Hampton, Virginia
Hampton, Virginia | |
|---|---|
Independent city | |
| City of Hampton | |
 Newport News, Hampton, Portsmouth and Norfolk, Virginia. Hampton is top right | |
| Motto(s): From the Sea to the Stars | |
 Location in the State of Virginia | |
 Hampton, Virginia Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 37°2′5″N 76°21′36″W / 37.03472°N 76.36000°W / 37.03472; -76.36000 | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | None (Independent city) |
| Settled | 1610[2] |
| Incorporated (town) | 1705[2] |
| Incorporated (city) | 1849[2] |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Donnie Tuck (D) [1] |
| • Vice Mayor | Linda Curtis (R)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Independent city | 350 km2 (136 sq mi) |
| • Land | 130 km2 (51 sq mi) |
| • Water | 220 km2 (85 sq mi) 62.3% |
| Elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Independent city | 137,436 (US: 194th) |
| • Density | 1,032/km2 (2,674/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,674,498 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Area code(s) | 757 |
| FIPS code | 51-35000[3] |
GNIS feature ID | 1495650[4] |
| Website | http://www.hampton.gov |

British invade Hampton during the War of 1812[5]

On September 17, 1861, Mrs. Mary Smith Peake taught the first classes to African American children on the grounds of what is now Hampton University at Hampton Roads in Virginia under the shade of the Emancipation Oak.
Hampton is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 137,436.[6]
As one of the seven major cities that compose the Hampton Roads metropolitan area, it is on the southeastern end of the Virginia Peninsula.
Hampton traces its history to the city's Old Point Comfort, the home of Fort Monroe for almost 400 years, which was named by the 1607 voyagers, led by Captain Christopher Newport, who first established Jamestown as an English colonial settlement. Since consolidation in 1952, Hampton has included the former Elizabeth City County and the incorporated town of Phoebus, consolidating by mutual agreement.
After the end of the American Civil War, historic Hampton University was established opposite from the town on the Hampton River, providing an education for many newly-freed former slaves and for area Native Americans. In the 20th century, the area became the location of Langley Air Force Base, NASA Langley Research Center, and the Virginia Air and Space Center. Hampton features many miles of waterfront and beaches.
For residents and visitors alike, the city features a wide array of business and industrial enterprises, retail and residential areas, and historical sites. Most recently, the new Peninsula Town Center development opened in May 2010 on the site of the former Coliseum Mall. Located in the area adjacent to the Hampton Coliseum and the Convention Center, the new urbanism-type project features a wide mix of retail stores, housing and other attractions.[7] Development of new residential development and additional public facilities (such as the new fishing pier recently opened) are underway at Buckroe Beach, long a noted resort area.[8]
Located on the Hampton Roads Beltway, it hosts the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel (HRBT) on Interstate 64. First opened in 1957, it was the world's first bridge-tunnel, crossing the mouth of the Hampton Roads harbor, which serves as the gateway to the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean from the eastern United States' largest ice-free harbor and its tributary rivers. Expanded in the 1970s, the HRBT remains Virginia's busiest and deepest such facility.
Contents
1 History
1.1 Fort Monroe
1.2 Modern military history
1.2.1 Langley AFB during the Vietnam War
2 Geography
2.1 Adjacent counties and cities
2.2 Climate
3 Demographics
4 Media
5 Culture
5.1 Sports
6 Colleges and universities
7 Major neighborhoods
8 Points of interest
9 Transportation
9.1 Roads and Highways
9.2 Local and regional public transportation
9.3 Intercity bus service
9.4 Amtrak
9.5 Air
10 Politics
11 Notable people
12 Sister cities
13 See also
14 Notes
15 References
16 Bibliography
17 External links
History
In December 1606, three ships carrying men and boys left England on a mission sponsored by a proprietary company. Headed by Captain Christopher Newport, they sailed across the Atlantic Ocean to North America. After a long voyage, they first landed at the entrance to the Chesapeake Bay on the south shore at a place they named Cape Henry (for Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, the elder son of their king).
During the first few days of exploration, they identified the site of Old Point Comfort (which they originally named "Point Comfort") as a strategic defensive location at the entrance to the body of water that became known as Hampton Roads. This is formed by the confluence of the Elizabeth, Nansemond, and James rivers. The latter is the longest river in Virginia.
Weeks later, on May 14, 1607, they established the first permanent English settlement in the present-day United States about 25 miles (40 km) further inland from the Bay which became the site of fortifications during the following 200 years.
Slightly south, near the entrance to Hampton River, the colonists seized the Native American community of Kecoughtan under Virginia's Governor, Sir Thomas Gates. The colonists established their own small town, with a small Anglican church (known now as St. John's Episcopal Church), on July 9, 1610. This came to be known as part of Hampton. (With Jamestown having been abandoned in 1699, Hampton claims to be the oldest continuously occupied English settlement in the United States).[9] Hampton was named for Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton, an important leader of the Virginia Company of London, for whom the Hampton River, Hampton Roads and Southampton County were also named. The area became part of Elizabeth Cittie [sic] in 1619, Elizabeth River Shire in 1634, and was included in Elizabeth City County when it was formed in 1643. By 1680, the settlement was known as Hampton, and it was incorporated as a town in 1705 and became the seat of Elizabeth City County.
In the latter part of August 1619, an English ship flying a Dutch flag, the White Lion, appeared off shore from Point Comfort. Its cargo included 20 plus Africans captured from the slave ship Sao Joao Bautista. These were the first Africans to come ashore on English-occupied land in what would become the United States. John Rolfe, the widower of Pocahontas, wrote in a letter that he was at Point Comfort and witnessed the arrival of the first Africans. Although these first Bantu men from Angola were considered indentured servants, their arrival marked the beginning of slavery in North America. Two of the first Africans to arrive at Old Point Comfort in 1619 were Antoney and Isabella. Their child, the first of African descent born in North America, was born baptized January 1624.
Shortly after the War of 1812, the US Army built a more substantial stone facility at Old Point Comfort. It was called Fort Monroe in honor of President James Monroe. The new installation and adjacent Fort Calhoun (on a man-made island across the channel) were completed in 1834.
Fort Monroe, Hampton and the surrounding area played several important roles during the American Civil War (1861–1865). Although most of Virginia became part of the Confederate States of America, Fort Monroe remained in Union hands. It became notable as a historic and symbolic site of early freedom for former slaves under the provisions of contraband policies and later the Emancipation Proclamation. After the War, former Confederate President, Jefferson Davis was imprisoned in the area now known as the Casemate Museum on the base.
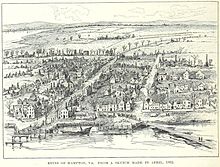
The ruins of Hampton in 1862
To the south of Fort Monroe, the Town of Hampton had the misfortune to be burned during both the American Revolutionary War and the American Civil War. From the ruins of Hampton left by evacuating Confederates in 1861, "Contraband" slaves (formerly owned by Confederates and under a degree of Union protection) built the Grand Contraband Camp, the first self-contained African American community in the United States. A number of modern-day Hampton streets retain their names from that community. The large number of contrabands who sought the refuge of Fort Monroe and the Grand Contraband Camp led to educational efforts which eventually included establishment of Hampton University, site of the famous Emancipation Oak.
The original site of the Native American's Kecoughtan Settlement was near the present site of a Hampton Roads Transit facility.[10] To the south of present-day Hampton, a small unrelated incorporated town also named Kecoughtan many years later and also located in Elizabeth City County was annexed by the city of Newport News in 1927. It is now part of that city's East End.
Hampton was incorporated as a city in 1849.[2] On March 30, 1908, Hampton was separated from Elizabeth City County and became an independent city.[11] However, it remained the county seat and continued to share many services with the county. On July 1, 1952, following approval of voters of each locality by referendum, the city of Hampton, the incorporated town of Phoebus and Elizabeth City County merged into the independent city of Hampton.[11] It was the first of a series of political consolidations in the Hampton Roads region during the third quarter of the 20th century.
Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe is the largest stone fort in the United States. It is now a national park area.[12]
Modern military history
Hampton has a rich and extensive 20th-century military history — home of Langley Air Force Base, the nation's first military installation dedicated solely to airpower and the home of the U.S. Air Force's 633d Air Base Wing and 1st and 192nd Fighter Wings. Hampton has been a center of military aviation training, research and development for nearly a hundred years, from early prop planes and Zeppelins to rocket parts and advanced fighters. Its proximity to Norfolk means that Hampton has long been home to many Navy families. Together, many Air Force and Navy families in the Hampton area experienced significant losses in war and peacetime due to family members in combat and peacetime military accidents.
Langley AFB during the Vietnam War
In particular, during the Vietnam War, Langley Air Force Base was a designated 'waiting base' and thousands of Air Force families were transferred to Hampton from all over the world to wait while their husbands and fathers served in Vietnam. Thousands of Navy families associated with Naval bases in Norfolk next door also waited in Hampton during this era. Vietnam was a very high casualty war for Air Force and Navy pilots (some types of planes experienced a 50% casualty rate), and Naval "river rats" who fought on the rivers of the Mekong Delta experienced high casualties as well. There accumulated over time, in the Hampton area, a high concentration of families of unnaccounted for wartime casualties.[13] In many cases Hampton-stationed military families of "Missing in Action" or "Prisoner of War" pilots and sailors spent many years in the area waiting to find out what had happened to their missing or captured airmen and sailors. The service and, in some cases, sacrifice of these pilots, airmen, sailors and their families, despite not having lifelong connections to the area, are a poignant and inspiring part of Hampton's history.[13][14]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 136 square miles (350 km2), of which 51 square miles (130 km2) is land and 85 square miles (220 km2) (62.3%) is water.[15]
Adjacent counties and cities
York County, Virginia (north)
Poquoson, Virginia (northeast)
Norfolk, Virginia (south)
Newport News, Virginia (south and west)
Portsmouth, Virginia (south)
Northampton County, Virginia - (east)
Climate
Hampton's mild four season climate means outdoor activities can be enjoyed year round. The weather in Hampton is temperate and seasonal. Summers are hot and humid with cool evenings.[citation needed] The mean annual temperature is 70 °F (21 °C), with an average annual snowfall of 6 inches (150 mm) and an average annual rainfall of 47 inches (1,200 mm). No measurable snow fell in 1999. The wettest seasons are the spring and summer, although rainfall is fairly constant all year round. The highest recorded temperature was 105.0 °F (40.6 °C) in 1980. The lowest recorded temperature was −7.0 °F (−21.7 °C) on January 21, 1985.[citation needed]
Additionally, the geographic location of the city, with respect to the principal storm tracks, is especially favorable, as it is south of the average path of storms originating in the higher latitudes, and north of the usual tracks of hurricanes and other major tropical storms, with the exception of Hurricane Isabel in 2003.[16]
| Climate data for Norfolk International Airport, Virginia (1981–2010 normals,[a] extremes 1874–present[b]) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 84 (29) | 82 (28) | 92 (33) | 97 (36) | 100 (38) | 102 (39) | 105 (41) | 105 (41) | 100 (38) | 95 (35) | 86 (30) | 82 (28) | 105 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 71.1 (21.7) | 73.2 (22.9) | 80.2 (26.8) | 86.4 (30.2) | 91.4 (33.0) | 95.5 (35.3) | 97.8 (36.6) | 95.8 (35.4) | 92.1 (33.4) | 85.6 (29.8) | 78.7 (25.9) | 72.5 (22.5) | 98.8 (37.1) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 48.1 (8.9) | 50.9 (10.5) | 58.2 (14.6) | 67.6 (19.8) | 75.4 (24.1) | 83.5 (28.6) | 87.4 (30.8) | 85.1 (29.5) | 79.3 (26.3) | 70.1 (21.2) | 61.1 (16.2) | 52.1 (11.2) | 68.3 (20.2) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 32.7 (0.4) | 34.4 (1.3) | 40.5 (4.7) | 48.9 (9.4) | 57.9 (14.4) | 67.1 (19.5) | 71.9 (22.2) | 70.7 (21.5) | 65.3 (18.5) | 54.0 (12.2) | 44.6 (7.0) | 36.1 (2.3) | 52.1 (11.2) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 17.6 (−8.0) | 21.2 (−6.0) | 27.2 (−2.7) | 35.7 (2.1) | 45.7 (7.6) | 55.5 (13.1) | 63.1 (17.3) | 61.6 (16.4) | 53.7 (12.1) | 39.7 (4.3) | 30.5 (−0.8) | 21.7 (−5.7) | 15.2 (−9.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −3 (−19) | 2 (−17) | 14 (−10) | 23 (−5) | 36 (2) | 45 (7) | 54 (12) | 49 (9) | 40 (4) | 27 (−3) | 17 (−8) | 5 (−15) | −3 (−19) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.40 (86) | 3.12 (79) | 3.68 (93) | 3.41 (87) | 3.41 (87) | 4.26 (108) | 5.14 (131) | 5.52 (140) | 4.76 (121) | 3.42 (87) | 3.15 (80) | 3.26 (83) | 46.53 (1,182) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 2.4 (6.1) | 2.0 (5.1) | 0.2 (0.51) | — | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | — | 1.2 (3.0) | 5.8 (15) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.4 | 9.5 | 10.6 | 10.1 | 10.6 | 9.9 | 11.1 | 10.1 | 8.8 | 7.6 | 8.5 | 9.8 | 117.0 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 4.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66.3 | 65.6 | 64.6 | 62.8 | 68.8 | 70.6 | 73.3 | 75.2 | 74.4 | 72.1 | 68.5 | 67.0 | 69.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 171.5 | 175.2 | 229.3 | 252.8 | 271.7 | 280.1 | 278.3 | 260.4 | 231.4 | 208.3 | 175.7 | 160.4 | 2,695.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 58 | 62 | 64 | 62 | 64 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 60 | 57 | 53 | 61 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[17][18][19] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1850 | 787 | — | |
| 1860 | 1,848 | 134.8% | |
| 1870 | 2,300 | 24.5% | |
| 1880 | 2,684 | 16.7% | |
| 1890 | 2,513 | −6.4% | |
| 1900 | 2,764 | 10.0% | |
| 1910 | 5,505 | 99.2% | |
| 1920 | 6,138 | 11.5% | |
| 1930 | 6,382 | 4.0% | |
| 1940 | 5,898 | −7.6% | |
| 1950 | 5,966 | 1.2% | |
| 1960 | 89,258 | 1,396.1% | |
| 1970 | 120,779 | 35.3% | |
| 1980 | 122,617 | 1.5% | |
| 1990 | 133,811 | 9.1% | |
| 2000 | 146,437 | 9.4% | |
| 2010 | 137,436 | −6.1% | |
| Est. 2016 | 135,410 | [20] | −1.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[21] 1790-1960[22] 1900-1990[23] 1990-2000[24] 2010-2013[6] | |||

Age distribution in Hampton
As of the census[25] of 2010, there were 137,436 people, 53,887 households, and 35,888 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,828.0 people per square mile (1,091.9/km²). There were 57,311 housing units at an average density of 1,106.8 per square mile (427.3/km²). The racial makeup of the city was 49.6% Black or African American, 42.7% White, 2.2% Asian, 0.4% Native American, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 1.3% from other races, and 3.7% from two or more races. 4.5% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 53,887 households out of which 32.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 46.2% were married couples living together, 16.4% had a female householder with no husband present, and 33.4% were non-families. 26.6% of all households were made up of individuals and 7.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.49 and the average family size was 3.02.
The age distribution is 24.2% under the age of 18, 12.6% from 18 to 24, 32.5% from 25 to 44, 20.4% from 45 to 64, and 10.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.6 males.
Population update: estimated population in July 2002: 145,921 (-0.4% change)
Males: 72,579 (49.6%), Females: 73,858 (50.4%)
Source
The Census estimate for 2005 shows that the city's population was down slightly to more, 145,579.[26]
The median income for a household in the city was $39,532, and the median income for a family was $46,110. Males had a median income of $31,666 versus $24,578 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,774. About 8.8% of families and 11.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.9% of those under age 18 and 8.6% of those age 65 or over.
Media
Hampton's daily newspaper is the Newport News-based Daily Press. Other papers include Norfolk's The Virginian-Pilot, Port Folio Weekly, the New Journal and Guide, and the Hampton Roads Business Journal.[27]Hampton Roads Magazine serves as a bi-monthly regional magazine for Hampton and the Hampton Roads area.[28]Hampton Roads Times serves as an online magazine for all the Hampton Roads cities and counties. Hampton is served by a variety of radio stations on the AM and FM dials, with towers located around the Hampton Roads area.[29]
Hampton is also served by several television stations. The Hampton Roads designated market area (DMA) is the 42nd largest in the U.S. with 712,790 homes (0.64% of the total U.S.).[30] The major network television affiliates are WTKR-TV 3 (CBS), WAVY 10 (NBC), WVEC-TV 13 (ABC), WGNT 27 (CW), WTVZ 33 (MyNetworkTV), WVBT 43 (Fox), and WPXV 49 (ION Television). The Public Broadcasting Service station is WHRO-TV 15. Hampton residents also can receive independent stations, such as WSKY broadcasting on channel 4 from the Outer Banks of North Carolina and WGBS-LD broadcasting on channel 11. Hampton is served by Verizon FiOS and Cox Cable.
Culture
Sports
Hampton is home to the Peninsula Pilots of the Coastal Plain League, a collegiate summer baseball league. The Pilots play at War Memorial Stadium in Hampton. The team began playing in Hampton in the 1980s.
Colleges and universities

Ogden Hall at Hampton University
- Hampton University
- Thomas Nelson Community College
Bryant and Stratton College has a branch campus at the Peninsula Town Center.
Public universities that are outside but near Hampton include Christopher Newport University, Old Dominion University, Norfolk State University, and The College of William and Mary.[31][32][33][34][35][36]
Major neighborhoods

The old "lighthouse" at Buckroe Beach was built as a part of the amusement park.
- Aberdeen Gardens
- Buckroe Beach
- Farmington
- Fox Hill
- Hampton Woods
- Northampton
- Newmarket
- Phoebus
- Victoria Boulevard Historic District
- Wythe
Points of interest

F-89J s/n 52-2129 on display at the Air Power Park and Museum in Hampton, Virginia.

The Virginia Air and Space Center, the official visitors center for both Langley Air Force Base and NASA Langley Research Center.

St. John's Church is the oldest English-speaking church in continuous existence in the United States and the only colonial structure in downtown Hampton.[9]
- Air Power Park
- Bluebird Gap Farm
- Buckroe Beach
- Downtown Hampton Historic District
- Emancipation Oak
Fort Monroe
- Chapel of the Centurion
- Fort Wool
- Hampton Coliseum
- Hampton National Cemetery
- Langley Air Force Base
- Langley Speedway
NASA–Langley Research Center
- National Institute of Aerospace
- Old Point Comfort
- Peninsula Town Center
- Strawberry Banks
- St. John's Church
- Veterans Affairs Medical Center
- Virginia Air and Space Center
- War Memorial Stadium
Transportation
Roads and Highways
In the Hampton Roads region, water crossings are a major issue for land-based transportation. The city is fortunate to have a good network of local streets and bridges to cross the various rivers and creeks. Many smaller bridges, especially those along Mercury Boulevard, were named to honor the original NASA astronauts, who had trained extensively at NASA's Langley facilities.
The city is located contiguously to the neighboring independent cities of both Newport News and Poquoson. Many roads and streets are available to travel between them. Likewise, Williamsburg, Yorktown and the counties of James City and York are also located nearby in the Peninsula subregion, and many roads lead to them.
To reach most of its other neighbors in the South Hampton Roads subregion, it is necessary to cross the harbor and/or the mouth of the James River. There are 3 major motor vehicle crossings. Among these are the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel (HRBT) and the Monitor-Merrimac Memorial Bridge-Tunnel (MMMBT), each forming part of the Hampton Roads Beltway. The HRBT is located on Interstate 64 near downtown Hampton and the MMMBT is a few miles away on Interstate 664 near downtown Newport News. (These two major interstates converge in Hampton near the Hampton Coliseum). The third crossing option is the James River Bridge, also in Newport News, which connects to Isle of Wight County and the town of Smithfield.
Hampton is also served by several major primary and secondary highways. These notably include U.S. Routes 17, 60 and 258, and Virginia State Routes 134 and 143.
Local and regional public transportation
The Hampton Transit Center, located 2 West Pembroke Boulevard, at the intersection of King Street, close to the downtown area, offers a hub for local and intercity public transportation. It hosts HRT buses, Greyhound/Trailways services and taxicabs.
Hampton Roads Transit (HRT) is the local provider of transit service within the city, as well offering a regional bus system with routes to and from seven other cities in Hampton Roads.[37]
Intercity bus service
Intercity bus service is provided by Greyhound Lines and its Carolina Trailways affiliate. The buses serve the Hampton Transit Center. Low cost curbside intercity bus service is also provided by Megabus, with service to Richmond, Washington, D.C., Baltimore, and Philadelphia.
Amtrak
Hampton is served by several Amtrak trains a day, with direct service from a station in nearby Newport News (on Warwick Boulevard just west of Mercury Boulevard) through Williamsburg and Richmond to points along the Northeast Corridor from Washington DC through Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York City all the way to Boston. At Richmond, connections can be made for other Amtrak destinations nationwide.
Air
Hampton is served by two commercial airports. Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport (IATA: PHF) is in Newport News, and Norfolk International Airport (IATA: ORF, ICAO: KORF, FAA LID: ORF) is across the harbor in Norfolk. Both are along portions of Interstate 64.
The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport in Newport News. Originally known as Patrick Henry Field (hence its airline code letters "PHF"), it was built on the site of Camp Patrick Henry, formerly a World War II facility. It is one of the fastest growing airports in the country, and it reported having served 1,058,839 passengers in 2005. The airport recently added a fourth airline carrier, Frontier Airlines, becoming the first new airline to come to the region in over eight years, despite the economic recession conditions. 2010 was to be the busiest year by passenger count in the airport's history.[38]
The larger Norfolk International Airport (often known locally by its code letters "ORF") also serves the region. The airport is near the Chesapeake Bay, along the city limits between Norfolk and Virginia Beach.[39] Seven airlines provide nonstop services to 25 destinations. During 2006, ORF had 3,703,664 passengers take off or land at its facility and 68,778,934 pounds of cargo were processed through its facilities.[40]
The Chesapeake Regional Airport provides general aviation services. It is in South Hampton Roads in the independent city of Chesapeake.[41]
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
2016 | 28.8% 17,902 | 66.3% 41,312 | 4.9% 3,063 |
2012 | 28.0% 18,640 | 70.6% 46,966 | 1.3% 884 |
2008 | 30.1% 20,476 | 69.1% 46,917 | 0.8% 550 |
2004 | 42.0% 23,399 | 57.4% 32,016 | 0.6% 326 |
2000 | 40.9% 19,561 | 57.4% 27,490 | 1.8% 836 |
1996 | 37.3% 16,596 | 55.0% 24,493 | 7.7% 3,418 |
1992 | 38.5% 19,219 | 46.9% 23,395 | 14.6% 7,264 |
1988 | 54.9% 24,034 | 43.6% 19,106 | 1.6% 678 |
1984 | 58.0% 25,537 | 41.3% 18,180 | 0.8% 351 |
1980 | 45.1% 17,023 | 49.0% 18,517 | 5.9% 2,225 |
1976 | 41.7% 15,021 | 53.3% 19,202 | 5.1% 1,825 |
1972 | 65.5% 21,897 | 31.9% 10,648 | 2.7% 890 |
1968 | 32.3% 10,532 | 34.7% 11,308 | 33.0% 10,766 |
1964 | 39.2% 8,731 | 60.8% 13,542 | 0.1% 15 |
1960 | 51.5% 7,623 | 48.2% 7,133 | 0.4% 52 |
1956 | 57.2% 7,432 | 39.3% 5,108 | 3.4% 443 |
1952 | 52.5% 5,505 | 47.2% 4,946 | 0.3% 30 |
1948 | 30.0% 371 | 58.9% 727 | 11.1% 137 |
1944 | 23.1% 297 | 76.7% 987 | 0.2% 3 |
1940 | 18.0% 215 | 81.7% 975 | 0.3% 4 |
1936 | 16.4% 190 | 83.6% 971 | 0.1% 1 |
1932 | 27.1% 294 | 71.2% 772 | 1.7% 18 |
1928 | 46.9% 544 | 53.1% 615 | |
1924 | 21.0% 129 | 76.6% 471 | 2.4% 15 |
1920 | 19.8% 152 | 78.4% 601 | 1.8% 14 |
1916 | 13.7% 56 | 85.4% 350 | 1.0% 4 |
1912 | 3.3% 13 | 88.5% 353 | 8.3% 33 |
Notable people
- American history
James Armistead, America's first African American spy, provided the information to the Continental Army that Cornwallis was headed to Yorktown in 1781. This led to the forced surrender of Cornwallis.
Samuel Chapman Armstrong, Union general in American Civil War; founder of Hampton Normal and Agricultural Institute, later Hampton University
James Barron, U.S. Navy commodore, captain of frigate USS Chesapeake.
Jefferson Davis, president of the Confederate States of America, imprisoned in a casemate at Fort Monroe after the American Civil War
Evelyn Grubb, POW wife, author, co-founder and National President of the National League of Families [13][43]
Booker Taliaferro Washington (commonly known as Booker T Washington), founder of Tuskegee Institute, educator, author, African-American statesman
George Robert Watkins, politician, member of Pennsylvania State Senate and United States Congress
George Wythe, classical scholar, first law professor in U.S., mayor of Williamsburg, attorney general of Virginia Colony, Continental Congress member, speaker of the state assembly, a framer of the federal Constitution
- Music
Robert Nathaniel Dett, notable composer, pianist, choir director, educator, administrator at Hampton Institute; a founder of United Service Organization
Steve Earle, popular country-rock musician and songwriter
Jeff Parker, experimental jazz and rock guitarist in the Chicago-based post-rock group Tortoise
Jerry Roush, vocalist known for his time in Sky Eats Airplane, Of Mice and Men, and Glass Cloud
DeVante Swing and Mr. Dalvin, of the R&B group Jodeci
Victor Wooten, bassist for the Grammy Award winning "Blu-Bop" group Béla Fleck and the Flecktones
Weldon Irvine, composer, pianist
DRAM (rapper), rapper, artist
- Science
Roy F. Brissenden, World War II pilot, physicist, aeronautical engineer, mechanical engineer, teacher, inventor, project leader at Hampton, Langley Research Center NACA/NASA
Mary Jackson, engineer and mathematician who contributed to America's aeronautics and space programs
Katherine Johnson, physicist, space scientist, and mathematician who contributed to America's aeronautics and space programs
Christopher C. Kraft, Jr., aeronautical engineer; administrator at Hampton, Langley Research Center NACA / NASA; flight director of the space program
Anne Rudloe, U.S. marine biologist
- Sports
Robert Banks, Linebacker/defensive end; national high school player of the year by the Columbus, Ohio Touchdown Club in 1982
Tajh Boyd, professional football player
Elton Brown, offensive lineman of the Arizona Cardinals
Jim Burrow, defensive back for the Green Bay Packers
Steve Cardenas, Brazilian jiu-jitsu martial artist & actor who starred as Rocky DeSantos; Red Ape Ninja Ranger and Zeo Ranger III Blue.
Jake Cave, outfielder for the Minnesota Twins
Ronald Curry, professional football player for the Oakland Raiders, former Hampton High School star football quarterback
La'Keshia Frett, former WNBA basketball player; led Phoebus High School to state championship in 1992
Shaun Gayle, special teams captain of the 1985 Super Bowl champion Chicago Bears football team, and played with the San Diego Chargers
Marques Hagans, quarterback/wide receiver with the St. Louis Rams
Chris Hanburger, popular Washington Redskins player in the 1970s and member of the Pro Football Hall of Fame
Michael Husted, former professional football player for the Tampa Bay Buccaneers, former Hampton High School placekicker
Allen Iverson, all-star basketball player for the Philadelphia 76ers
Jerod Mayo, NFL linebacker for the New England Patriots
Art Price, professional football player for the Atlanta Falcons
Dwight Stephenson, professional football player for the Miami Dolphins and member of the Pro Football Hall of Fame
John Sturdivant, professional football player
Tyrod Taylor, professional football quarterback for the Buffalo Bills
Mike Tomlin, professional football coach for the Pittsburgh Steelers
Michael Vick, professional football player for the Atlanta Falcons 2001-2006, Philadelphia Eagles 2009-2013, New York Jets 2014, Pittsburgh Steelers 2015–2016
Jimmy F. Williams, professional football player for the Atlanta Falcons
Xavier Adibi, former professional football linebacker
- Other
David Funderburk, U.S. Ambassador to Romania, U.S. Congressman
Oz Scott, director
Jean Yokum, president of Langley Federal Credit Union
Kelvin Taylor (actor) , actor from Hampton.
Sister cities
Hampton has four sister cities:[44][45]
 Southampton, England, United Kingdom
Southampton, England, United Kingdom
 Vendôme, Loir-et-Cher, France
Vendôme, Loir-et-Cher, France
 Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
 Anyang, Gyeonggi, South Korea
Anyang, Gyeonggi, South Korea
See also
- List of Mayors of Hampton, Virginia
- List of famous people from Hampton Roads
- List of athletes from Hampton Roads
- Buckroe Beach
- Bluebird Gap Farm
Hampton Roads (many regional aspects covered)- Old Point Comfort
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Hampton, Virginia
- Virginia Peninsula
Notes
^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
^ Official records for Norfolk kept January 1874 to December 1945 at the Weather Bureau Office in downtown, and at Norfolk Int'l since January 1946. For more information, see Threadex
References
^ ab http://hampton.gov/1816/Mayor-Donnie-Tuck
^ abcd "Hampton History and Facts". City of Hampton, Virginia. Archived from the original on September 26, 2010. Retrieved August 26, 2009..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
^ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. October 25, 2007. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
^ Lossing, Benson (1868). The Pictorial Field-Book of the War of 1812. Harper & Brothers, Publishers. p. 683.
^ ab "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on January 6, 2014. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
^ "Peninsula Town Center". Peninsula Town Center. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on July 15, 2010. Retrieved July 3, 2010.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ ab Tormey, James (April 2009). How Firm a Foundation. Richmond, Virginia: Diets Press. p. 184. ISBN 978-0-87517-135-7.
^ WMCAR - Historic Kecoughtan Archived August 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
^ ab http://historical-county.newberry.org/website/Virginia/documents/VA_Consolidated_Chronology.htm#Consolidated_Chronology Archived July 27, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
^ https://www.nps.gov/fomr/planyourvisit/basicinfo.htm
^ abc Jose, Carol, You Are Not Forgotten: A Family's Quest for Truth and the Founding of the National League of Families, New York Vandamere Press; first edition (September 1, 2008). (US), 2008.
ISBN 0-918339-71-5,
ISBN 978-0-918339-71-3.
^ Video of CSPAN special segment, author Carol Jose speaks about book You Are Not Forgotten on the National League of Families, http://www.c-spanvideo.org/program/282539-1
^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
^ Information from NOAA.
^
"NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2016-09-07.
^ "Station Name: VA NORFOLK INTL AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2016-09-07.
^ "WMO Climate Normals for NORFOLK/INTL, VA 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2014-03-10.
^ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
^ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
^ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
^ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
^ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
^ "Hampton city QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". Archived from the original on December 8, 2015. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "Hampton Roads News Links". abyznewslinks.com. Retrieved August 6, 2007.
^ "Hampton Roads Magazine". Hampton Roads Magazine. Retrieved August 6, 2007.
^ "Hampton Roads Radio Links". ontheradio.net. Retrieved August 6, 2007.
^ Holmes, Gary. "Nielsen Reports 1.1% increase in U.S. Television Households for the 2006-2007 Season." Nielsen Media Research. September 23, 2006. Retrieved on September 28, 2007.
^ "Christopher Newport University". Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "William & Mary". Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "ODU". Old Dominion University. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "Norfolk State University". Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ Hampton University
^ "Welcome to the Peninsula's Community College". Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ Hampton Roads Transit. "- Hampton Roads Transit -". Retrieved December 5, 2015.
^ "Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport". Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. Archived from the original on December 4, 2000. Retrieved February 25, 2008.
^ "Norfolk International Airport Mission and History". Norfolk International Airport. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2007.
^ "Norfolk International Airport Statistics" (PDF). Norfolk International Airport. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2007.
^ "Chesapeake Regional Airport". Retrieved January 12, 2008.
^ http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS
^ "Evelyn Grubb, 74; Advocated Humane Treatment for POWs of Vietnam Era" Los Angeles Times Obituary, January 4, 2006, http://articles.latimes.com/2006/jan/04/local/me-grubb4
^ "SCI: Sister City Directory". Sister Cities International. Archived from the original on April 14, 2012. Retrieved November 4, 2011.
^ "Sister Cities of Hampton, Virginia". Retrieved November 4, 2011.
Bibliography
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hampton, Virginia. |
- City of Hampton
Hampton Roads Economic Development Alliance – serving Hampton- City Data detail
 . The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
. The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
Coordinates: 37°02′06″N 76°21′36″W / 37.034946°N 76.360126°W / 37.034946; -76.360126


