São Tomé Island
| Native name: Ilha de São Tomé | |
|---|---|
 Map of São Tomé island (1922) | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Gulf of Guinea |
| Coordinates | 0°14′N 6°36′E / 0.233°N 6.600°E / 0.233; 6.600 |
| Archipelago | Bight of Bonny |
| Area | 854 km2 (330 sq mi) |
| Length | 48 km (29.8 mi) |
| Width | 32 km (19.9 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,024 m (6,640 ft) |
| Highest point | Pico de São Tomé |
| Administration | |
São Tomé and Príncipe | |
| Province | São Tomé Province |
| Largest settlement | São Tomé (pop. 56,166) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 171,856 (2011) |
| Pop. density | 183.84 /km2 (476.14 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Mestico, angolares (descendants of Angolan slaves), forros (descendants of freed slaves), servicais (contract laborers from Angola, Mozambique, and Cape Verde), tongas (children of servicais born on the islands), Europeans (primarily Portuguese) |

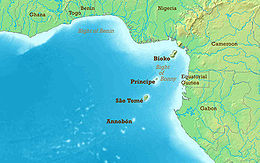
São Tomé location in Africa

São Tomé Island
São Tomé Island, at 854 km2 (330 sq mi), is the largest island of São Tomé and Príncipe and is home to about 157,000 or 96% of the nation's population. The island is divided into six districts. It is located 2 km (1¼ miles) north of the equator.
Contents
1 Geography
2 Languages
3 Geology
4 Environment and economy
5 Natural history
5.1 Birds
6 Administrative divisions
7 Towns and villages
8 References
Geography
São Tomé Island is about 48 kilometres (30 miles) long (north-south) by 32 kilometres (20 miles) wide (east-west). It rises to 2,024 metres (6,640 feet) at Pico de São Tomé and includes the capital city, São Tomé, on the northeast coast. The nearest city on mainland Africa is the port city of Port Gentil in Gabon located 240 kilometres (150 miles) to the east.
The island is surrounded by a number of small islands, including Ilhéu das Rolas, Ilhéu das Cabras and Ilhéu Gabado.
Languages
The main language is Portuguese, but there are many speakers of Forro and Angolar (Ngola), two Portuguese-based creole languages.
Geology
The entire island of São Tomé is a massive shield volcano that rises from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, over 3,000 m (10,000 ft) below sea level. It formed along the Cameroon line, a line of volcanoes extending from Cameroon southwest into the Atlantic Ocean. Most of the lava erupted on São Tomé over the last million years has been basalt. The youngest dated rock on the island is about 100,000 years old, but numerous more recent cinder cones are found on the southeast side of the island.
Environment and economy
The higher slopes of the island are forested and form part of the Parque Natural Obô de São Tomé, but agriculture is important near the north and east coasts. The chief exports are cocoa, coffee, copra, and palm products, while there is also a fishing industry.
Large reserves of oil are in the ocean between Nigeria and São Tomé. The discovery has been lamented by some as endangering the nation's political stability and natural environment. In response to these concerns the government of São Tomé and Príncipe has drawn up legislation in an attempt to ensure the efficient and equitable use of oil revenues over time.
Natural history
Birds
The island has a total of 63 regular bird species, plus an additional 36 vagrant and unconfirmed species. Of these, 19 are endemic and 3 near endemic; in addition, the local subspecies of olive ibis (Bostrychia olivacea bocagei) is endemic and considered critically endangered. Six species are considered vulnerable, and two critically endangered (São Tomé fiscal and São Tomé grosbeak).[1]
Administrative divisions
São Tomé is divided into the following six districts (seat within brackets):
Água Grande (São Tomé)
Cantagalo (Santana)
Caué (São João dos Angolares)
Lembá (Neves)
Lobata (Guadalupe)
Mé-Zóchi (Trindade)
Towns and villages
Villages on the island include:
- Agua-Coco
- Agua Ize
- Alice
- Alto Douro
- Andrade
- Bela Vista
- Blublu
- Bom Successo
- Buenos Aires
- Dona Augusta
- Dona Eugenia
- Enjale
- Formiga
- General Fonseco
- Graça
- Granja
- Guadalupe
- Guegue Norte
- Henrique
- Java
- Lemos
- Mbombo
- Mbondi
- Monte Café
- Monte Herminios
- Monte Rosa
- Neves
- Nova Olinda
- Nzumbi
- Plato Café
- Ponta Figo
- Portinho
- Porto Alegre
- Preserverança
- Quimpo
- Ribeira Afonso
- Santa Catarina
- Santa Clotilde
- Santa Cruz
- Santa Josefina
- Santana
- Santo António
- São João dos Angolares
- São José
- São Tomé
- Saudade
- Trindade
- Ubabundo

São Tomé Island

São Sebastião Lighthouse

Boca do Inferno, São Tomé

Pico Cão Grande, São Tomé Island

Fauna in Lobata District, São Tomé

Coffee production in São Tomé

Igreja de Nossa Senhora de Guadalupe, in Guadalupe, São Tomé Island.

São Tomé

Lagoa Azul, STP

One of the traditional Roças in São Tomé and Príncipe

Cocoa beans drying, São Tomé

Shrimp and French fries as served in a local hotel, São Tomé

Guadalupe, São Tomé

Sea turtle as seen in São Tomé Island

Municipal market of São Tomé City
References
^ African Bird Club – São Tomé e Príncipe
"Sao Tome". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
- CIA Word Fact Book
Wikisource has the text of an 1879 American Cyclopædia article about São Tomé Island. |
Coordinates: 0°14′N 6°36′E / 0.233°N 6.600°E / 0.233; 6.600















