-12-31). p. 1. ISBN 978-3447055123.
^ Grabowski, Richard; Self, Sharmistha; Shields, William (2012). Economic Development: A Regional, Institutional, and Historical Approach (2nd ed.). Routledge (published September 25, 2012). p. 59. ISBN 978-0765633538.
^ Ng, Arden. "East Asia is the World's Largest Economy at $29.6 Trillion USD, Including 4 of the Top 25 Countries Globally". Blueback.
^ Currie, Lorenzo (2013). Through the Eyes of the Pack. Xlibris Corp. p. 163. ISBN 978-1493145171.
^ Asato, Noriko (2013). Handbook for Asian Studies Specialists: A Guide to Research Materials and Collection Building Tools. Libraries Unlimited. p. 1. ISBN 978-1598848427.
^ ab Miller, David Y. (2007). Modern East Asia: An Introductory History. Routledge. p. xi. ISBN 978-0765618221.
^ Aminian, Nathalie; Fung, K.C.; Ng, Francis. "Integration of Markets vs. Integration by Agreements" (PDF). Policy Research Working Paper. World Bank.
^ ab "Northeast Asia." Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved on August 10, 2009.
^ Economic Research Institute for Northeast Asia (1999). Japan and Russia in Northeast Asia: Partners in the 21st Century. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 248.
^ ab "United Nations Statistics Division – Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)". United Nations Statistics Division. 2015-05-06. Retrieved 2010-07-24.
^ "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings". United Nations Statistics Division. 11 February 2013. Retrieved 28 May 2013.
^ R. Keith Schopper's East Asia: Identities and Change in the Modern World
^ Joshua A. Fogel (UC Santa Barbara/University of Indiana) Nationalism, the Rise of the Vernacular, and the Conceptualization of Modernization in East Asian Comparative Perspective
^ United Nations Environment Programme (mentions sinosphere countries) Approaches to Solution of Eutrophication [1]
^ Christopher M. Dent (2008). East Asian regionalism. London: Routledge. pp. 1–8.
^ Charles Harvie, Fukunari Kimura, and Hyun-Hoon Lee (2005), New East Asian regionalism. Cheltenham and Northamton: Edward Elgar, pp. 3–6.
^ Peter J. Katzenstein and Takashi Shiraishi (2006), Beyond Japan: the dynamics of East Asian regionalism. Ithaca: Cornell University Press, pp. 1–33
^ abcd "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2018". IMF.
^ Listed as "Hong Kong SAR" by IMF
^ Listed as "Macao SAR" by IMF
^ "Country codes". iso.org.
^ From 1949 to 1971, the ROC was referred as "China" or "Nationalist China".
^ "Country codes". iso.org.
^ "World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision". ESA.UN.org (custom data acquired via website). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
^ "Human Development Reports". www.hdr.undp.org. Retrieved 2018-10-14.
^ Seoul was the de jure capital of the DPRK from 1948 to 1972.
^ Taipei is the ROC's seat of government by regulation. Constitutionally, there is no official capital appointed for the ROC.
^ CIA Factbook: "Han Chinese 91.6%" out of a reported population of 1,379 billion (July 2017 est.)
^ 人口推計 – 平成 28年 12月 報(PDF).
^ "新疆维吾尔自治区统计局". www.xjtj.gov.cn.
^ Gordon, Raymond G. Jr., ed. (2005). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (15th ed.). Dallas: SIL International. ISBN 1-55671-159-X. OCLC 224749653.
^ Lim, SK. Asia Civilizations: Ancient to 1800 AD. ASIAPAC. p. 56. ISBN 978-9812295941.
^ ab Goscha, Christopher (2016). The Penguin History of Modern Vietnam: A History. Allen Lane. ISBN 978-1846143106.
^ Amy Chua; Jed Rubenfeld (2014). The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America. Penguin Press HC. p. 122. ISBN 978-1594205460.
^ ab Walker, Hugh Dyson (2012). East Asia: A New History. AuthorHouse. p. 2.
^ Lewis, Mark Edward (2012). China's Cosmopolitan Empire: The Tang Dynasty. Belknap Press (published April 9, 2012). p. 156. ISBN 978-0674064010.
^ ab Edwin O. Reischauer, "The Sinic World in Perspective," Foreign Affairs 52.2 (January 1974): 341—348. JSTOR
^ Lim, SK. Asia Civilizations: Ancient to 1800 AD. ASIAPAC. p. 89. ISBN 978-9812295941.
^ Richter, Frank-Jurgen (2002). Redesigning Asian Business: In the Aftermath of Crisis. Quorum Books. p. 15. ISBN 978-1567205251.
^ Vohra 1999, p. 22
^ abc Amy Chua; Jed Rubenfeld (2014). The Triple Package: How Three Unlikely Traits Explain the Rise and Fall of Cultural Groups in America. Penguin Press HC. pp. 121–122. ISBN 978-1594205460.
^ Wenzel-Teuber, Katharina (2012). "People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011" (PDF). Religions & Christianity in Today's China. II (3). pp. 29–54. ISSN 2192-9289. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 April 2017.
^ ab Wenzel-Teuber, Katharina (2017). "Statistics on Religions and Churches in the People's Republic of China – Update for the Year 2016" (PDF). Religions & Christianity in Today's China. VII (2). pp. 26–53. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2017.
^ Shirley Kan (December 2009). Taiwan: Major U.S. Arms Sales Since 1990. DIANE Publishing. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-4379-2041-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to East Asia. |
| Look up east asia in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
 East Asia travel guide from Wikivoyage
East Asia travel guide from Wikivoyage- High resolution map of East Asian region













