Sound (geography)

The Aldersund in Helgeland, Norway separates the island of Aldra (left side) from the continent
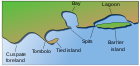
In geography, a sound is a large sea or ocean inlet, deeper than a bight and wider than a fjord; or a narrow sea or ocean channel between two bodies of land (see also strait).[1][2]
There is little consistency in the use of "sound" in English-language place names.
Contents
1 Overview
2 Etymology
3 Bodies of water called sounds
3.1 Australia
3.2 Bahamas
3.3 Bermuda
3.4 British Virgin Islands
3.5 Canada
3.6 Cayman Islands
3.7 Chile
3.8 Falkland Islands
3.9 France
3.10 Ireland
3.11 Mexico
3.12 New Zealand
3.13 Philippines
3.14 Scandinavia
3.15 Solomon Islands
3.16 United Kingdom
3.17 United States
3.17.1 United States Virgin Islands
4 References
5 External links
Overview

View over the Øresund (English: The Sound), from Helsingborg, Sweden
A sound is often formed by the seas flooding a river valley. This produces a long inlet where the sloping valley hillsides descend to sea-level and continue beneath the water to form a sloping sea floor. The Marlborough Sounds in New Zealand are a good example of this type of formation.
Sometimes a sound is produced by a glacier carving out a valley on a coast then receding, or the sea invading a glacier valley. The glacier produces a sound that often has steep, near vertical sides that extend deep under water. The sea floor is often flat and deeper at the landward end than the seaward end, due to glacial moraine deposits. This type of sound is more properly termed a fjord (or fiord). The sounds in Fiordland, New Zealand, have been formed this way.
A sound generally connotes a protected anchorage. They can be part of most large islands.
In the more general northern European usage, a sound is a strait or the most narrow part of a strait. In Scandinavia and around the Baltic Sea, there are more than a hundred straits named Sund, mostly named for the island they separate from the continent or a larger island.
In contrast, the Sound is the internationally recognized,[3] short name for the Øresund, the narrow stretch of water that separates Denmark and Sweden, and is the main waterway between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea. It is also a colloquial short name, among others, for Plymouth Sound, England.
In areas explored by the British in the late 18th Century, particularly the northwest coast of North America, the term "sound" was applied to inlets containing large islands, such as Howe Sound in Vancouver and Puget Sound in Washington State. It was also applied to bodies of open water not fully open to the ocean, such as Caamaño Sound or Queen Charlotte Sound in Canada, or broadenings or mergings at the openings of inlets, like Cross Sound in Alaska and Fitz Hugh Sound in British Columbia.
In the United States, Long Island Sound separates Long Island from the eastern shores of the Bronx, Westchester County, and southern Connecticut, but on the Atlantic Ocean side of Long Island, the body of water between Long Island and its barrier beaches is termed the Great South Bay. Pamlico Sound is a similar lagoon that lies between North Carolina and its barrier beaches, the Outer Banks, in a similar situation. The Mississippi Sound separates the Gulf of Mexico from the mainland, along much of the gulf coasts of Alabama and Mississippi. On the West Coast, Puget Sound, by contrast, is a deep arm of the ocean.
Etymology
The term sound is derived from the Anglo-Saxon or Old Norse word sund, which also means "swimming".[2]
The word sund is already documented in Old Norse and Old English as meaning "gap" (or "narrow access"). This suggests a relation to verbs meaning "to separate", such as absondern and aussondern (German), söndra (Swedish), sondre (Norwegian), as well as the English noun sin, German Sünde ("apart from God's law"), and Swedish synd. English has also the adjective "asunder" and the noun "sundry', and Swedish has the adjective sönder ("broken").
In Swedish and in both Norwegian languages, "sund" is the general term for any strait. In Swedish and Nynorsk, it is even part of names worldwide, such as in Swedish "Berings sund" and "Gibraltar sund", and in Nynorsk "Beringsundet" and "Gibraltarsundet".
Bodies of water called sounds
Australia
Broad Sound near Clairview, Queensland
Camden Sound at Kuri Bay, Western Australia
Cockburn Sound, Western Australia
- Denham Sound, part of Shark Bay in Western Australia
King George Sound at Albany, Western Australia
King Sound at Derby, Western Australia
- Montague Sound, near Bigge Island, Western Australia
- Noosa Sound, Noosa, Queensland
York Sound, Western Australia
Bahamas
Exuma Sound, bordered by Eleuthera, Cat Island and Great Exuma, among others- Millars Sound, New Providence[4]
- North Sound, Bimini
Rock Sound, Eleuthera
Bermuda
Great Sound, towards the island's northwest end
Harrington Sound, towards the northeast end
Little Sound, part of Great Sound
British Virgin Islands
- North Sound, Virgin Gorda
- South Sound, Virgin Gorda
Canada
Amet Sound on the northern coast of Nova Scotia on the Northumberland Strait
Barkley Sound on the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia
Baynes Sound between Denman Island and Vancouver Island, British Columbia
Chatham Sound, off the North Coast of British Columbia
Clayoquot Sound in Vancouver Island, British Columbia
Cumberland Sound in Baffin Island's east coast
Desolation Sound between the Discovery Islands and the coast of British Columbia
Eclipse Sound between Baffin Island and Bylot Island in Nunavut
Eureka Sound between Ellesmere Island and Axel Heiberg Island in Nunavut
Fitz Hugh Sound on the Central Coast of British Columbia
- Hamilton Sound between Fogo Island and the Island of Newfoundland
Howe Sound, an inlet northwest of Vancouver, British Columbia
Jones Sound between Devon Island and Ellesmere Island in Nunavut
Kyuquot Sound on the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia
Lancaster Sound between Devon Island and Baffin Island in Nunavut
Massey Sound between Amund Ringnes Island and Axel Heiberg Island in Nunavut
Nansen Sound between Ellesmere Island and Axel Heiberg Island in Nunavut
- Newman Sound in Terra Nova National Park, Newfoundland and Labrador
Nootka Sound on the west coast of Vancouver Island, British Columbia
- Northumberland Sound between Maclean Strait and Norwegian Bay, Nunavut
Owen Sound in Ontario
Parry Sound in Ontario
Peel Sound between Prince of Wales Island and Somerset Island in Nunavut
Quatsino Sound on northern Vancouver Island
Queen Charlotte Sound off British Columbia
- Random Sound near Clarenville in Newfoundland and Labrador
Roes Welcome Sound between Southampton Island and Hudson Bay's west shore in Nunavut
- Severn Sound in Ontario
Viscount Melville Sound between Banks Island and Melville Island in Nunavut
Cayman Islands
- Frank Sound on Grand Cayman
- Little Sound on Grand Cayman
- North Sound on Grand Cayman
- South Hole Sound on Little Cayman
- South Sound on Grand Cayman
Chile
- Almirantazgo Sound
- Darwin Sound
- Otway Sound
- Reloncaví Sound
- Skyring Sound
- Última Esperanza Sound
Falkland Islands
Adventure Sound in East Falkland
Berkeley Sound in East Falkland
Byron Sound in West Falkland
Choiseul Sound in East Falkland
Falkland Sound between East Falkland and West Falkland
France
- The Sound of Chausey.
Ireland
- Achill Sound, that separates Achill Island from the mainland
Mexico
Campeche Sound in Campeche
New Zealand
"The Marlborough Sounds" is a local term for a complex of bays and inlets on the northern tip of South Island, which comprises three main sounds:
- Kenepuru Sound
- Pelorus Sound
- Queen Charlotte Sound
Much further south, there are many sounds in the southwestern tip of South Island which make up the coast of Fiordland National Park. From north to south they are:
- Milford Sound
- Sutherland Sound
- Bligh Sound
- George Sound
- Caswell Sound
- Charles Sound
- Nancy Sound
- Thompson Sound
- Doubtful Sound
- Dagg Sound
- Breaksea Sound
- Dusky Sound
Edwardson Sound (an arm of Chalky Inlet)
Cunaris Sound (an arm of Chalky Inlet)
Isthmus Sound (an arm of Preservation Inlet)
Long Sound (an extension of Preservation Inlet)
Philippines
Dinagat Sound, separates the islands of Dinagat and Siargao
Malampaya Sound, in the Province of Palawan. The Malampaya Natural Gas Project is named after this area because it is close to it.
- The Sound, another name in English for Øresund, a body of water between Sweden and Denmark
- On the coasts of (western) Baltic Sea and Norway there are more than a hundred straits named "Sund" (the Scandinavian and German version of "sound"), mostly in connection with the name of the island they divide from the continent or a mainland.
Solomon Islands
- New Georgia Sound
United Kingdom
Calf Sound between Isle of Man and the Calf of Man
Heigham Sound, connected by Candle Dyke to the River Thurne, Norfolk[5]
Plymouth Sound in Plymouth, Devon
- Sounds of Scotland
United States

A live oak on Knotts Island, North Carolina, overlooks the Currituck Sound.
Albemarle Sound in North Carolina
Anna Maria Sound in Florida
Back Sound in North Carolina
Block Island Sound between Block Island and mainland Rhode Island
Bogue Sound in North Carolina
Breton Sound in Louisiana
Broad Sound near Boston
Calibogue Sound in South Carolina
Chandeleur Sound in Louisiana
Core Sound in North Carolina
Croatan Sound in North Carolina
Cross Sound in Alaska
Currituck Sound in North Carolina
Frederick Sound in Alaska
Fishers Island Sound between Fishers Island, New York and Connecticut
Hobe Sound in Florida
Kotzebue Sound in Alaska
Long Island Sound between Long Island, New York and Connecticut
Mississippi Sound in Mississippi and Alabama
Nantucket Sound off Nantucket, Massachusetts
Norton Sound in Alaska
Ossabaw Sound near Savannah, Georgia
Pamlico Sound in North Carolina
Pine Island Sound near Cape Coral, Florida
Plum Island Sound in Plum Island, Massachusetts
Port Royal Sound in South Carolina
Prince William Sound in Alaska
Puget Sound in Washington
Rhode Island Sound off Rhode Island
Roanoke Sound in North Carolina
St. Catherine's Sound in Liberty County, Georgia
Saint Helena Sound near Beaufort, South Carolina
Salem Sound near Salem, Massachusetts
St. George Sound in Appalachicola Bay, Florida
St. Simons Sound in Glynn County, Georgia
Salisbury Sound in Alaska
Santa Rosa Sound in the Florida Panhandle
Sitka Sound in Alaska
Somes Sound in Mount Desert Island, Maine (arguably a fjard)
Tangier Sound in Maryland & Virginia on Chesapeake Bay
Vineyard Sound off Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts
Wassaw Sound near Savannah, Georgia
United States Virgin Islands
- Pillsbury Sound between Saint Thomas and Saint John
References
^ "sound-3". TheFreeDictionary.com. Retrieved 3 March 2013..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab "sound-4". Oxford English Dictionary. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
^ "Baltic Straits". Chapter 2.3: International straits and canals. UNESCO Maritime Law. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
^ "Millars Sound". GeoNames. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
^ "River Thurne: West Somerton to Candle Dyke including Horsey Mere and Hickling Broad". Peter's Norfolk and Suffolk Broads Cruising Guide. Archived from the original on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
External links
![]() Media related to Sounds (geography) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sounds (geography) at Wikimedia Commons