Temporal muscle
| Temporalis | |
|---|---|
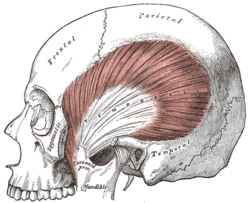 The temporalis; the zygomatic arch and masseter have been removed. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Temporal lines on the parietal bone of the skull and the superior temporal surface of the sphenoid bone |
| Insertion | Coronoid process of the mandible |
| Artery | Deep temporal arteries |
| Nerve | Deep temporal nerves, branch(es) of the anterior division of the mandibular nerve (V3) |
| Actions | Elevation and retraction of mandible |
| Antagonist | Platysma muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus temporalis |
| MeSH | D013703 |
| TA | A04.1.04.005 |
| FMA | 49006 |
Anatomical terms of muscle [edit on Wikidata] | |
The temporal muscle, also known as the temporalis, is one of the muscles of mastication. It is a broad, fan-shaped muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.[1]
Contents
1 Structure
1.1 Development
1.2 Innervation
1.3 Blood supply
2 Function
3 Pathology
4 Additional images
5 References
6 External links
Structure
In humans, it arises from the temporal fossa and the deep part of temporal fascia. It passes medial to the zygomatic arch and forms a tendon which inserts onto the coronoid process of the mandible, with its insertion extending into the retromolar fossa posterior to the most distal mandibular molar.[2] In other mammals, the muscle usually spans the dorsal part of the skull all the way up to the medial line. There, it may be attached to a sagittal crest, as can be seen in early hominins like Paranthropus aethiopicus.
The temporal muscle is covered by the temporal fascia, also known as the temporal aponeurosis. This fascia is commonly used in tympanoplasty, or surgical reconstruction of the eardrum.
The muscle is accessible on the temples, and can be seen and felt contracting while the jaw is clenching and unclenching.
Development
The temporalis is derived from the first pharyngeal arch in development.
Innervation
As with the other muscles of mastication, control of the temporal muscle comes from the third (mandibular) branch of the trigeminal nerve. Specifically, the muscle is innervated by the deep temporal nerves.
Blood supply
The muscle receives its blood supply from the deep temporal arteries which anastomose with the middle temporal artery.
Function
The temporal muscle is the most powerful muscle of the temporomandibular joint. The temporal muscle can be divided into two functional parts; anterior and posterior. The anterior portion runs vertically and its contraction results in elevation of the mandible (closing the mouth). The posterior portion has fibers which run horizontally and contraction of this portion results in retrusion of the mandible.[3]
When lower dentures are fitted, they should not extend into the retromolar fossa to prevent trauma of the mucosa due to the contraction of the temporalis muscle.[2]
Pathology
The temporalis is likely to be involved in jaw pain and headaches. Bruxism, the habitual grinding of teeth typically while sleeping, and clenching of the jaw while stressed can lead to overwork of the temporalis and results in pain. A myotendinous rupture of the temporalis can occur during a seizure due to extreme clenching of the jaw. During a seizure the contralateral temporalis muscle can enter spastic paralysis, this clenching in extreme cases can lead to a rupture specifically on the myotendinous insertion at the coronoid process of the mandible.[4]
Additional images

Temporal muscle (red).

Muscles of head and neck
Temporal muscle.Deep dissection.Mummification process.
References
^ Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 98
^ ab Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 194
^ Scheid, R. C., Woelfel, J. B., & Woelfel, J. B. (2007). Woelfel's dental anatomy: Its relevance to dentistry. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pg 41.
^ Naffa, Lena; Yasmeen, Tandon; Rubin, Michael (2014). "Myotendinous rupture of temporalis muscle: A rare injury following seizure". World Journal of Radiology. 6 (6): 388–391. doi:10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.388. PMC 4072824. PMID 24976940..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Temporal muscles. |
Anatomy photo:27:04-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Infratemporal Fossa: The Temporalis Muscle"- The anatomical basis for surgical preservation of temporal muscle, Kadri, et al., J Neurosurg 2004, 100:517–522 at http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/documents/singerlab/files/Kadri%20et%20al.pdf
- Temporalis Muscle Transfer, The Methodist Hospital System, Houston, TX, at http://www.methodistfacialparalysis.com/temporalis/



